A minority leader plays a crucial role in representing and leading the opposition party within legislative bodies, shaping policies and strategies to influence government actions despite having fewer seats. Understanding the responsibilities and challenges faced by a minority leader can provide insights into political dynamics and power balances. Discover how this position affects legislative processes and why it matters for Your political awareness in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
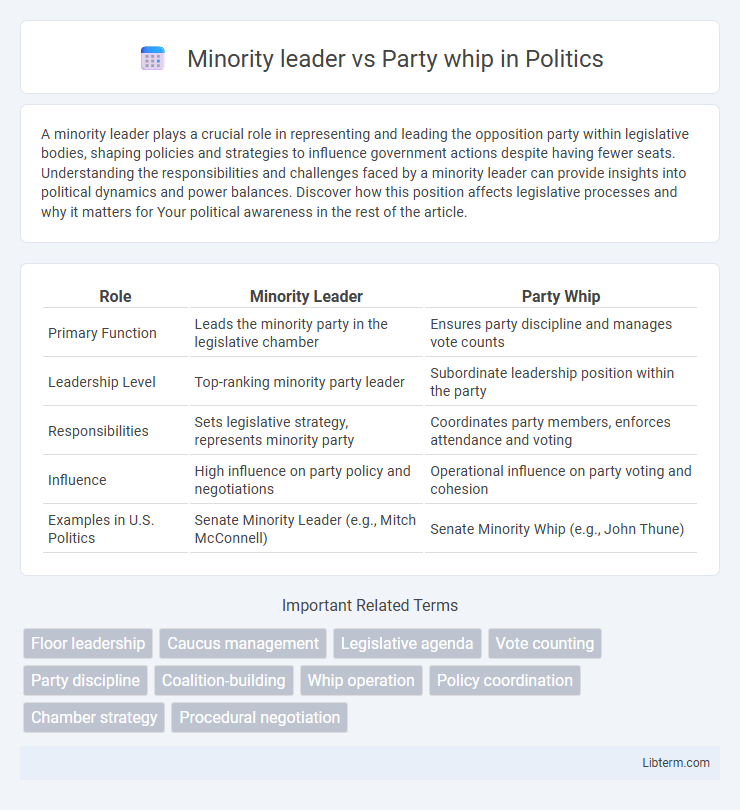
| Role | Minority Leader | Party Whip |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Leads the minority party in the legislative chamber | Ensures party discipline and manages vote counts |
| Leadership Level | Top-ranking minority party leader | Subordinate leadership position within the party |
| Responsibilities | Sets legislative strategy, represents minority party | Coordinates party members, enforces attendance and voting |
| Influence | High influence on party policy and negotiations | Operational influence on party voting and cohesion |
| Examples in U.S. Politics | Senate Minority Leader (e.g., Mitch McConnell) | Senate Minority Whip (e.g., John Thune) |
Introduction to Legislative Leadership Roles
The Minority Leader serves as the head of the opposition party in a legislative chamber, responsible for setting the party's agenda and strategy against the majority. The Party Whip is tasked with ensuring party discipline, securing votes, and communicating between leadership and members. Both roles are crucial for organizing legislative priorities and maintaining party cohesion within the legislative process.
Who is the Minority Leader?
The Minority Leader is the head of the political party with the second-largest number of seats in a legislative body, responsible for coordinating the party's legislative strategy and serving as the primary spokesperson. Unlike the Party Whip, who focuses on managing party discipline and vote counting, the Minority Leader sets the policy agenda and leads opposition efforts against the majority party. This role is critical in shaping legislative debates and negotiating with the majority party leadership.
Defining the Party Whip
The Party Whip is a key legislative role responsible for maintaining party discipline, ensuring members attend important votes, and securing support for party policies within the legislative body. Unlike the Minority Leader who sets policy direction and acts as the chief spokesperson for the minority party, the Party Whip's primary function is organizational, coordinating vote counts and communication between leadership and rank-and-file members. The effectiveness of the Party Whip directly influences legislative success by managing party cohesion and strategizing vote management.
Key Responsibilities of the Minority Leader
The Minority Leader serves as the primary strategist and spokesperson for the opposition party, responsible for coordinating party policy, managing legislative agendas, and negotiating with the majority party to influence lawmaking. This leader organizes minority party members to present a unified stance during debates and votes, ensuring effective opposition or collaboration when beneficial. The Minority Leader also plays a pivotal role in rallying party resources and communicating priorities to the media and public.
Core Duties of the Party Whip
The Party Whip plays a crucial role in maintaining party discipline by ensuring members attend voting sessions and adhere to party positions. Core duties include counting votes before important legislation, communicating the party leadership's stance, and mobilizing party members to support key policies. Unlike the Minority Leader who strategizes legislative agendas, the Whip concentrates on vote management and internal coordination to secure legislative success.
Hierarchical Structure: Minority Leader vs Party Whip
The Minority Leader holds the highest-ranking position within the party's minority caucus, responsible for setting legislative priorities and strategizing party goals, while the Party Whip operates under the Minority Leader to maintain party discipline and ensure member attendance and voting alignment. In the hierarchical structure, the Minority Leader directs overall party strategy, whereas the Party Whip manages communication between leadership and rank-and-file members to enforce cohesion. This clear chain of command enhances coordinated decision-making and legislative effectiveness within the party minority.
Influence on Party Strategy and Discipline
The Minority Leader shapes overall party strategy by setting legislative priorities and coordinating opposition tactics with fellow party members. The Party Whip enforces discipline by ensuring attendance, securing votes, and managing communication between leadership and rank-and-file members. While the Minority Leader drives strategic direction, the Party Whip focuses on maintaining unity and translating strategy into effective voting behavior.
Selection Process: Minority Leader and Party Whip
The Minority Leader is typically elected by the members of the minority party in the legislative body through a formal caucus vote, reflecting the collective choice of party legislators. In contrast, the Party Whip is selected either by the party leadership or voted on by the party members, often based on experience and ability to enforce discipline and manage legislative strategy. Both roles require strong leadership skills, but the Minority Leader holds a more prominent position as the official spokesperson and strategist for the minority party.
Notable Historical Figures in Each Role
Notable historical figures in the role of Minority Leader include Nancy Pelosi, who has served as a pivotal leader in the U.S. House of Representatives, and Mitch McConnell, known for his strategic leadership in the Senate. In contrast, Party Whips like James Clyburn and Dick Cheney have been instrumental in maintaining party discipline and ensuring legislative agendas pass smoothly. These leaders are recognized for their influential roles in shaping party strategy and legislative success during critical periods in American politics.
Comparing Minority Leader and Party Whip: Key Differences
The Minority Leader serves as the chief spokesperson and strategist for the minority party in a legislative body, responsible for setting policy priorities and coordinating party activities, while the Party Whip focuses on ensuring member attendance and securing votes for key legislation. The Minority Leader often negotiates directly with the majority party and represents the minority party's interests publicly, whereas the Party Whip operates behind the scenes, managing party discipline and communication among members. Key differences include the Minority Leader's role in leadership and public representation versus the Whip's emphasis on internal party organization and vote-counting.
Minority leader Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com