Privately-funded projects offer greater flexibility and quicker decision-making compared to public initiatives, often leading to innovative solutions tailored to specific market needs. Your ability to invest in such ventures can drive growth and foster entrepreneurship in emerging industries. Explore the rest of the article to understand how privately-funded opportunities can transform your business landscape.
Table of Comparison
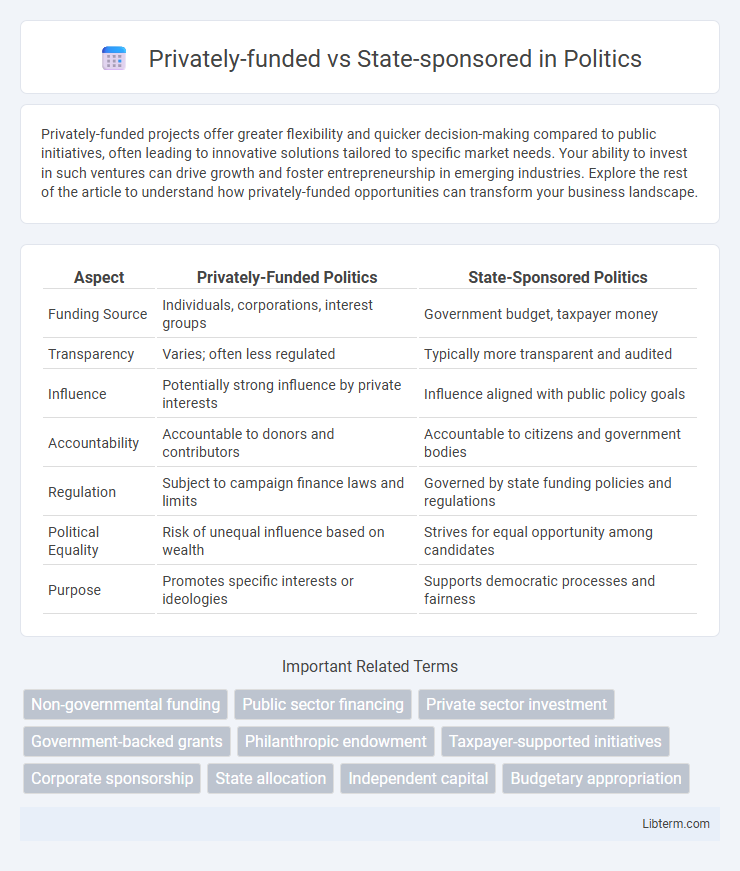
| Aspect | Privately-Funded Politics | State-Sponsored Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Individuals, corporations, interest groups | Government budget, taxpayer money |
| Transparency | Varies; often less regulated | Typically more transparent and audited |
| Influence | Potentially strong influence by private interests | Influence aligned with public policy goals |
| Accountability | Accountable to donors and contributors | Accountable to citizens and government bodies |
| Regulation | Subject to campaign finance laws and limits | Governed by state funding policies and regulations |
| Political Equality | Risk of unequal influence based on wealth | Strives for equal opportunity among candidates |
| Purpose | Promotes specific interests or ideologies | Supports democratic processes and fairness |
Introduction to Privately-Funded and State-Sponsored Models
Privately-funded models rely on investments and donations from individuals, corporations, or private organizations to finance projects and initiatives, emphasizing innovation and market-driven goals. State-sponsored models receive government funding and support, prioritizing public interest, regulatory compliance, and long-term societal benefits. Both approaches influence the scope, accountability, and objectives of the initiatives they support.
Key Differences Between Privately-Funded and State-Sponsored Initiatives
Privately-funded initiatives are typically driven by corporate or individual investments aiming for profit, innovation, and market competitiveness, often with flexible timelines and proprietary objectives. State-sponsored initiatives prioritize public interest, social welfare, and national strategic goals, supported by government budgets and regulatory frameworks to ensure broader accessibility and long-term stability. Key differences include funding sources, accountability structures, and the alignment of goals between private profit and public benefit.
Advantages of Privately-Funded Projects
Privately-funded projects benefit from greater flexibility in decision-making and faster implementation due to fewer bureaucratic constraints. They often attract innovative technologies and specialized expertise by leveraging competitive market incentives and entrepreneurial approaches. These projects typically exhibit higher efficiency and cost-effectiveness, driven by profit motives and performance-based management.
Benefits of State-Sponsored Programs
State-sponsored programs provide consistent funding and regulatory oversight, ensuring accessibility and equity in education, healthcare, and social services. These programs benefit from economies of scale, allowing for broader reach and cost efficiency compared to privately-funded initiatives. State sponsorship often fosters long-term sustainability and accountability, supporting public welfare and community development.
Funding Sources and Financial Sustainability
Privately-funded projects rely on investments from individual donors, corporations, and private foundations, emphasizing diverse revenue streams to maintain financial sustainability without government dependency. State-sponsored initiatives secure funding primarily from government budgets, grants, and public taxes, ensuring stable but often politically influenced financial support. Financial sustainability for privately-funded efforts depends on continuous engagement with stakeholders and innovative fundraising, while state-sponsored programs benefit from institutional backing but face risks of budget cuts and policy shifts.
Accountability and Governance Structures
Privately-funded organizations typically exhibit accountability through internal governance mechanisms such as boards of directors and shareholder oversight, prioritizing efficiency and profit-driven goals. State-sponsored entities operate under public accountability frameworks, governed by governmental regulations and legislative oversight to ensure compliance with policy objectives and public interest. The governance structures of state-sponsored bodies often include transparency requirements, public reporting, and political accountability, contrasting with the market-driven governance of privately-funded institutions.
Impact on Innovation and Research Development
Privately-funded research drives rapid innovation through competitive markets and flexible resource allocation, promoting breakthroughs in technology and product development. State-sponsored research often supports long-term projects with broader societal benefits, funding high-risk or fundamental studies that may lack immediate commercial appeal. The synergy between private investment and public funding creates a balanced ecosystem, accelerating technological advancements and fostering sustainable research growth.
Access, Equity, and Social Implications
Privately-funded initiatives often provide quicker access to advanced technologies but may exacerbate equity gaps due to higher costs and limited availability for marginalized groups. State-sponsored programs tend to prioritize broader access and social equity by subsidizing services and implementing policies aimed at inclusivity. The social implications of private funding can include increased stratification, whereas state sponsorship seeks to promote social cohesion and universal benefits.
Case Studies: Comparing Real-World Examples
Privately-funded initiatives like SpaceX focus on innovation and rapid development through commercial investment, achieving milestones such as reusable rockets and private astronaut missions. In contrast, state-sponsored programs like NASA benefit from government funding and long-term strategic goals, driving large-scale scientific research and exploration projects, including Mars rovers and deep space probes. Comparing these models reveals differing priorities: private ventures emphasize cost-efficiency and market responsiveness, while government agencies prioritize extensive research, national interests, and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends and Policy Considerations
Privately-funded initiatives in technology and research are expected to accelerate innovation through flexible investment strategies and rapid scalability, often prioritizing commercial viability. State-sponsored projects typically focus on long-term national interests, security, and public welfare, supported by substantial regulatory frameworks and stable funding. Future policy considerations must balance fostering private sector dynamism with safeguarding public interests, ensuring ethical standards, data privacy, and equitable access to emerging technologies.
Privately-funded Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com