Push polls are a controversial campaign technique that masquerades as opinion surveys but are designed to influence voters under the guise of collecting information. They often use leading or biased questions to frame a candidate or issue negatively, manipulating public perception. Discover how push polls work and how to recognize them to protect your vote by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
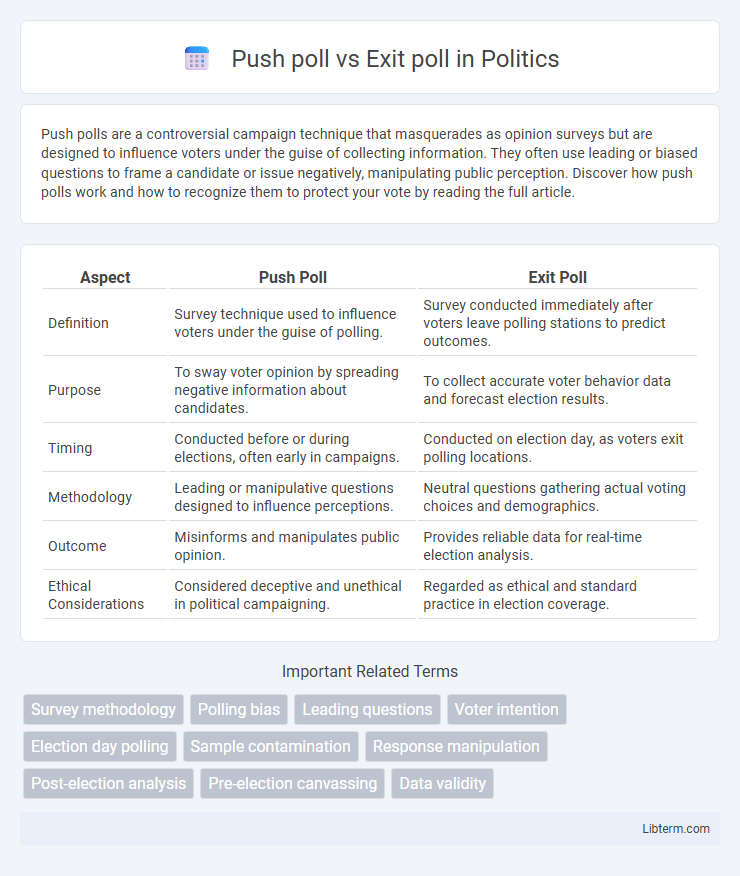
| Aspect | Push Poll | Exit Poll |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Survey technique used to influence voters under the guise of polling. | Survey conducted immediately after voters leave polling stations to predict outcomes. |
| Purpose | To sway voter opinion by spreading negative information about candidates. | To collect accurate voter behavior data and forecast election results. |
| Timing | Conducted before or during elections, often early in campaigns. | Conducted on election day, as voters exit polling locations. |
| Methodology | Leading or manipulative questions designed to influence perceptions. | Neutral questions gathering actual voting choices and demographics. |
| Outcome | Misinforms and manipulates public opinion. | Provides reliable data for real-time election analysis. |
| Ethical Considerations | Considered deceptive and unethical in political campaigning. | Regarded as ethical and standard practice in election coverage. |
Understanding Push Polls: Definition and Purpose
Push polls are a campaign tactic designed to influence voters under the guise of conducting a poll, often by presenting biased or misleading questions to sway opinions. Unlike exit polls, which gather unbiased voter behavior data immediately after voting, push polls aim to disseminate negative information about an opponent to shape public perception. Their primary purpose is persuasion rather than accurate data collection, making them more a form of political advertising than genuine polling.
Exit Polls Explained: Key Features and Methods
Exit polls are surveys conducted immediately after voters leave polling stations, designed to predict election results and analyze voter behavior with high accuracy. They employ systematic sampling methods and stratified random sampling to ensure representative data across demographics, enabling precise estimations of voting patterns and demographic influences. Key features include rapid data collection, detailed questionnaires on voter motivations, and statistical weighting to adjust for sampling biases, making exit polls vital tools for media coverage and political analysis.
Main Differences Between Push Polls and Exit Polls
Push polls are designed to influence voter opinions by spreading biased or misleading information under the guise of a survey, while exit polls collect unbiased data by asking voters whom they actually voted for immediately after they leave the polling station. Push polls often use leading questions to sway opinions, whereas exit polls employ neutral questions to accurately predict election outcomes. The primary difference lies in the intent: push polls manipulate voter perception, exit polls gather factual voting data.
How Push Polls Influence Public Opinion
Push polls influence public opinion by disseminating biased or misleading information disguised as survey questions, aiming to sway voter attitudes rather than collect genuine data. Unlike exit polls that capture voter choices post-election impartially, push polls manipulate perceptions through suggestive inquiries designed to create negative impressions about candidates. This technique can distort the electoral process by shaping voter beliefs and intentions based on controlled misinformation.
The Role of Exit Polls in Election Reporting
Exit polls provide immediate insights into voter behavior and election outcomes by surveying voters as they leave polling stations, offering accurate predictions before official results are tallied. These polls help media outlets and analysts identify voting trends, demographic participation, and candidate support with a high degree of reliability. Unlike push polls, which aim to influence opinions, exit polls serve as objective tools for election reporting and democratic transparency.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Push Polls
Push polls raise significant ethical concerns due to their deceptive nature, as they are designed to manipulate voter opinions rather than gather genuine data. Unlike exit polls, which aim to accurately capture voter behavior and trends, push polls often employ misleading questions or biased information to influence election outcomes. This manipulation undermines democratic processes by spreading misinformation and violating principles of transparency and honesty in political communication.
Accuracy and Reliability: Push Polls vs Exit Polls
Exit polls generally offer higher accuracy and reliability because they collect real-time data directly from voters as they leave polling stations, minimizing recall bias. Push polls, designed more for persuasion than data collection, often yield unreliable results due to their leading or biased questioning techniques. Consequently, exit polls remain a trusted source for projected election outcomes, whereas push polls lack credibility as a reliable measure of voter intent.
Recognizing Push Polls: Red Flags and Indicators
Push polls disguise themselves as surveys but aim to manipulate opinions by spreading misleading or biased information about candidates. Indicators of push polls include loaded or suggestive questions designed to influence rather than gather genuine feedback, frequent use of negative or leading language, and unusually high call volumes with scripted messages targeting specific voter concerns. Recognizing these red flags helps voters critically evaluate the intent behind polling calls and avoid being misled by deceptive tactics.
Impact of Exit Polls on Election Outcomes
Exit polls significantly influence election outcomes by providing early insights into voter behavior and candidate performance, often shaping public perception and media narratives before official results are announced. These polls can affect voter turnout in regions where elections remain open, potentially swaying undecided voters or altering campaign strategies in real-time. In contrast, push polls are designed to manipulate opinions rather than gather genuine data, lacking the empirical impact that exit polls have on forecasting and electoral dynamics.
Best Practices: Using Polls Responsibly in Campaigns
Push polls and exit polls serve distinct roles in political campaigns, with push polls often criticized for their manipulative intent, while exit polls aim to gather unbiased voter data. Best practices for using polls responsibly include ensuring transparency in methodology, avoiding leading or loaded questions, and respecting voter privacy to maintain credibility. Campaigns should prioritize exit polls for accurate insights and strictly reject push polling tactics to uphold ethical standards and public trust.
Push poll Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com