Establishment refers to the creation or founding of an organization, business, or institution, signifying the beginning of its operational presence. Understanding the key factors involved in successful establishment can significantly impact long-term growth and stability. Explore this article to learn how your establishment can thrive in a competitive environment.
Table of Comparison
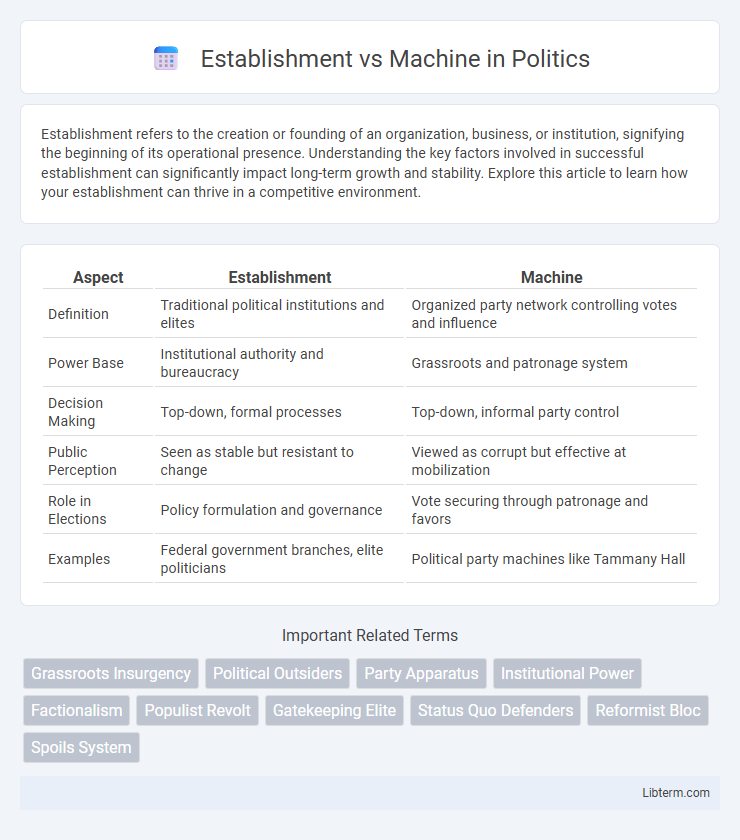
| Aspect | Establishment | Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional political institutions and elites | Organized party network controlling votes and influence |
| Power Base | Institutional authority and bureaucracy | Grassroots and patronage system |
| Decision Making | Top-down, formal processes | Top-down, informal party control |
| Public Perception | Seen as stable but resistant to change | Viewed as corrupt but effective at mobilization |
| Role in Elections | Policy formulation and governance | Vote securing through patronage and favors |
| Examples | Federal government branches, elite politicians | Political party machines like Tammany Hall |
Understanding the Establishment and the Machine
Understanding the Establishment involves analyzing entrenched institutions and power structures that influence economic and political systems. The Machine represents the systemic mechanisms and networks that enforce and perpetuate the stability of these institutions through bureaucratic processes and technological control. Examining both concepts reveals how authority and control are maintained within complex social frameworks.
Historical Roots of the Establishment
The historical roots of the Establishment trace back to entrenched social, political, and economic elites who have maintained centralized power through traditions, institutions, and networks of influence. Originating in aristocratic systems and colonial administrations, the Establishment has evolved as a dominant force shaping governance, policy, and cultural norms across societies. This entrenched dominance often contrasts with the rise of disruptive machines and technology-driven innovations challenging entrenched power structures.
Evolution of the Political Machine
The evolution of the political machine reflects a shift from traditional establishment politics toward highly organized, network-driven systems of governance characterized by centralized control and patronage. Political machines historically leveraged ethnic and immigrant communities to consolidate power through vote mobilization, often intertwining political authority with local business interests and social services. As these machines adapted to modern regulations and media scrutiny, they evolved by incorporating sophisticated data analytics and digital outreach to maintain influence and voter loyalty in an increasingly complex political landscape.
Key Differences: Establishment vs Machine
Establishment refers to a business or organizational entity, while a machine is a physical apparatus used for production or operation. Key differences include that establishments encompass administrative functions, workforce, and operational management, whereas machines primarily focus on mechanical tasks and automation processes. Establishments rely on machines as assets to increase productivity but maintain broader organizational and economic roles beyond mere machinery.
Power Structures and Influence Networks
Establishment power structures consist of formal institutions, traditional authorities, and hierarchical organizations that maintain influence through established protocols and legal frameworks. Machine politics operate through informal networks, patronage systems, and localized influence, often relying on personal relationships and reciprocal favors to control resources and decision-making. These two systems intersect constantly, with establishment entities co-opting machine networks to consolidate power while machines exploit institutional weaknesses to expand their reach.
The Role of Elites in Shaping Policy
Elites play a pivotal role in shaping policy by leveraging their access to resources, networks, and institutional knowledge within both the Establishment and the Machine. The Establishment comprises traditional power holders who influence policy through established norms, political offices, and bureaucratic channels, whereas the Machine operates through organized political networks and party apparatus to mobilize votes and enforce discipline. Understanding the dynamic between these elite groups reveals how policy decisions are negotiated, contested, and implemented in complex political systems.
Grassroots Movements vs Institutional Control
Grassroots movements challenge institutional control by mobilizing community-driven initiatives that prioritize local needs over centralized authority. These efforts emphasize participatory democracy, often bypassing established machines that rely on hierarchical structures and bureaucratic processes. The tension between establishment power and grassroots activism shapes political landscapes, influencing policy through bottom-up pressure rather than top-down directives.
Impact on Democracy and Governance
The conflict between Establishment and Machine politics significantly influences democracy and governance by shaping policy priorities and public trust. Establishment politics often emphasize stability and institutional continuity, whereas Machine politics rely on patronage networks that can undermine democratic transparency and accountability. This dynamic creates pressures on governance structures, sometimes leading to corruption, reduced citizen participation, and weakened democratic institutions.
Modern Examples: Establishment and Machine in Action
Modern examples of establishment versus machine dynamics are evident in political campaigns where traditional party organizations face challenges from data-driven technological platforms. Machine politics rely heavily on sophisticated algorithms and social media analytics to mobilize voters and influence public opinion, contrasting with the establishment's conventional grassroots mobilization and hierarchical decision-making. This shift highlights how digital infrastructures and artificial intelligence redefine power structures in contemporary governance.
Future Trends: Relevance in Contemporary Politics
Establishment and machine politics continue to shape electoral dynamics by leveraging organizational networks and patronage systems to influence voter behavior. Future trends indicate a shift toward digital platforms and data-driven campaigns, enhancing the reach and efficiency of political machines while challenging traditional establishment hierarchies. The relevance of these models persists in contemporary politics as parties adapt to technological advancements and changing voter expectations.
Establishment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com