Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and practices to maintain social stability and continuity. It advocates for cautious change, valuing experience and established norms over radical innovation. Explore this article to understand how conservatism shapes political, cultural, and social landscapes today.
Table of Comparison
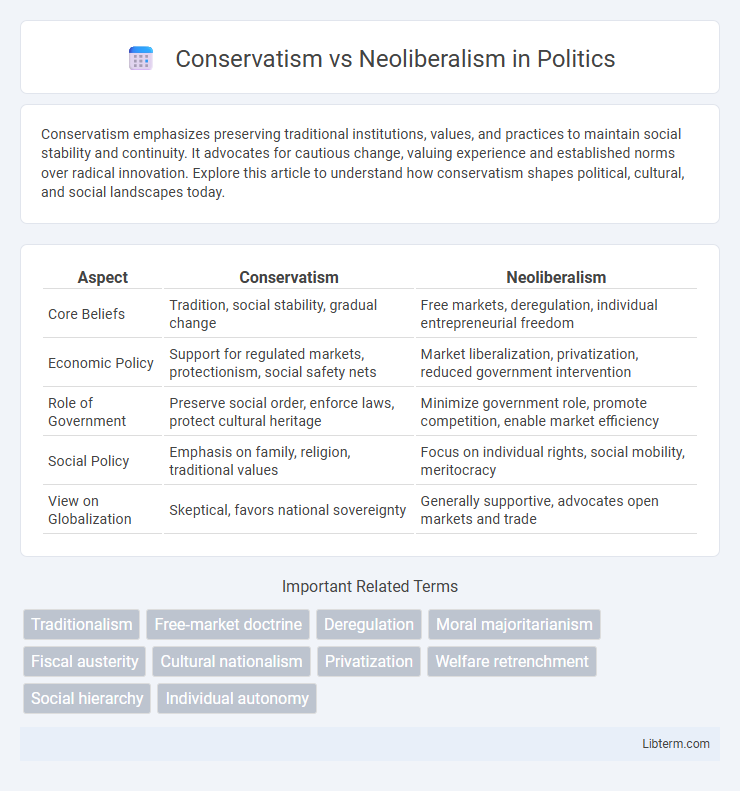
| Aspect | Conservatism | Neoliberalism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Beliefs | Tradition, social stability, gradual change | Free markets, deregulation, individual entrepreneurial freedom |
| Economic Policy | Support for regulated markets, protectionism, social safety nets | Market liberalization, privatization, reduced government intervention |
| Role of Government | Preserve social order, enforce laws, protect cultural heritage | Minimize government role, promote competition, enable market efficiency |
| Social Policy | Emphasis on family, religion, traditional values | Focus on individual rights, social mobility, meritocracy |
| View on Globalization | Skeptical, favors national sovereignty | Generally supportive, advocates open markets and trade |
Defining Conservatism: Core Principles
Conservatism centers on preserving traditional institutions, cultural heritage, and social order, emphasizing stability and continuity in governance. Core principles include a preference for gradual change over radical reform, belief in limited government intervention, and valuing personal responsibility alongside free-market capitalism. This ideology prioritizes maintaining established moral frameworks and national identity to foster societal cohesion.
Understanding Neoliberalism: Key Tenets
Neoliberalism emphasizes free-market capitalism, deregulation, and reduced government intervention to drive economic growth and individual freedom. It advocates for privatization of public services, open global trade, and competition as mechanisms to increase efficiency and innovation. Core principles include fiscal austerity, tax cuts for businesses, and the promotion of entrepreneurship within a globalized economy.
Historical Origins of Conservatism and Neoliberalism
Conservatism originated in the late 18th century as a reaction to the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social hierarchy, and skepticism toward rapid change. Neoliberalism emerged in the mid-20th century, particularly post-World War II, as a revival of classical liberal ideas focusing on free markets, deregulation, and limited government intervention. While conservatism stresses preserving established institutions and values, neoliberalism advocates for economic liberalization and global capitalism as drivers of progress.
Economic Policies: Regulation vs. Free Market
Conservatism emphasizes regulation to maintain economic stability, advocating for government intervention to protect industries and preserve traditional market structures. Neoliberalism champions free market principles, promoting deregulation, privatization, and limited government involvement to foster competition and innovation. The economic policy debate centers on balancing state control against market freedom to maximize growth and efficiency.
Role of Government: Limited vs. Interventionist Approaches
Conservatism advocates for a limited government role, emphasizing free markets, individual responsibility, and minimal state intervention to preserve traditional social orders. Neoliberalism supports an interventionist government that actively regulates markets, promotes globalization, and implements policies to correct market failures and foster economic growth. These differing approaches reflect contrasting views on balancing state power with economic freedom and social stability.
Social Values: Tradition vs. Individualism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional social values, such as family structures, religious beliefs, and cultural heritage, viewing them as essential for social stability and cohesion. Neoliberalism prioritizes individualism, advocating for personal freedom, self-reliance, and minimal state intervention in social and economic matters. This ideological difference results in contrasting approaches to policies on issues like marriage, education, and welfare, reflecting a deep divide between collective norms and personal autonomy.
Globalization: National Interests vs. Market Integration
Conservatism emphasizes protecting national interests by prioritizing sovereignty, cultural identity, and economic security against the risks of globalization. Neoliberalism advocates for deep market integration, promoting free trade, deregulation, and open borders to enhance global economic efficiency and innovation. The tension between these ideologies shapes policies on tariffs, immigration, and multinational agreements, reflecting competing priorities between preserving state control and maximizing global market access.
Political Influence: Conservatism and Neoliberalism in Practice
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, advocating for limited government intervention and prioritizing social stability, which often translates into policies supporting national sovereignty and cultural values. Neoliberalism promotes free-market capitalism, deregulation, and privatization, influencing political agendas that favor economic globalization and reduced state control in markets. Both ideologies shape policy decisions, with conservatism reinforcing existing power structures while neoliberalism drives economic reforms focused on market efficiency and individual entrepreneurship.
Criticisms and Controversies: Debates and Dissent
Conservatism faces criticism for its resistance to social change and perceived promotion of inequality, while neoliberalism is often challenged for prioritizing market freedom over social welfare and exacerbating economic disparities. Debates highlight conservatives' emphasis on tradition and order contrasted with neoliberalism's advocacy for deregulation and privatization, stirring dissent about the balance between state intervention and free markets. Controversies continue over neoliberal policies' impact on public services and conservatism's stance on cultural issues, fueling ongoing ideological conflicts.
Future Trends: The Evolving Ideological Landscape
Conservatism is increasingly adapting to technological advancements and demographic shifts by emphasizing tradition alongside pragmatic governance, while neoliberalism faces critiques over economic inequality and sustainability concerns, prompting a gradual integration of social welfare policies. Future trends suggest a hybridization where conservative values blend with market-oriented reforms, and neoliberalism evolves towards inclusive capitalism and environmental responsibility. This evolving ideological landscape reflects a global response to political polarization, climate change, and economic globalization challenges.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com