Partisanship drives strong loyalty to political parties, often leading individuals to prioritize party unity over bipartisan cooperation or objective policy evaluation. This division fosters a polarized environment where dialogue is reduced, and ideological battles intensify. Discover how partisanship impacts your political engagement and the broader implications for society in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
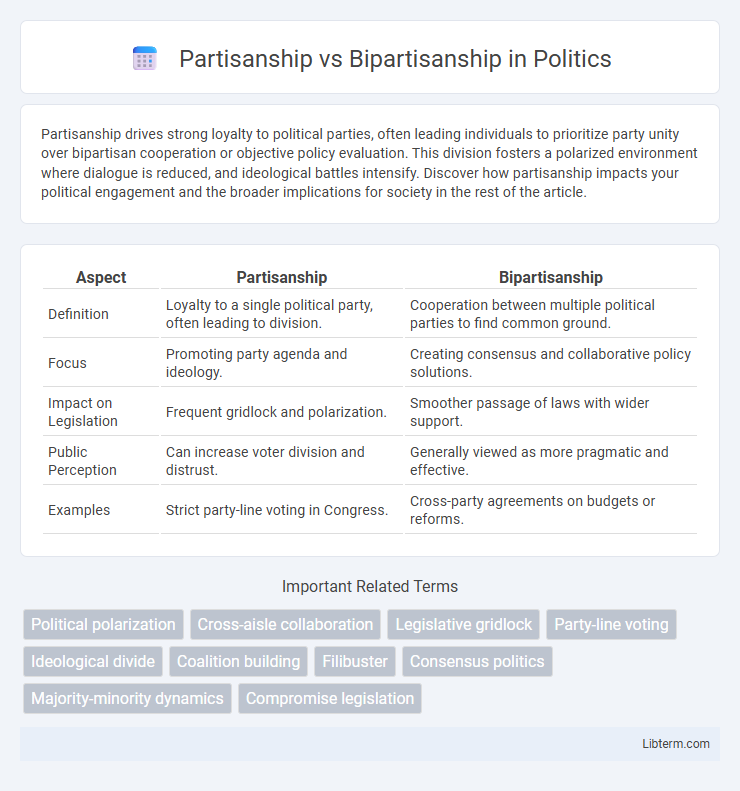
| Aspect | Partisanship | Bipartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loyalty to a single political party, often leading to division. | Cooperation between multiple political parties to find common ground. |
| Focus | Promoting party agenda and ideology. | Creating consensus and collaborative policy solutions. |
| Impact on Legislation | Frequent gridlock and polarization. | Smoother passage of laws with wider support. |
| Public Perception | Can increase voter division and distrust. | Generally viewed as more pragmatic and effective. |
| Examples | Strict party-line voting in Congress. | Cross-party agreements on budgets or reforms. |
Understanding Partisanship: Definition and Origins
Partisanship refers to strong, unwavering loyalty to a specific political party or ideology, often resulting in biased decision-making and limited cooperation across party lines. Its origins date back to early political systems where groups formed around shared beliefs and goals, reinforcing group identity and opposition to rival factions. Understanding partisanship helps explain persistent political polarization and challenges in achieving bipartisan consensus in legislative processes.
The Roots of Bipartisanship in Political Systems
Bipartisanship in political systems originates from the foundational need to foster cooperation among competing parties to achieve stable governance and effective policymaking. Historical precedents, such as coalition governments and consensus-driven decision-making, highlight the pragmatic roots of bipartisanship in balancing diverse interests and preventing legislative deadlock. Structural factors like electoral systems, political culture, and institutional frameworks significantly influence the prevalence and strength of bipartisan collaboration across democracies.
Key Differences Between Partisanship and Bipartisanship
Partisanship involves strong allegiance to a specific political party, often leading to polarized decision-making and resistance to opposing viewpoints. Bipartisanship emphasizes cooperation and compromise between multiple political parties to achieve common legislative goals and promote political stability. Key differences include the level of collaboration, with partisanship prioritizing party loyalty and bipartisanship fostering cross-party negotiation and consensus-building.
Historical Examples of Partisanship in Government
Historical examples of partisanship in government include the intense sectional conflicts leading up to the Civil War, where Democratic and Whig parties fiercely opposed each other on issues like slavery and states' rights. The late 19th-century Gilded Age politics showcased deep partisan battles between Republicans and Democrats over economic policies and civil service reforms. More recently, the Watergate scandal exemplified extreme partisanship as political factions clashed over governmental abuses and constitutional accountability.
Notable Instances of Bipartisanship in Policy Making
Notable instances of bipartisanship in policy making include the 1964 Civil Rights Act, where both Democrats and Republicans collaborated to end racial segregation and discrimination. The 2009 Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) expansion showcased bipartisan efforts to provide healthcare coverage for low-income children. More recently, the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act demonstrated cross-party cooperation to address national infrastructure challenges and promote economic growth.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Partisan Politics
Partisan politics fosters strong party loyalty and clear policy distinctions, enabling decisive legislative action and cohesion within political groups. However, it often leads to polarization, gridlock, and diminished bipartisan cooperation, hindering comprehensive policy solutions and increasing political tension. The dominance of partisan agendas can marginalize minority opinions and reduce the effectiveness of governance in addressing complex, cross-cutting issues.
The Role of Bipartisanship in Legislative Success
Bipartisanship plays a crucial role in legislative success by enabling the passage of laws through cooperation between opposing political parties. Collaborative efforts increase the likelihood of enacting policies that reflect a broader consensus, reducing gridlock and fostering stability in governance. Historical examples, such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964, demonstrate how bipartisan support can lead to significant and lasting legislative achievements.
Partisanship’s Impact on Political Polarization
Partisanship intensifies political polarization by deepening ideological divides between parties, resulting in decreased cooperation and legislative gridlock. Strong partisan loyalty often leads to echo chambers, reinforcing biases and reducing willingness to compromise on policy issues. This entrenched division undermines effective governance and fuels public distrust in political institutions.
Bipartisanship and Its Effect on Public Trust
Bipartisanship fosters collaboration between political parties, enhancing legislative efficiency and promoting policies that reflect diverse perspectives. This cooperation increases public trust by demonstrating a commitment to common goals rather than partisan agendas, leading to greater confidence in government institutions. Studies show that bipartisan efforts correlate with higher approval ratings and increased citizen engagement in the political process.
The Future of Partisanship and Bipartisanship in Modern Politics
The future of partisanship and bipartisanship in modern politics hinges on increasing political polarization and the rising demand for collaborative governance. Technological advancements and social media influence have amplified partisan divides yet also offer platforms for cross-party dialogue and coalition-building. Emerging political strategies emphasize balancing ideological commitment with pragmatic cooperation to address complex societal challenges effectively.
Partisanship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com