Primary elections serve as a crucial process in selecting a political party's candidate for the general election, allowing party members to vote for their preferred contender. This democratic method helps narrow down the field of candidates, shaping the political landscape and influencing future policies. Discover how primary elections impact your vote and democracy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
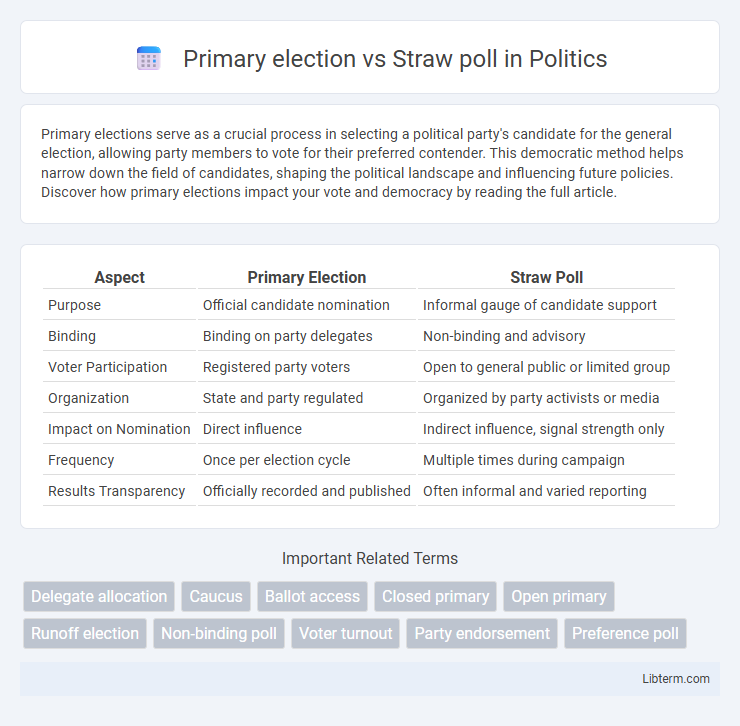
| Aspect | Primary Election | Straw Poll |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Official candidate nomination | Informal gauge of candidate support |
| Binding | Binding on party delegates | Non-binding and advisory |
| Voter Participation | Registered party voters | Open to general public or limited group |
| Organization | State and party regulated | Organized by party activists or media |
| Impact on Nomination | Direct influence | Indirect influence, signal strength only |
| Frequency | Once per election cycle | Multiple times during campaign |
| Results Transparency | Officially recorded and published | Often informal and varied reporting |
Understanding the Primary Election Process
Primary elections are state-administered voting processes where registered party members select their preferred candidates for the general election, influencing delegate allocation and party nominations. Straw polls are informal, non-binding surveys that gauge voter preferences and candidate support early in the election cycle but lack official influence on delegate counts or final nominations. Understanding the primary election process involves recognizing its role in formal candidate selection, governed by state laws and party rules, contrasting with straw polls' advisory function in measuring public opinion.
What is a Straw Poll?
A straw poll is an informal, unofficial vote used to gauge the popularity or opinion of candidates or issues within a specific group or event. Unlike a primary election, which is a formal, state-sanctioned process that determines party nominees for public office, a straw poll has no legal standing and usually serves as an early indicator of candidate support or public sentiment. Straw polls are often conducted at political gatherings, conventions, or local meetings to provide insight into voter preferences before official elections.
Key Differences Between Primary Elections and Straw Polls
Primary elections are official, state-sanctioned processes that determine a political party's candidate for general elections, involving registered voters casting ballots under formal rules. Straw polls are informal, non-binding surveys or votes often conducted at political events to gauge candidate popularity or public opinion without impacting official nomination outcomes. The key difference lies in legitimacy and influence: primary elections have legal authority in candidate selection, whereas straw polls serve as preliminary indicators lacking formal power.
Purpose and Importance of Primary Elections
Primary elections serve as official, state-sanctioned processes to select party candidates for general elections, playing a critical role in legitimizing candidate nominations and ensuring voter participation in the democratic process. Straw polls, by contrast, are informal, non-binding votes often used to gauge candidate popularity or public opinion early in a campaign without influencing official election outcomes. The importance of primary elections lies in their ability to provide a structured, transparent mechanism for party members to choose representatives, thereby shaping the political landscape and promoting accountability within the electoral system.
The Role of Straw Polls in Political Campaigns
Straw polls serve as informal surveys gauging voter sentiment and can influence campaign strategies by identifying early frontrunners. Unlike primary elections, which officially select party nominees, straw polls provide quick, low-cost feedback on candidate viability. Political campaigns leverage straw poll results to adjust messaging, mobilize supporters, and attract media attention during the early stages of the election cycle.
Voter Participation: Primaries vs. Straw Polls
Voter participation in primary elections is typically higher due to their official role in selecting party candidates for general elections, involving registered voters and often state-run processes. Straw polls generally see lower participation because they are informal, non-binding surveys conducted to gauge early support and enthusiasm, often limited to party members or activists at specific events. The difference in voter turnout reflects the varying importance and impact of each method on the political process.
Impact on Party Nominations
Primary elections directly impact party nominations by determining official candidates through voter participation and delegate allocation, influencing the general election lineup. Straw polls serve as informal indicators of candidate popularity and grassroots support, often shaping momentum and media narratives without binding nomination decisions. The combined influence of primaries and straw polls helps parties gauge candidate viability and voter preferences early in the nomination process.
Historical Examples of Primary Elections and Straw Polls
Primary elections, such as the 1968 New Hampshire Democratic primary which helped shape the nomination of Hubert Humphrey, demonstrate formal state-organized processes that directly influence party candidates. Straw polls like the 1979 Iowa Republican Straw Poll played a prominent role in gauging early candidate support without binding delegates, exemplifying grassroots enthusiasm and media attention. Historical examples reveal primary elections as decisive in candidate selection, while straw polls often serve as informal indicators of momentum within party races.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Primary elections offer a structured voting process with official ballots, ensuring greater legitimacy and wider voter participation, but they require significant time, funding, and organization for effective implementation. Straw polls provide a quick, informal gauge of public opinion with minimal cost and effort, yet their non-binding nature and susceptibility to bias limit their reliability for predicting election outcomes. Both methods serve different strategic purposes: primaries are essential for formal candidate selection, while straw polls excel in assessing early voter preferences and testing campaign momentum.
Primary Elections vs. Straw Polls: Which Is More Influential?
Primary elections are official voting processes organized by state governments to select party nominees for general elections, involving registered voters and binding outcomes. Straw polls are informal, non-binding surveys conducted by interest groups or media outlets to gauge early voter preferences but lack the legal authority to impact candidate selection directly. Primary elections carry more influence on the electoral process as their results determine delegate allocation and party nominations, shaping the trajectory of political campaigns.
Primary election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com