Conservatism is a political philosophy emphasizing tradition, social stability, and gradual change rather than radical reform. It values established institutions and cultural continuity to preserve societal order and national identity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how conservatism shapes modern policies and your role within this enduring ideology.
Table of Comparison
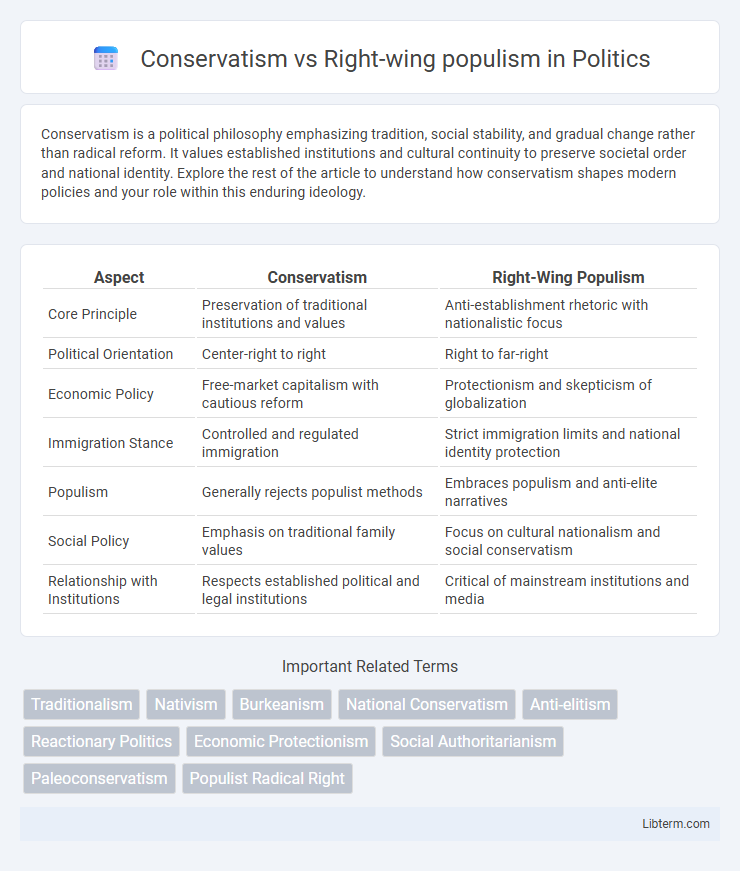
| Aspect | Conservatism | Right-Wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Preservation of traditional institutions and values | Anti-establishment rhetoric with nationalistic focus |
| Political Orientation | Center-right to right | Right to far-right |
| Economic Policy | Free-market capitalism with cautious reform | Protectionism and skepticism of globalization |
| Immigration Stance | Controlled and regulated immigration | Strict immigration limits and national identity protection |
| Populism | Generally rejects populist methods | Embraces populism and anti-elite narratives |
| Social Policy | Emphasis on traditional family values | Focus on cultural nationalism and social conservatism |
| Relationship with Institutions | Respects established political and legal institutions | Critical of mainstream institutions and media |
Origins and Historical Development
Conservatism originated in the late 18th century as a response to the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social order, and gradual change rooted in Enlightenment and religious principles. Right-wing populism emerged in the late 20th century, combining nationalist rhetoric with anti-elitist sentiments, often reacting to globalization, immigration, and economic uncertainty. While conservatism focuses on preserving established institutions and cultural continuity, right-wing populism mobilizes mass support through identity politics and direct appeals to "the people" against perceived political, economic, and cultural threats.
Core Ideological Principles
Conservatism emphasizes tradition, social stability, and gradual societal change, prioritizing institutions like family, religion, and a free-market economy. Right-wing populism combines nationalist rhetoric with anti-elitist sentiments, often advocating for strict immigration controls and protectionist economic policies to defend perceived cultural identity. While conservatism upholds continuity and institutional authority, right-wing populism mobilizes popular discontent against political elites and globalization effects.
Socioeconomic Policies
Conservatism typically emphasizes free-market capitalism, fiscal responsibility, and limited government intervention in the economy, advocating for policies that promote individual entrepreneurship and private property rights. Right-wing populism, while often endorsing some conservative economic principles, tends to incorporate protectionist measures, welfare chauvinism, and opposition to globalization to protect domestic jobs and prioritize native citizens. The socioeconomic focus of right-wing populism often blends nationalist rhetoric with demands for economic security, contrasting with conservatism's broader emphasis on market-driven growth and institutional stability.
Approach to National Identity
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional national identity through cultural heritage, historical continuity, and established customs. Right-wing populism prioritizes a more exclusionary national identity, often defining it in opposition to immigrants, minorities, or globalization influences. This approach typically promotes sovereignty and nationalist rhetoric to mobilize support.
Views on Globalization
Conservatism generally advocates for cautious engagement with globalization, emphasizing national sovereignty, cultural preservation, and controlled immigration to protect traditional values and economic stability. Right-wing populism rejects globalization more vehemently, portraying it as a threat to national identity, economic security, and social cohesion, often promoting protectionist policies and anti-immigrant rhetoric. Both perspectives criticize aspects of globalization but differ in intensity and focus, with right-wing populism adopting a more aggressive and emotional stance against global integration.
Attitudes Toward Tradition and Change
Conservatism emphasizes the preservation of traditional institutions, social norms, and cultural heritage, advocating gradual change to maintain societal stability. Right-wing populism combines a strong defense of traditional values with a critique of political elites, often promoting rapid, radical change to restore perceived lost national identity. Both reject progressive social reforms but differ in their approach: conservatism favors cautious adaptation, while right-wing populism pushes for immediate, populist-driven transformation.
Relationship with Democracy
Conservatism traditionally supports democratic institutions by emphasizing stability, rule of law, and gradual change within established political frameworks. Right-wing populism often challenges democratic norms by promoting anti-elitist rhetoric, skepticism toward pluralism, and sometimes endorsing authoritarian measures to represent "the people." The tension between conservatism and right-wing populism centers on divergent views of democracy's role in safeguarding order versus expressing popular will.
Political Messaging and Rhetoric
Conservatism employs political messaging centered on tradition, social stability, and incremental change, emphasizing respect for established institutions and norms. Right-wing populism utilizes rhetoric that highlights anti-elitism, nationalism, and direct appeals to the "common people," often framing political elites as corrupt and out of touch. Both approaches leverage identity and emotion, but right-wing populism intensifies dichotomies between in-groups and out-groups to mobilize support.
Key Figures and Movements
Key figures in conservatism include Margaret Thatcher and Ronald Reagan, who emphasized free-market capitalism, traditional values, and strong national defense. Right-wing populism is spearheaded by leaders like Donald Trump and Marine Le Pen, focusing on nationalism, anti-immigration policies, and skepticism toward global institutions. Movements such as the Tea Party in the United States and the Alternative for Germany (AfD) party illustrate the rise of right-wing populism, contrasting with established conservative parties that promote institutional stability and gradual change.
Contemporary Challenges and Criticisms
Conservatism faces contemporary challenges such as adapting to rapid social changes while maintaining traditional values, often criticized for resistance to progressive reforms and perceived elitism. Right-wing populism, characterized by nationalist rhetoric and anti-establishment sentiments, encounters criticism for fostering polarization, xenophobia, and undermining democratic norms. Both movements struggle with balancing identity politics and inclusivity in increasingly diverse societies, impacting their political legitimacy and societal cohesion.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com