Globalization shapes economies by increasing cross-border trade, investment, and cultural exchange, fostering interconnected markets and innovation. It influences labor markets and consumer choices, while also raising concerns about economic inequality and cultural homogenization. Explore the rest of the article to understand how globalization impacts Your life and the global community.
Table of Comparison
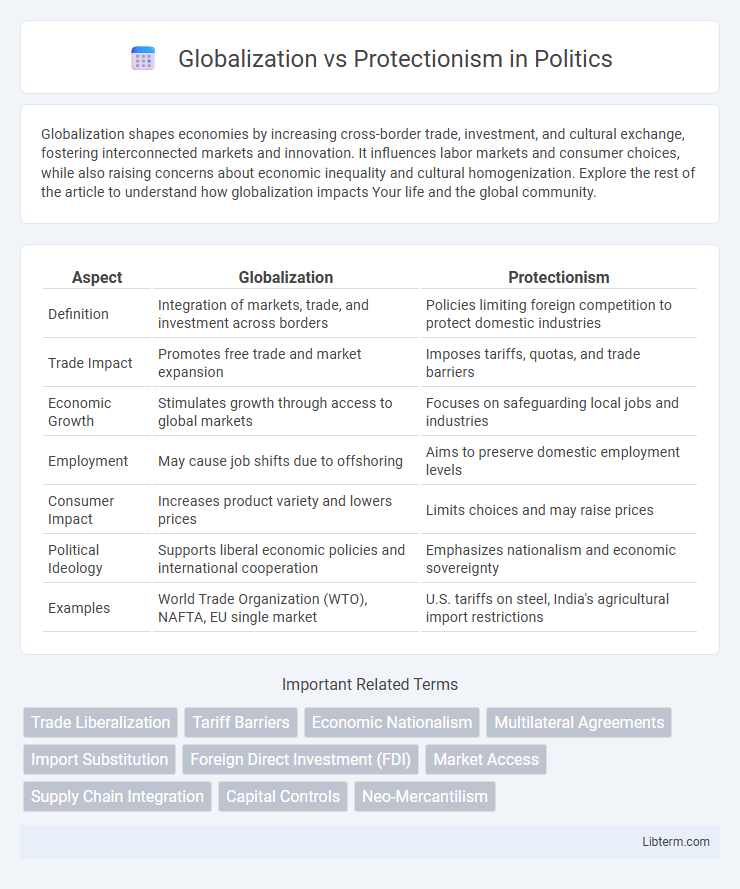
| Aspect | Globalization | Protectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of markets, trade, and investment across borders | Policies limiting foreign competition to protect domestic industries |
| Trade Impact | Promotes free trade and market expansion | Imposes tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers |
| Economic Growth | Stimulates growth through access to global markets | Focuses on safeguarding local jobs and industries |
| Employment | May cause job shifts due to offshoring | Aims to preserve domestic employment levels |
| Consumer Impact | Increases product variety and lowers prices | Limits choices and may raise prices |
| Political Ideology | Supports liberal economic policies and international cooperation | Emphasizes nationalism and economic sovereignty |
| Examples | World Trade Organization (WTO), NAFTA, EU single market | U.S. tariffs on steel, India's agricultural import restrictions |
Introduction to Globalization and Protectionism
Globalization involves the increasing interconnectedness of economies through trade, investment, technology, and cultural exchange, fostering global market integration and economic growth. Protectionism refers to government policies that restrict imports through tariffs, quotas, and regulations to shield domestic industries from foreign competition. These contrasting approaches shape international economic relations and significantly impact global trade dynamics and national economic policies.
Historical Context and Evolution
Globalization emerged prominently after World War II, driven by institutions like the IMF, World Bank, and GATT, promoting free trade and economic integration to rebuild war-torn economies. Protectionism, conversely, influenced early 20th-century policies, especially during the Great Depression, as countries imposed tariffs and trade barriers to shield domestic industries. Over time, the tension between globalization's liberal trade agenda and protectionism's focus on national economic sovereignty has shaped trade negotiations and economic policy worldwide.
Key Drivers of Globalization
Technological advancements, such as the rise of digital communication and transportation innovations, have significantly lowered barriers to international trade and investment, fueling globalization. Multinational corporations expand their operations across borders to optimize production and access new markets, further driving global economic integration. Trade liberalization through international agreements and organizations reduces tariffs and regulatory constraints, accelerating the global flow of goods, services, and capital.
Main Arguments for Protectionism
Protectionism advocates emphasize the need to safeguard domestic industries from foreign competition by imposing tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers to preserve jobs and economic stability. They argue that protecting emerging industries allows them to develop competitive advantages before exposing them to global markets. Furthermore, protectionism supports national security by limiting dependence on foreign suppliers for critical goods and services.
Economic Impacts: Growth vs Security
Globalization drives economic growth by promoting free trade, expanding markets, and increasing efficiency through specialization and innovation. Protectionism, while potentially limiting growth, enhances economic security by safeguarding domestic industries and preserving jobs from foreign competition. Balancing globalization's growth benefits with protectionism's focus on security is crucial for sustainable economic policymaking.
Effects on Employment and Wages
Globalization often leads to job creation in export-oriented industries while causing wage suppression and job displacement in sectors exposed to international competition. Protectionism can shield domestic jobs from foreign competition but may result in higher production costs, reduced efficiency, and limited wage growth due to less competitive pressure. Empirical data shows that countries embracing open trade policies tend to experience higher average wages and lower unemployment rates compared to those with restrictive trade barriers.
Influence on Innovation and Competitiveness
Globalization fosters innovation by enabling knowledge exchange, access to diverse markets, and collaboration across borders, which drives competitiveness through economies of scale and technological advancement. Protectionism restricts these benefits by imposing trade barriers that limit market access, reduce competitive pressure, and hinder the diffusion of new technologies, ultimately slowing innovation. Countries embracing open trade policies typically experience higher innovation rates and stronger global competitiveness compared to those adopting protectionist measures.
Social and Cultural Implications
Globalization fosters cultural exchange and social integration by promoting diversity and cross-cultural understanding, enriching societies through shared ideas and customs. Protectionism, however, can preserve local traditions and social structures by limiting foreign influence and maintaining cultural identity. The tension between these approaches shapes the social fabric, influencing community cohesion and cultural resilience amid global economic dynamics.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
The case study of China exemplifies successful globalization through export-led growth and foreign investment attraction, resulting in rapid economic development and poverty reduction. Conversely, Zimbabwe's protectionist policies in the 2000s, characterized by import restrictions and land reform, led to economic collapse and hyperinflation, highlighting the risks of isolating domestic markets. The contrasting outcomes underline the complex interplay between global market integration and protective measures in shaping national economic trajectories.
Future Trends and Policy Recommendations
Future trends indicate a continued rise in digital globalization, with emerging technologies enhancing cross-border trade and services while necessitating updated international regulatory frameworks. Protectionism may persist in sectors critical to national security and supply chain resilience, driving governments to adopt strategic tariffs and investment screenings. Policy recommendations emphasize balancing open markets with targeted safeguards, promoting multilateral cooperation on digital trade standards, and investing in workforce adaptation for evolving global economic dynamics.
Globalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com