Majority rule is a fundamental principle in democratic decision-making where the option supported by the greater number of participants prevails. This method ensures decisions reflect the preference of the majority while balancing fairness and efficiency. Discover how majority rule impacts governance and your participation in collective choices by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
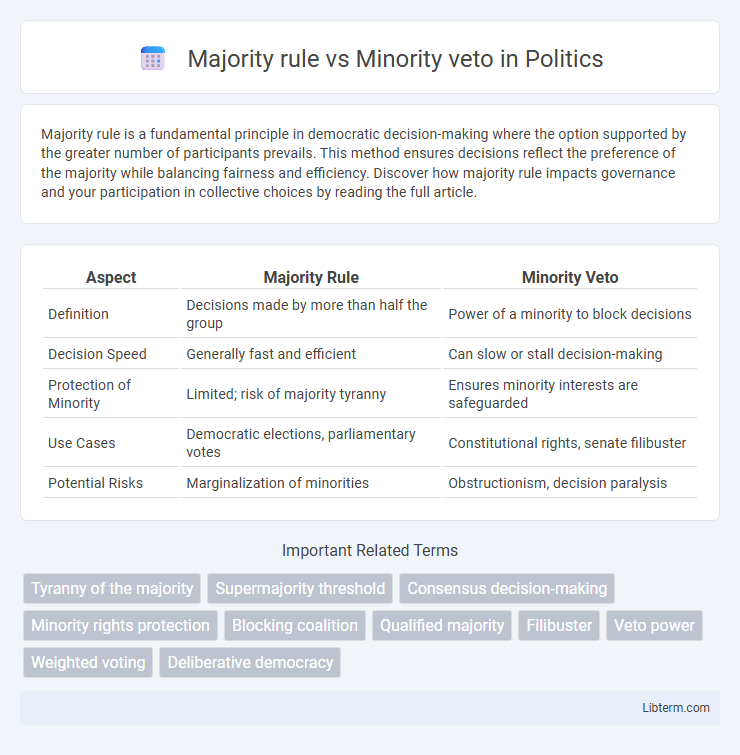
| Aspect | Majority Rule | Minority Veto |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decisions made by more than half the group | Power of a minority to block decisions |
| Decision Speed | Generally fast and efficient | Can slow or stall decision-making |
| Protection of Minority | Limited; risk of majority tyranny | Ensures minority interests are safeguarded |
| Use Cases | Democratic elections, parliamentary votes | Constitutional rights, senate filibuster |
| Potential Risks | Marginalization of minorities | Obstructionism, decision paralysis |
Understanding Majority Rule: Definition and Principles
Majority rule is a decision-making principle where the option supported by more than half of the participants is chosen, ensuring that the preferences of the greater number prevail in democratic processes. It emphasizes equality by granting each member an equal vote, promoting efficiency and clear outcomes in legislative or organizational settings. This principle contrasts with minority veto systems, where a small group can block decisions, often leading to slower or less representative results.
What is Minority Veto? Key Concepts Explained
Minority veto is a decision-making mechanism allowing a smaller group within a larger assembly to block or prevent a proposal from being adopted, despite majority support. This concept safeguards minority interests by ensuring that critical decisions require broader consensus or supermajority approval to pass. It contrasts with majority rule, where decisions are made solely based on the preference of the larger group without special protections for minorities.
Historical Origins of Majority Rule and Minority Veto
Majority rule originated in ancient Athens, where democratic assemblies made decisions based on the preference of the greater number, establishing a foundational principle for modern democratic governance. Minority veto traces back to the Roman Republic's Tribune of the Plebs, where minority representatives held the power to block legislation threatening their interests. These contrasting mechanisms reflect evolving approaches to balancing collective decision-making and protecting minority rights throughout political history.
Majority Rule in Modern Democracies
Majority rule in modern democracies ensures decisions reflect the preference of the greater number of voters, reinforcing legitimacy and social cohesion. It facilitates efficient governance by enabling swift enactment of policies supported by most constituents, particularly in parliamentary and presidential systems. However, safeguards like constitutional limits and minority rights protections are essential to prevent the tyranny of the majority and protect diverse interests.
Minority Veto: Safeguarding Minority Rights
Minority veto powers serve as critical safeguards in democratic systems, ensuring that minority groups retain influence over decisions that could disproportionately impact their rights or interests. This mechanism prevents the tyranny of the majority by allowing smaller factions to block proposals that threaten their fundamental rights or unique concerns. By embedding minority veto, institutions promote inclusivity, protect diversity, and uphold justice within decision-making processes.
Advantages of Majority Rule in Governance
Majority rule in governance promotes efficiency by enabling decisive and swift decision-making, reflecting the preference of the greater number of constituents. It fosters a sense of legitimacy and collective ownership, enhancing political stability and social cohesion. By prioritizing the will of the majority, it reduces the risk of stagnation and gridlock often associated with minority veto powers.
Challenges and Criticisms of Majority Rule
Majority rule often faces criticisms for potentially marginalizing minority groups, leading to a "tyranny of the majority" where the interests of smaller factions are overlooked or suppressed. This system can create challenges in achieving true fairness and inclusivity, especially in diverse societies with varied political, cultural, or social viewpoints. Critics argue that without safeguards like minority veto powers or protections, majority rule may undermine democratic principles by limiting pluralism and diversity in decision-making processes.
When Minority Veto Blocks Progress: Case Studies
Minority veto occurs when a small group within a decision-making body holds disproportionate power to block proposals, causing legislative gridlock and policy stagnation. Case studies in corporate boards, international organizations like the EU, and legislative assemblies reveal how minority vetoes can stall critical reforms, delay economic development, and hinder crisis responses. Understanding the dynamics behind minority vetoes in these contexts underscores the need for balanced governance structures that promote both protection of minority interests and efficient decision-making.
Finding Balance: Majority Rule vs. Minority Protections
Finding balance in democratic decision-making involves ensuring majority rule does not suppress minority rights, preserving diverse viewpoints and preventing tyranny of the majority. Mechanisms like minority vetoes serve as crucial safeguards, allowing smaller groups to block measures that could harm their essential interests. Effective governance combines majority decisions with minority protections to foster inclusion, stability, and fairness in policy outcomes.
Future Perspectives: Evolving Democratic Decision-Making
Future perspectives in democratic decision-making emphasize balancing majority rule with minority veto to enhance inclusivity and fairness. Emerging models integrate technology such as blockchain for transparent voting and AI to analyze diverse opinions, ensuring minority rights without stalling decisions. This evolution aims to create adaptive governance structures that reflect pluralistic societies and mitigate polarization.
Majority rule Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com