Supranational unions facilitate cooperation and shared governance among member states, enhancing economic integration, political stability, and collective decision-making beyond national borders. These unions often implement common policies and regulations to address global challenges such as trade, security, and environmental protection. Explore the article to understand how supranational unions impact Your country's role in international affairs.
Table of Comparison
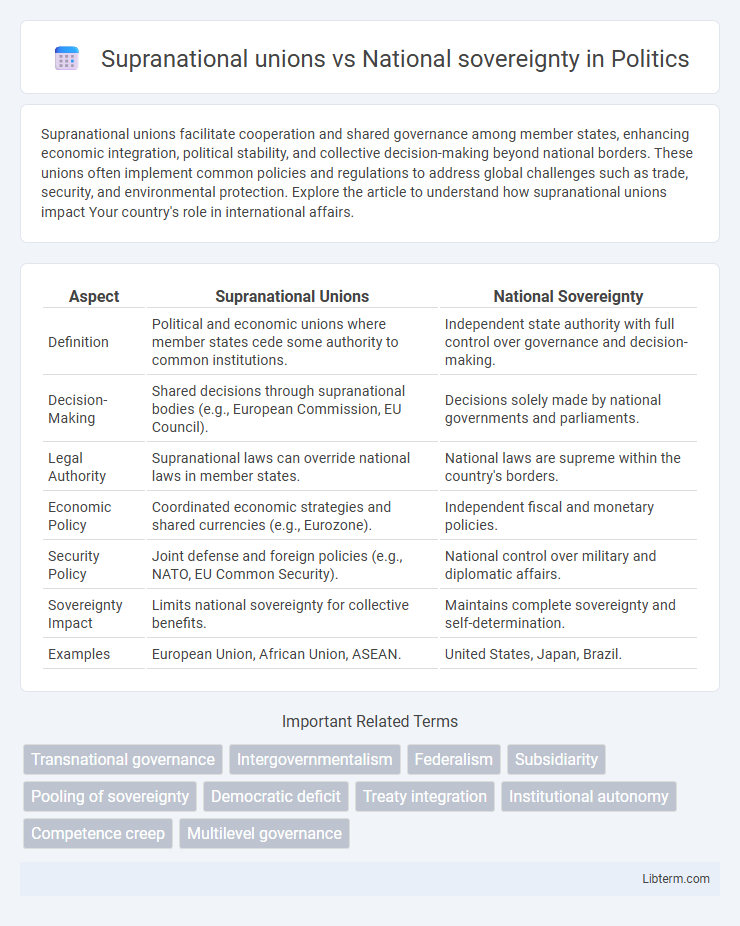
| Aspect | Supranational Unions | National Sovereignty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political and economic unions where member states cede some authority to common institutions. | Independent state authority with full control over governance and decision-making. |
| Decision-Making | Shared decisions through supranational bodies (e.g., European Commission, EU Council). | Decisions solely made by national governments and parliaments. |
| Legal Authority | Supranational laws can override national laws in member states. | National laws are supreme within the country's borders. |
| Economic Policy | Coordinated economic strategies and shared currencies (e.g., Eurozone). | Independent fiscal and monetary policies. |
| Security Policy | Joint defense and foreign policies (e.g., NATO, EU Common Security). | National control over military and diplomatic affairs. |
| Sovereignty Impact | Limits national sovereignty for collective benefits. | Maintains complete sovereignty and self-determination. |
| Examples | European Union, African Union, ASEAN. | United States, Japan, Brazil. |
Introduction to Supranational Unions and National Sovereignty
Supranational unions represent a collective of member states that cede some degree of national sovereignty to a higher authority to achieve common goals in areas such as trade, security, and legislation. National sovereignty entails the absolute authority of a state to govern itself without external interference, preserving its legal and political independence. The tension between supranational unions and national sovereignty arises from balancing shared decision-making with maintaining autonomous control over domestic affairs.
Defining Supranational Unions: Scope and Purpose
Supranational unions are entities where member states delegate authority to a higher organization that can make decisions binding on all members in specific policy areas such as trade, security, or environmental regulations. These unions aim to foster collective governance, economic integration, and political cooperation beyond individual national interests. The scope of supranational unions typically includes regulatory harmonization, dispute resolution, and coordinated policy implementation that transcends national sovereignty limitations.
Understanding National Sovereignty in the Modern World
National sovereignty in the modern world remains a fundamental principle, defining a state's authority to govern itself without external interference. Supranational unions, such as the European Union, challenge traditional notions of sovereignty by requiring member states to share decision-making powers in areas like trade, security, and environmental policy. This shift necessitates a balance between maintaining autonomous national policies and participating in collective governance frameworks that address global and regional challenges.
Key Examples of Supranational Unions Globally
The European Union (EU) exemplifies a powerful supranational union where member states cede aspects of national sovereignty to achieve economic integration, uniform regulations, and collective political influence. The African Union (AU) promotes regional cooperation and conflict resolution while respecting national sovereignty, focusing on continental development and peacekeeping efforts. ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) balances economic collaboration and political consultation among Southeast Asian countries, preserving national sovereignty while fostering regional stability and growth.
The Historical Evolution of Sovereignty
The historical evolution of sovereignty reflects a shift from absolute national autonomy towards shared authority within supranational unions, illustrating how states gradually cede certain powers to achieve collective goals. The Peace of Westphalia in 1648 established the principle of national sovereignty, but the formation of entities like the European Union demonstrates a modern adaptation where states pool sovereignty for economic integration and political cooperation. This transition highlights the tension and balance between maintaining state independence and embracing supranational governance to address transnational challenges.
Tensions Between Collective Decision-Making and National Autonomy
Supranational unions such as the European Union often face tensions between collective decision-making and national sovereignty, as member states must balance ceding some control to centralized institutions against preserving their autonomous policy agendas. These tensions manifest in disputes over regulatory standards, fiscal policies, and immigration rules where national governments resist uniform mandates that conflict with domestic priorities. The challenge lies in harmonizing shared governance frameworks while respecting the unique legal, cultural, and political contexts of individual nations within the union.
Benefits of Supranational Membership for Member States
Supranational unions offer member states enhanced economic stability and increased political influence on the global stage through collective decision-making and resource sharing. Access to larger markets within the union boosts trade opportunities and attracts foreign investment, driving economic growth and innovation. Collaborative policies on security, environmental protection, and infrastructure development strengthen national capacities and resilience beyond individual capabilities.
Challenges and Criticisms of Supranational Influence
Supranational unions often face challenges related to the erosion of national sovereignty, as member states must cede some legislative and judicial powers to centralized institutions, leading to tension between national governments and supranational bodies like the European Union. Critics argue that supranational influence can undermine democratic accountability and limit the ability of nations to independently determine policies on immigration, economic regulation, and cultural identity. This shift in authority frequently sparks debates over legitimacy, with concerns about a democratic deficit in supranational decision-making processes reducing the political responsiveness to citizens of individual states.
Case Studies: European Union and Its Impact on Sovereignty
The European Union exemplifies the tension between supranational unions and national sovereignty through its policy frameworks that require member states to conform to common regulations, impacting national decision-making autonomy. Case studies such as Brexit highlight the pushback against perceived sovereignty erosion, where the UK prioritized reclaiming legislative control over following EU directives. The EU's legal supremacy, seen in rulings by the European Court of Justice, often supersedes national laws, creating debates on the balance between shared governance and independent state sovereignty.
Future Prospects: Balancing Integration and Independence
Future prospects for supranational unions involve enhancing economic cooperation and political cohesion while preserving national sovereignty to maintain cultural identity and political autonomy. Emerging frameworks emphasize flexible integration models that allow member states to opt in or out of specific policies, promoting a balance between collective decision-making and independent governance. Technological advancements and global challenges like climate change drive deeper collaboration, yet the resurgence of nationalism necessitates mechanisms to safeguard national interests within supranational structures.
Supranational unions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com