Sockpuppeting involves creating fake online identities to manipulate opinions or deceive others, often undermining trust in digital communities. This unethical practice can skew social media discussions, reviews, and forums, impacting your ability to find genuine information. Discover how to spot sockpuppeting and protect yourself by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
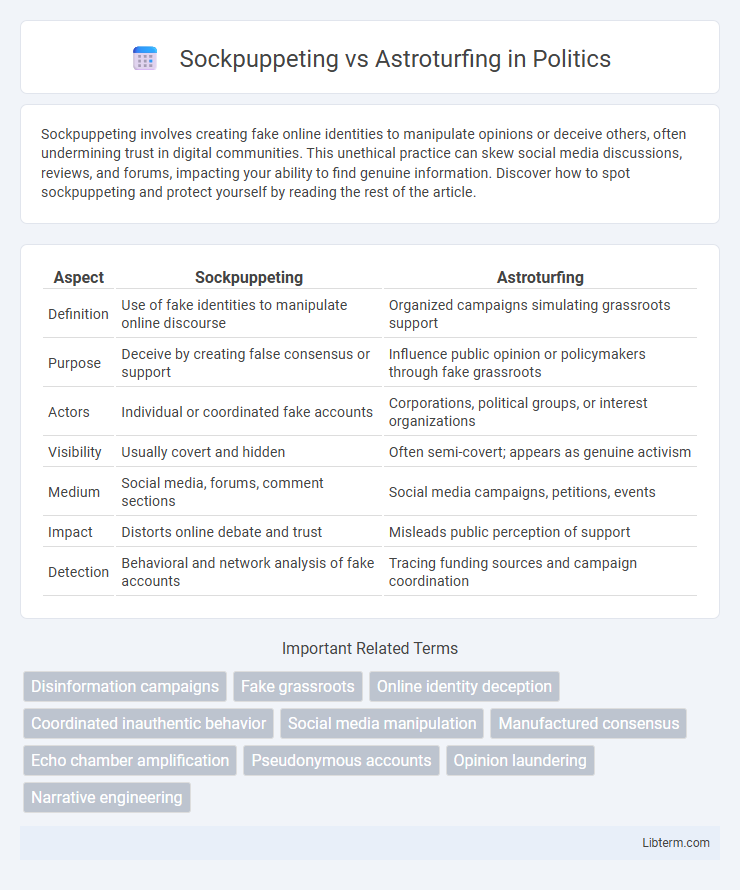
| Aspect | Sockpuppeting | Astroturfing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of fake identities to manipulate online discourse | Organized campaigns simulating grassroots support |
| Purpose | Deceive by creating false consensus or support | Influence public opinion or policymakers through fake grassroots |
| Actors | Individual or coordinated fake accounts | Corporations, political groups, or interest organizations |
| Visibility | Usually covert and hidden | Often semi-covert; appears as genuine activism |
| Medium | Social media, forums, comment sections | Social media campaigns, petitions, events |
| Impact | Distorts online debate and trust | Misleads public perception of support |
| Detection | Behavioral and network analysis of fake accounts | Tracing funding sources and campaign coordination |
Understanding Sockpuppeting
Sockpuppeting involves creating fake online identities to manipulate public opinion by posting misleading reviews or comments, often obscuring the true source. This deceptive tactic differs from astroturfing, which simulates grassroots movements by coordinating multiple fake accounts to give false impressions of widespread support. Understanding sockpuppeting requires recognizing how single actors use fabricated personas to influence discussions and evade detection.
What is Astroturfing?
Astroturfing is a deceptive practice where organized campaigns create the illusion of genuine grassroots support by using fake identities or paid promoters to influence public opinion. Unlike sockpuppeting, which involves individuals managing multiple online personas, astroturfing operates on a larger scale to manipulate social, political, or commercial narratives. This tactic undermines authentic engagement and distorts democratic processes by fabricating consensus through coordinated misinformation.
Key Differences Between Sockpuppeting and Astroturfing
Sockpuppeting involves creating multiple fake identities to manipulate online discussions or amplify opinions, while astroturfing is the practice of orchestrating a deceptive campaign that mimics grassroots support for a cause or product. Key differences include sockpuppeting focusing on individual fake personas, whereas astroturfing encompasses coordinated efforts that appear as genuine public endorsement. Both tactics manipulate public perception, but sockpuppeting operates on a micro-level of false identities, and astroturfing operates on a macro-level of fabricated collective movements.
Motivations Behind Online Deception
Sockpuppeting involves creating fake online identities to manipulate opinions and create a false sense of support, often motivated by personal gain, reputation management, or influencing discussions covertly. Astroturfing aims to simulate grassroots movements by orchestrating widespread deceptive campaigns, driven by motivations such as political agendas, corporate interests, or social influence. Both tactics exploit online anonymity to distort public perception and manipulate social dynamics for strategic advantages.
Common Tactics Used in Sockpuppeting
Sockpuppeting commonly involves creating multiple fake online identities to manipulate public opinion, post favorable comments, or discredit opponents by pretending to be independent users. These tactics include using coordinated profiles to amplify messages, planting misleading reviews, and engaging in deceptive conversations to fabricate consensus. Sockpuppeting often exploits anonymity and weak platform verification systems to evade detection and maintain influence.
Strategies of Astroturfing Campaigns
Astroturfing campaigns employ sophisticated strategies such as orchestrating fake grassroots movements by using coordinated bots, paid commenters, and fabricated social media accounts to create the illusion of widespread public support. These campaigns strategically target influential platforms and key opinion leaders to amplify false narratives and manipulate public opinion at scale. Advanced tactics include monitoring real-time engagement metrics to adjust messaging, deploying disinformation through shadow networks, and disguising the source of the campaign to evade detection by platforms and regulators.
Real-World Examples of Sockpuppeting
Sockpuppeting involves creating fake online identities to manipulate public opinion, as seen in the 2011 case of the Associated Press, where employees posed as consumers to post positive reviews of their own work. In another example, during the 2016 US presidential election, multiple accounts linked to political campaigns were exposed for engaging in sockpuppeting to spread misinformation. These real-world instances highlight the use of deceptive identities to influence digital discourse and public perception.
Famous Astroturfing Incidents
Astroturfing involves orchestrated campaigns to create the illusion of widespread grassroots support, with famous incidents like the 2009 ExxonMobil-funded campaign denying climate change and the 2016 Volkswagen emissions scandal cover-up. Sockpuppeting, in contrast, refers to individuals using multiple online identities to manipulate public opinion or evade detection, often supporting astroturfing efforts. These deceptive tactics undermine authentic public discourse by skewing perceptions of consensus and credibility.
The Impact on Online Communities
Sockpuppeting manipulates online communities by fabricating multiple identities to amplify specific viewpoints, undermining genuine discourse and trust. Astroturfing creates the illusion of widespread grassroots support by orchestrating coordinated campaigns, misleading users about the authenticity of opinions and skewing public perception. Both tactics erode the credibility of online platforms, distorting community engagement and decision-making processes.
How to Detect and Prevent Sockpuppeting and Astroturfing
Detecting sockpuppeting involves monitoring for repetitive user behavior, IP address similarities, and unnatural posting patterns, while astroturfing detection relies on identifying coordinated campaigns, fake grassroots movements, and inconsistent messaging sources. Prevent prevention tactics include implementing multi-factor authentication, employing AI-powered behavior analysis tools, and enforcing stricter verification processes to ensure user authenticity. Regular audits and community reporting mechanisms also strengthen defenses against both sockpuppeting and astroturfing in online platforms.
Sockpuppeting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com