A select committee is a temporary legislative body established to investigate or address specific issues beyond the scope of standing committees. These committees play a crucial role in gathering detailed information and making recommendations to improve policy decisions. Explore the rest of this article to understand how a select committee can impact your legislative process.
Table of Comparison
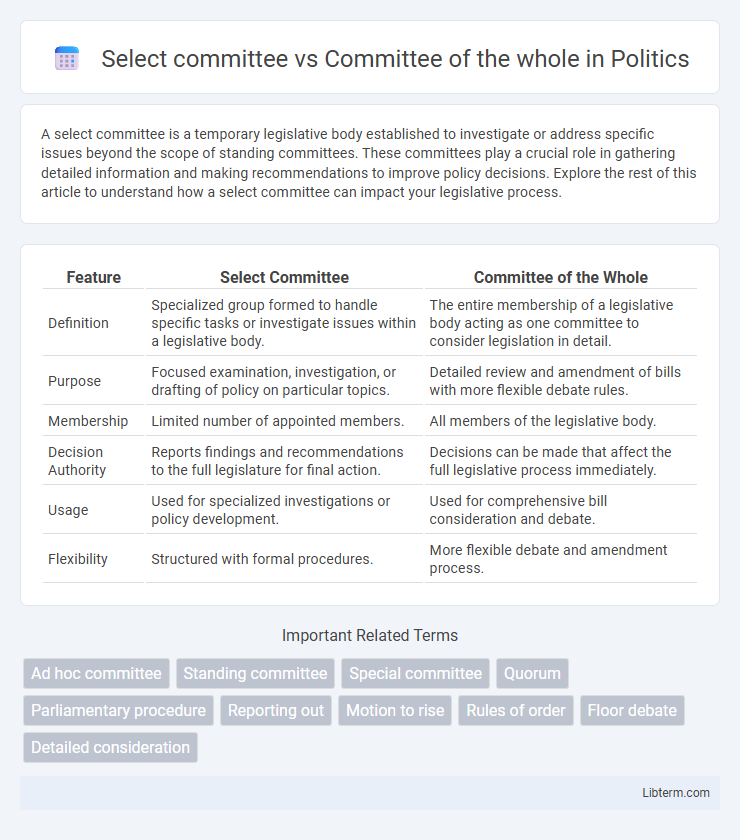
| Feature | Select Committee | Committee of the Whole |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized group formed to handle specific tasks or investigate issues within a legislative body. | The entire membership of a legislative body acting as one committee to consider legislation in detail. |
| Purpose | Focused examination, investigation, or drafting of policy on particular topics. | Detailed review and amendment of bills with more flexible debate rules. |
| Membership | Limited number of appointed members. | All members of the legislative body. |
| Decision Authority | Reports findings and recommendations to the full legislature for final action. | Decisions can be made that affect the full legislative process immediately. |
| Usage | Used for specialized investigations or policy development. | Used for comprehensive bill consideration and debate. |
| Flexibility | Structured with formal procedures. | More flexible debate and amendment process. |
Introduction to Legislative Committees
Select committees are temporary legislative bodies established to investigate specific issues or address particular legislative matters with specialized focus. Committees of the whole involve the entire legislative assembly acting as a single committee to facilitate detailed discussion and expedite the consideration of bills. Both structures enhance legislative efficiency by allowing in-depth review and debate beyond the standard floor sessions.
Definition of Select Committee
A Select Committee is a specialized group established by a legislative body to investigate or consider specific issues, often temporary and focused on detailed examination or inquiry. Unlike the Committee of the Whole, which consists of the entire legislative assembly meeting to expedite the consideration of bills, a Select Committee typically has a limited membership and mandates targeting particular subjects. Select Committees provide in-depth analysis and detailed reports, playing a crucial role in legislative oversight and specialized investigations.
Definition of Committee of the Whole
A Committee of the Whole is a parliamentary procedure in which the entire legislative body sits as a committee to consider complex or detailed matters more informally, allowing freer debate and amendment of bills. Unlike select committees, which are smaller groups appointed to investigate specific issues or tasks, the Committee of the Whole involves all members to facilitate thorough examination and discussion. This structure enhances legislative efficiency by enabling detailed scrutiny without the formality of a full legislative session.
Formation and Membership Comparison
A Select Committee is formed for a specific purpose with members appointed based on expertise or interest, often temporary and limited in scope, while a Committee of the Whole consists of all members of the legislative body acting as a single committee to facilitate detailed discussion. Membership in a Select Committee is selective and specialized, typically smaller, whereas the Committee of the Whole includes the entire legislative chamber to allow broader participation. The formation of Select Committees is usually by resolution or legislative order, contrasting with the automatic formation of the Committee of the Whole when a legislative session resolves into it.
Powers and Functions: A Contrast
Select committees possess specialized investigative powers to examine specific issues or legislation, often holding hearings, collecting evidence, and producing detailed reports for legislative action. In contrast, the Committee of the Whole involves all members of a legislative body, operating with relaxed rules to facilitate thorough debate, amendment, and consideration of bills but lacks the authority to finalize or pass legislation independently. The Select committee's focused scrutiny complements the Committee of the Whole's broad deliberative role, ensuring both detailed analysis and comprehensive member participation in the legislative process.
Operational Procedures and Rules
Select committees operate with specialized mandates, following formal procedural rules tailored to specific issues, enabling focused investigations and targeted reporting. Committees of the whole involve the entire legislative body, adopting more flexible and expedited rules to facilitate open debate and efficient consideration of legislation. The operational distinction lies in the select committee's detailed scrutiny versus the committee of the whole's broader discussion framework.
Areas of Application in Legislation
Select committees specialize in detailed examination of specific legislative issues, such as finance, health, or foreign affairs, enabling focused scrutiny and expert testimony. Committees of the whole convene the entire legislative body to facilitate more informal debate and consideration of broad or complex bills, often used during clause-by-clause review. Select committees are common in parliamentary systems for investigative purposes, while committees of the whole streamline decision-making on comprehensive legislation within legislatures.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Select committees offer specialized expertise, enabling detailed examination of specific issues, which improves legislative efficiency and informed decision-making. However, their narrow focus can limit broader perspectives and slow the overall legislative process. Committees of the whole facilitate comprehensive debate and faster consideration of legislation by involving all members but may lack the specialized scrutiny provided by select committees.
Real-World Examples
The Select Committee on Intelligence in the U.S. House of Representatives is a prime example of a select committee, formed to address specific issues like national security oversight, distinct from the standing committees. In contrast, the U.S. House often uses the Committee of the Whole to expedite the legislative process, allowing the entire membership to debate bills with relaxed rules and faster decision-making, notably during budget resolutions or major fiscal legislation. These mechanisms demonstrate tailored legislative functions: select committees provide focused expertise and investigation, while Committees of the Whole enhance procedural efficiency in broad debates.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Implications
Select committees focus on specific issues, conducting detailed investigations and producing targeted reports, whereas committees of the whole involve all members of a legislative body to facilitate open debate and expedite decision-making. The select committee's specialization enhances legislative oversight and policy refinement, while the committee of the whole promotes broad participation and consensus-building. Understanding these distinctions informs legislative strategies, impacting efficiency, transparency, and democratic engagement in lawmaking processes.
Select committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com