A responsive policy adapts swiftly to changing circumstances, ensuring decisions remain relevant and effective. It emphasizes real-time feedback, continuous evaluation, and flexibility to address emerging challenges efficiently. Discover how implementing a responsive policy can enhance your organization's resilience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
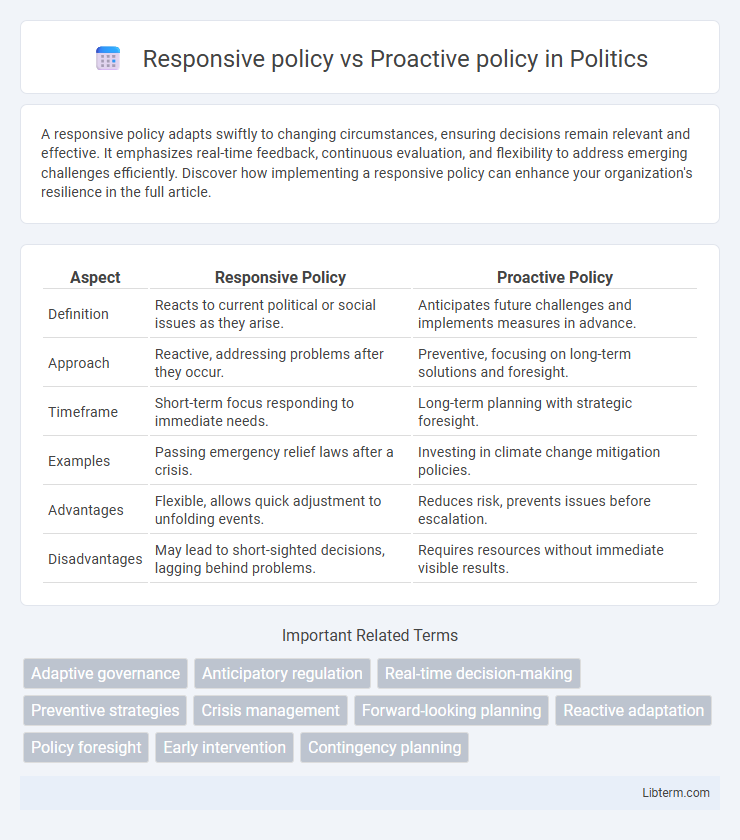
| Aspect | Responsive Policy | Proactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reacts to current political or social issues as they arise. | Anticipates future challenges and implements measures in advance. |
| Approach | Reactive, addressing problems after they occur. | Preventive, focusing on long-term solutions and foresight. |
| Timeframe | Short-term focus responding to immediate needs. | Long-term planning with strategic foresight. |
| Examples | Passing emergency relief laws after a crisis. | Investing in climate change mitigation policies. |
| Advantages | Flexible, allows quick adjustment to unfolding events. | Reduces risk, prevents issues before escalation. |
| Disadvantages | May lead to short-sighted decisions, lagging behind problems. | Requires resources without immediate visible results. |
Introduction to Responsive and Proactive Policies
Responsive policies react to events or problems after they occur, emphasizing short-term solutions and immediate issue resolution. Proactive policies anticipate potential challenges through forecasting and strategic planning, aiming to prevent issues before they arise. Organizations benefit from balancing responsive strategies for crisis management with proactive policies to optimize long-term outcomes and resource allocation.
Defining Responsive Policy: Key Characteristics
Responsive policy is characterized by its reactive nature, addressing issues as they arise rather than anticipating them. It relies heavily on data analysis and stakeholder feedback to formulate solutions tailored to current problems. This policy approach prioritizes flexibility and adaptability, enabling quick adjustments to changing circumstances.
Understanding Proactive Policy: Core Elements
Understanding proactive policy involves anticipating future challenges and implementing strategic measures before issues arise, thereby minimizing risks and enhancing system resilience. Core elements include predictive analytics, continuous monitoring, stakeholder engagement, and adaptive frameworks that enable timely interventions. This approach contrasts with responsive policy, which reacts to problems post-occurrence, often resulting in delayed mitigation and higher costs.
Historical Context: Evolution of Policy Approaches
Responsive policy emerged in the mid-20th century, characterized by reactive measures addressing issues after they arise, often influenced by immediate social and economic crises. Proactive policy gained traction in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, emphasizing anticipatory strategies and preventive frameworks to mitigate risks before problems escalate. This evolution reflects a shift from short-term crisis management to long-term planning, driven by advancements in data analytics and a growing understanding of complex systemic challenges.
Advantages of Responsive Policies
Responsive policies offer the advantage of flexibility, allowing governments and organizations to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and emerging issues. These policies reduce risks by enabling timely adjustments based on real-time data and stakeholder feedback, minimizing potential negative impacts. Furthermore, responsive policies foster inclusivity and transparency by encouraging continuous dialogue with affected communities, enhancing legitimacy and public trust.
Benefits of Proactive Policy Implementation
Proactive policy implementation enables organizations to anticipate future challenges and address issues before they escalate, resulting in reduced risks and enhanced operational efficiency. This approach fosters continuous improvement through data-driven decision-making, ensuring policies evolve with emerging trends and stakeholder needs. By adopting proactive policies, companies can gain competitive advantages, improve compliance, and build stronger stakeholder trust through transparent and forward-looking governance.
Comparing Effectiveness: When Each Policy Excels
Responsive policies excel in crisis management by swiftly addressing immediate problems through reactive measures, making them ideal for unpredictable or rapidly changing situations where quick adjustments are crucial. Proactive policies outperform in long-term strategy by anticipating future challenges and implementing preventive actions, thereby reducing risks and fostering sustainable growth. Effectiveness depends on context: responsive approaches suit urgent, unforeseen disruptions while proactive strategies thrive in stable environments seeking to minimize future issues.
Real-World Examples: Responsive vs Proactive Policies
Responsive policies address issues after they occur, exemplified by disaster relief programs implemented following hurricanes like Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Proactive policies focus on prevention and anticipation, as seen in Japan's earthquake-resistant building codes and early warning systems that mitigate damage before earthquakes strike. Countries with proactive public health strategies, such as South Korea's rapid COVID-19 testing and contact tracing, showcase effective containment compared to reactive approaches.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Responsive policy often struggles with delayed decision-making due to its reactive nature, making it difficult to address emerging issues promptly. Proactive policy, while aiming to anticipate and prevent problems, faces challenges such as resource allocation uncertainties and the risk of implementing premature interventions without accurate predictions. Both approaches are limited by the complexity of dynamic social, economic, and environmental factors that complicate effective policy design and execution.
Choosing the Right Policy Approach for Different Scenarios
Choosing between a responsive and proactive policy approach depends on the urgency and predictability of the issue at hand. Responsive policies are effective for addressing unforeseen crises quickly, minimizing immediate damage through adaptive measures. Proactive policies are optimal for long-term challenges, establishing preventive frameworks that reduce future risks and enhance sustainability.
Responsive policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com