Effective moderation ensures a balanced and respectful environment by carefully managing content and interactions. It helps prevent harmful behavior while promoting positive engagement within communities. Discover how moderation techniques can improve your online experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
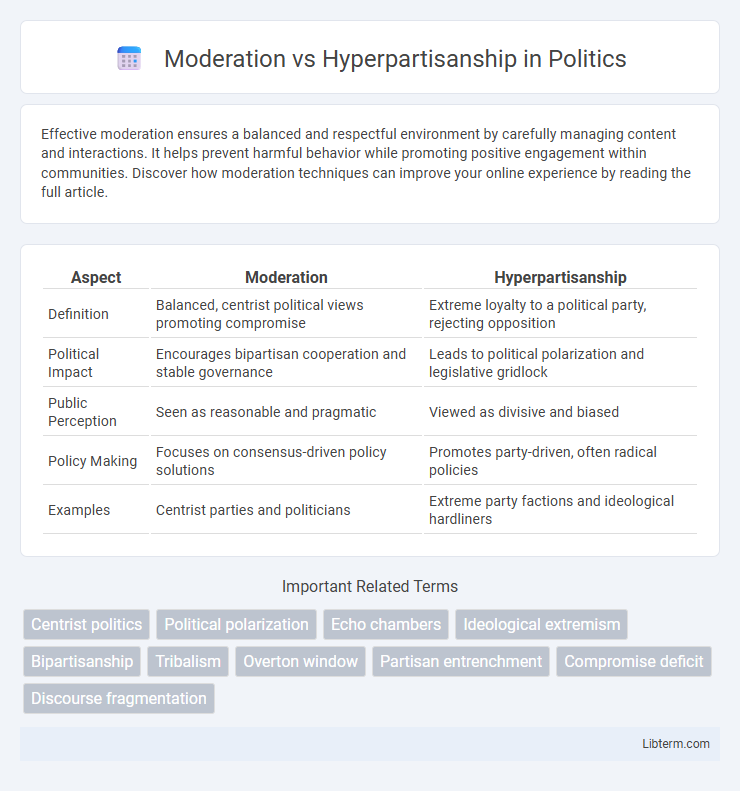
| Aspect | Moderation | Hyperpartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Balanced, centrist political views promoting compromise | Extreme loyalty to a political party, rejecting opposition |
| Political Impact | Encourages bipartisan cooperation and stable governance | Leads to political polarization and legislative gridlock |
| Public Perception | Seen as reasonable and pragmatic | Viewed as divisive and biased |
| Policy Making | Focuses on consensus-driven policy solutions | Promotes party-driven, often radical policies |
| Examples | Centrist parties and politicians | Extreme party factions and ideological hardliners |
Understanding Moderation and Hyperpartisanship
Moderation involves balanced viewpoints and willingness to consider diverse perspectives, fostering constructive political dialogue and compromise. Hyperpartisanship reflects extreme loyalty to a political party, often leading to polarization, reduced collaboration, and gridlock in decision-making processes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for analyzing the impact on legislative effectiveness and democratic governance.
The Roots of Political Moderation
Political moderation often emerges from diverse social backgrounds and cross-cutting identities, encouraging individuals to seek balanced solutions and compromise. Exposure to multiple viewpoints and the desire to maintain social cohesion incentivize moderate stances over ideological extremes. Studies show that electoral systems with proportional representation and competitive districts also foster moderation by rewarding centrist candidates.
What Drives Hyperpartisanship?
Hyperpartisanship is driven primarily by social identity theory, where individuals increasingly align with political groups that bolster their self-concept and group loyalty. Media echo chambers and algorithm-driven content exacerbate polarization by reinforcing existing biases and creating insular information bubbles. Psychological factors such as cognitive dissonance and motivated reasoning further entrench extreme partisan views, diminishing openness to compromise and moderation.
Historical Shifts: Moderation vs. Hyperpartisanship
Historical shifts in American politics reveal fluctuating patterns between moderation and hyperpartisanship, where eras like the post-World War II period favored bipartisan cooperation and compromise, while the late 20th and early 21st centuries saw increasing ideological polarization. Data from the Pew Research Center highlights growing partisan divides in congressional voting behavior, with fewer cross-party alliances and heightened political polarization since the 1990s. This transition toward hyperpartisanship has influenced legislative gridlock, public trust in government, and voter engagement trends.
Impact on Democratic Discourse
Moderation fosters inclusive democratic discourse by encouraging compromise and understanding across diverse political viewpoints, reducing polarization. Hyperpartisanship deepens ideological divides, leading to fragmented public debate and decreased willingness to consider opposing perspectives. The impact of hyperpartisanship on democratic institutions includes diminished trust, legislative gridlock, and weakened social cohesion.
Consequences for Policy-Making
Moderation in policy-making fosters bipartisan cooperation, resulting in more balanced and sustainable legislation that addresses diverse stakeholder needs. Hyperpartisanship sharpens ideological divides, often causing legislative gridlock and policy stagnation, which undermines effective governance and public trust. The consequences include impaired ability to respond to complex societal challenges and increased polarization within political institutions.
Social Media’s Role in Hyperpartisanship
Social media platforms amplify hyperpartisanship by creating echo chambers where users predominantly engage with content that reinforces their existing beliefs, intensifying political polarization. Algorithms prioritize sensational and emotionally charged posts, increasing exposure to extreme viewpoints and reducing opportunities for moderate discourse. This dynamic undermines balanced political discussions and fuels division across digital communities.
Bridging the Divide: Strategies for Promoting Moderation
Effective strategies for promoting moderation include fostering open dialogue between opposing political factions and encouraging critical thinking to reduce hyperpartisan bias. Implementing bipartisan initiatives and community engagement programs helps bridge ideological divides by highlighting shared values and common goals. Educational reforms that emphasize media literacy and empathy further support efforts to diminish polarization and strengthen democratic cohesion.
Real-World Examples of Moderation and Hyperpartisanship
Senator Joe Manchin of West Virginia exemplifies political moderation through his bipartisan efforts to negotiate legislation, often bridging gaps between Republicans and Democrats. In contrast, the 2013 U.S. government shutdown highlights hyperpartisanship, where extreme party loyalty led to a political deadlock, resulting in a 16-day closure. The German Bundestag showcases moderation with its coalition governments that necessitate compromise, whereas the polarization seen in Brazil's recent elections reflects growing hyperpartisan divisions.
The Future of Political Engagement
The future of political engagement hinges on balancing moderation and hyperpartisanship, where nuanced dialogue fosters collaboration across ideological divides while hyperpartisanship often leads to polarization and gridlock. Emphasizing critical thinking and media literacy can empower citizens to engage constructively, reducing the influence of echo chambers and misinformation. Digital platforms are evolving to support more inclusive political discourse, encouraging diverse viewpoints and civic participation in democratic processes.
Moderation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com