Liberal democracy emphasizes individual freedoms, rule of law, and fair elections to ensure government accountability and protect citizens' rights. It balances majority rule with protection of minorities through constitutional limits and independent institutions. Explore the article to understand how liberal democracy shapes modern governance and your role within it.
Table of Comparison
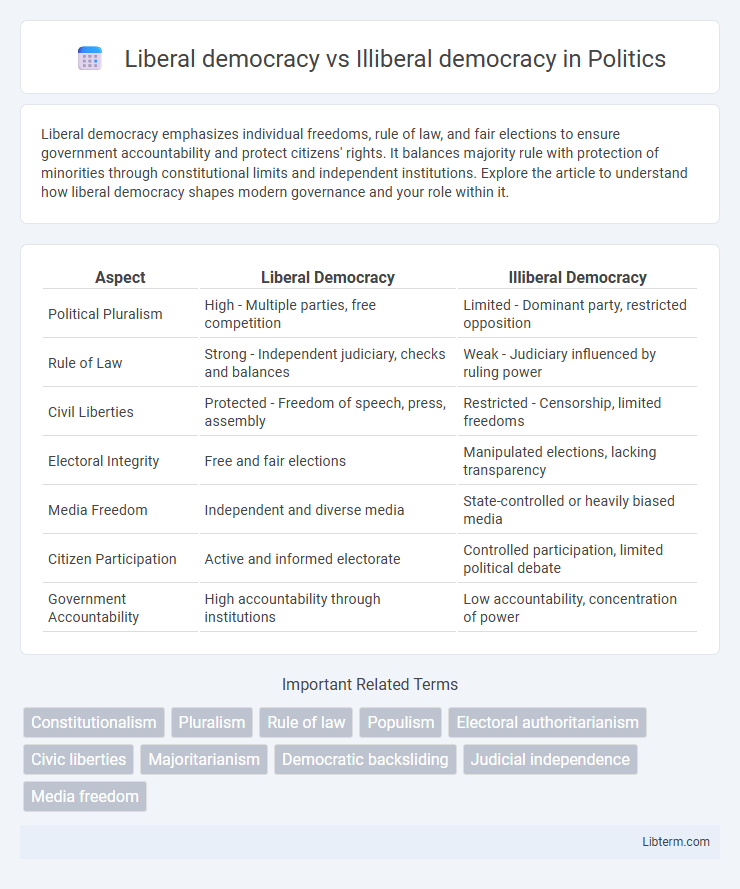
| Aspect | Liberal Democracy | Illiberal Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Political Pluralism | High - Multiple parties, free competition | Limited - Dominant party, restricted opposition |
| Rule of Law | Strong - Independent judiciary, checks and balances | Weak - Judiciary influenced by ruling power |
| Civil Liberties | Protected - Freedom of speech, press, assembly | Restricted - Censorship, limited freedoms |
| Electoral Integrity | Free and fair elections | Manipulated elections, lacking transparency |
| Media Freedom | Independent and diverse media | State-controlled or heavily biased media |
| Citizen Participation | Active and informed electorate | Controlled participation, limited political debate |
| Government Accountability | High accountability through institutions | Low accountability, concentration of power |
Defining Liberal Democracy: Core Principles
Liberal democracy is defined by the protection of individual rights, rule of law, separation of powers, and free, fair elections ensuring government accountability. Emphasis is placed on civil liberties such as freedom of speech, press, and assembly, alongside an independent judiciary that safeguards these rights. These core principles create a political environment where minority rights are preserved and governmental power is limited through institutional checks and balances.
Understanding Illiberal Democracy: Key Characteristics
Illiberal democracy is characterized by the presence of elections that are ostensibly competitive but lack fundamental civil liberties such as freedom of speech, press, and assembly. Key features include centralized executive power, weakened judicial independence, restricted political pluralism, and limited checks and balances, leading to the erosion of democratic norms. This system often maintains the facade of democratic institutions while undermining transparency, accountability, and individual rights.
Historical Evolution: From Liberal to Illiberal Regimes
Liberal democracy historically emerged from Enlightenment principles emphasizing individual rights, rule of law, and separation of powers, establishing frameworks for free elections and civil liberties. Over time, some liberal democracies experienced shifts toward illiberal democracy, characterized by elected leaders undermining institutional checks, restricting media freedom, and eroding civil liberties while maintaining nominal electoral processes. This transition reflects a global trend where democratic backsliding challenges liberal norms, often driven by populist movements exploiting socio-economic grievances and weakening democratic institutions.
Rule of Law: Comparing Legal Frameworks
Liberal democracies uphold the rule of law through independent judiciary systems that enforce constitutional rights and ensure government accountability. Illiberal democracies possess legal frameworks but often weaken judicial independence, allowing the executive branch to manipulate laws and restrict civil liberties. This fundamental difference leads to varying degrees of legal protection, transparency, and adherence to universal human rights standards.
Civil Liberties and Human Rights: A Comparative Analysis
Liberal democracy prioritizes civil liberties and human rights by ensuring freedom of speech, independent judiciary, and protection against government abuses, fostering political pluralism and individual autonomy. Illiberal democracy, despite holding elections, often restricts these freedoms through media censorship, weakened judicial independence, and suppression of dissent, undermining the rule of law. Comparative analysis reveals that liberal democracies maintain stronger institutional checks and guarantees for human rights, whereas illiberal regimes use democratic frameworks superficially while eroding fundamental liberties.
Free Press and Media Freedom: Divergent Approaches
Liberal democracy upholds free press and media freedom as essential pillars, ensuring independent journalism thrives without government interference, fostering transparency and accountability. Illiberal democracy restricts media freedom through censorship, state control, and suppression of dissenting voices, undermining unbiased information flow. These divergent approaches significantly impact public access to truthful reporting and democratic participation.
Electoral Systems: Genuine Choice vs Manipulation
Liberal democracies feature electoral systems that provide genuine choice through free, fair, and competitive elections, ensuring accountability and representation. Illiberal democracies often manipulate electoral rules, restrict opposition, and use disinformation, undermining the legitimacy of the vote and consolidating power. Genuine choice in liberal systems contrasts sharply with the orchestrated manipulation seen in illiberal regimes, affecting overall political pluralism and citizen trust.
Checks and Balances: Institutional Safeguards
Liberal democracy features robust checks and balances through independent branches of government, ensuring protection of civil liberties and rule of law. Illiberal democracy often weakens these institutional safeguards by concentrating power in the executive and undermining judicial independence. This erosion of checks and balances results in limited accountability and diminished protection of minority rights.
Societal Impacts: Stability, Prosperity, and Dissent
Liberal democracies foster societal stability through strong institutions, protection of individual rights, and a free press, which collectively encourage sustained economic prosperity and peaceful expression of dissent. In contrast, illiberal democracies often experience suppressed dissent and weakened checks on power, leading to social unrest and economic volatility despite maintaining electoral processes. The erosion of civil liberties in illiberal systems typically hampers long-term development and fuels polarization within society.
The Global Trend: Challenges and Future Prospects
Liberal democracy, characterized by free elections, rule of law, and protection of individual rights, faces global challenges from the rise of illiberal democracies, where electoral processes exist but are undermined by authoritarian practices and weakened institutions. Countries like Hungary, Turkey, and Russia exemplify this shift, posing significant threats to democratic norms and international stability. Future prospects depend on strengthening democratic resilience through civil society engagement, international cooperation, and safeguarding judicial independence to counter authoritarian tendencies.
Liberal democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com