Austerity refers to government policies aimed at reducing public sector debt through spending cuts and tax increases, often during economic downturns. These measures can lead to significant impacts on social services, economic growth, and public welfare. Discover how austerity might affect your community and the broader economy by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
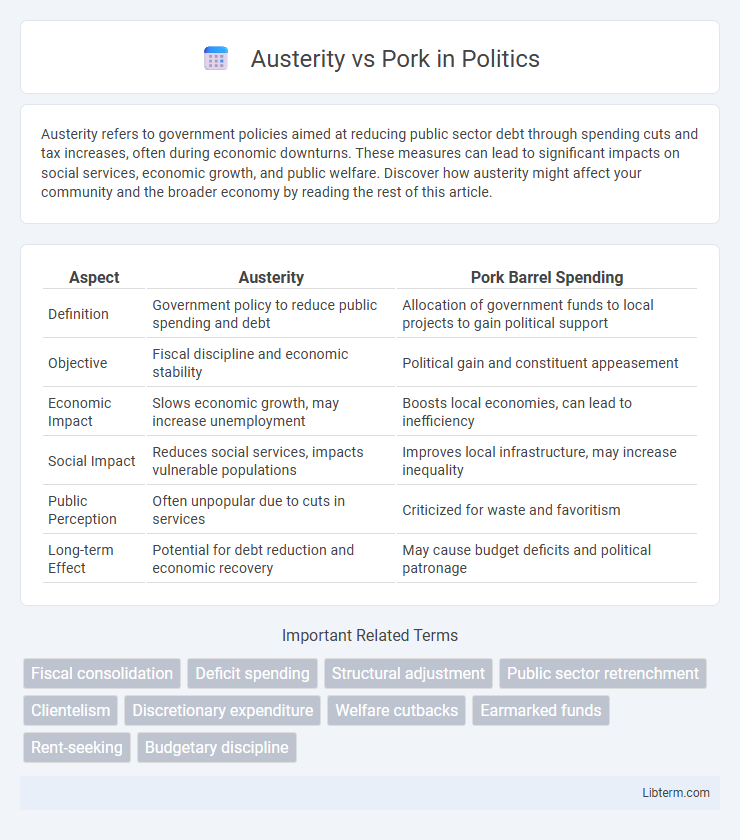
| Aspect | Austerity | Pork Barrel Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government policy to reduce public spending and debt | Allocation of government funds to local projects to gain political support |
| Objective | Fiscal discipline and economic stability | Political gain and constituent appeasement |
| Economic Impact | Slows economic growth, may increase unemployment | Boosts local economies, can lead to inefficiency |
| Social Impact | Reduces social services, impacts vulnerable populations | Improves local infrastructure, may increase inequality |
| Public Perception | Often unpopular due to cuts in services | Criticized for waste and favoritism |
| Long-term Effect | Potential for debt reduction and economic recovery | May cause budget deficits and political patronage |
Understanding Austerity: Definition and Origins
Austerity refers to economic policies aimed at reducing government deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both, typically implemented during periods of financial crisis to restore fiscal balance. Originating from post-World War I and Great Depression practices, austerity measures emphasize reducing public debt and controlling budget deficits to stabilize the economy and regain investor confidence. The approach often sparks debate due to its impact on social services and economic growth, contrasting with pork-barrel spending, which involves allocating government funds for localized projects to benefit specific constituencies.
What is Pork Barrel Spending?
Pork barrel spending refers to government expenditure directed toward localized projects secured primarily to bring money to a representative's district, often to gain political support. This type of spending typically funds infrastructure, public works, or community services that may not have broad national benefits but serve local interests. Critics argue pork barrel spending contributes to inefficient budget allocation and undermines fiscal austerity by inflating government deficits.
The Economic Rationale Behind Austerity
The economic rationale behind austerity centers on reducing government budget deficits through spending cuts and tax increases to restore fiscal balance and investor confidence. Proponents argue that austerity controls public debt levels, curbs inflation, and stabilizes the economy by preventing unsustainable borrowing. Critics contend that austerity can shrink GDP growth and increase unemployment by cutting essential public services and investment.
Examining the Political Motivations for Pork
Political motivations for pork barrel spending often stem from the desire to secure reelection by delivering tangible benefits to constituents, thereby strengthening local support and political capital. Elected officials prioritize allocating funds to visible projects within their districts to appease voters and interest groups, which can overshadow broader austerity measures aimed at reducing fiscal deficits. This tension between immediate political gain through pork and long-term economic stability drives the persistent debate between austerity policies and targeted government expenditures.
Austerity’s Impact on Public Services and Growth
Austerity measures typically result in significant cuts to public services, leading to reduced access to healthcare, education, and social welfare programs. These reductions often slow economic growth by decreasing public sector employment and consumer spending, which in turn undermines overall demand. Research indicates that prolonged austerity can exacerbate income inequality and hinder long-term economic recovery.
Pork Barrel Spending and Electoral Incentives
Pork barrel spending refers to government expenditures directed toward localized projects designed to benefit a legislator's constituents, often used to secure electoral support. Electoral incentives drive politicians to allocate funds toward such projects to maximize voter approval and increase re-election chances, even if these expenditures contribute to fiscal inefficiency. Austerity measures, aiming to reduce budget deficits, often clash with pork barrel practices because cutbacks limit resources available for these politically motivated projects.
Real-World Case Studies: Austerity in Action
Austerity measures implemented in Greece during the 2010 debt crisis involved harsh spending cuts and tax hikes aimed at reducing the budget deficit but resulted in deep recessions and soaring unemployment rates. Contrastingly, the United States' post-2008 stimulus emphasized targeted pork-barrel spending to boost economic recovery and preserve jobs, showing mixed results in long-term fiscal health. These real-world case studies highlight the tension between austerity-driven fiscal discipline and pork-barrel spending's short-term economic support.
Pork Projects: Successes and Failures
Pork projects, often characterized by government spending directed toward localized benefits to secure political support, have seen mixed results in economic development and public welfare. Successful pork projects typically generate tangible infrastructure improvements, job creation, and community investment, while failures often involve misallocation of funds, cost overruns, and limited long-term impact. Evaluating pork projects requires analyzing transparency, accountability, and alignment with broader policy objectives to distinguish effective investments from mere political maneuvering.
Public Perception: Austerity vs Pork
Public perception of austerity measures often leans toward viewing them as necessary for fiscal responsibility, though many criticize the social impact on vulnerable populations. In contrast, pork barrel spending is frequently perceived negatively, associated with government waste and favoritism, fostering distrust among taxpayers. Voter sentiment typically favors transparency and accountability, demanding efficient use of public funds without excessive cuts or unnecessary expenditures.
Policy Outcomes: Striking the Right Balance
Austerity policies often aim to reduce government deficits through spending cuts, which can stabilize debt levels but risk slowing economic growth and increasing unemployment. Pork-barrel spending injects targeted funds into local projects, promoting short-term economic boosts and political support but potentially leading to inefficient resource allocation and higher deficits. Striking the right balance involves implementing fiscally responsible measures while strategically investing in high-impact areas to foster sustainable growth and social welfare.
Austerity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com