Government regulation plays a critical role in maintaining market stability and protecting public interests by enforcing laws that govern business practices and consumer rights. It ensures that industries operate fairly, promotes safety standards, and prevents monopolistic behaviors that could harm Your economic freedoms. Discover how these regulations impact various sectors and what it means for You in the detailed analysis ahead.
Table of Comparison
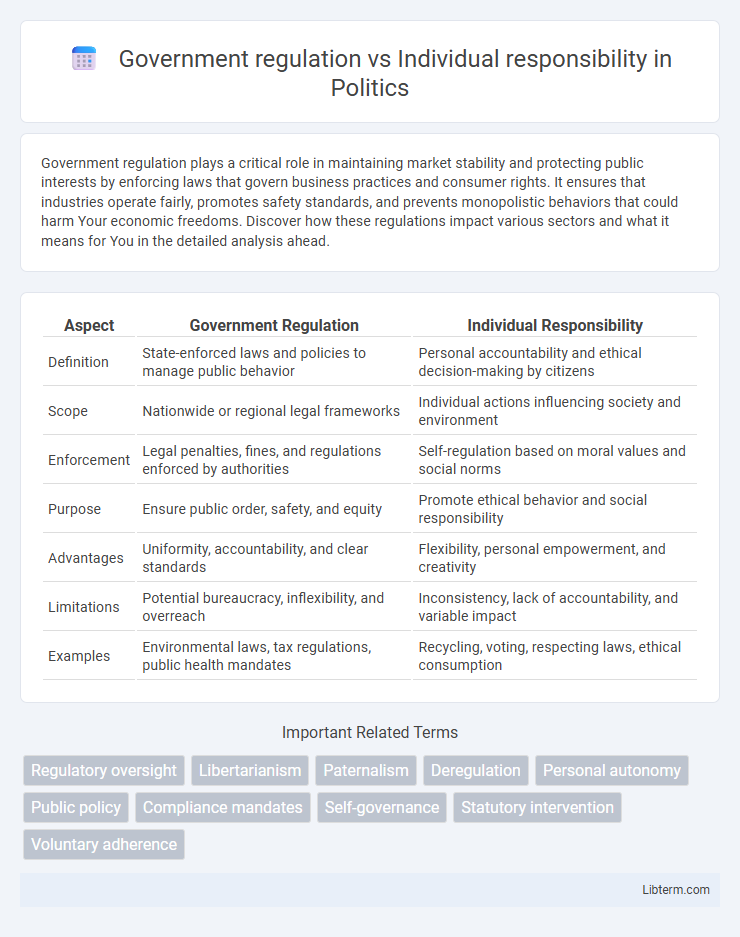
| Aspect | Government Regulation | Individual Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-enforced laws and policies to manage public behavior | Personal accountability and ethical decision-making by citizens |
| Scope | Nationwide or regional legal frameworks | Individual actions influencing society and environment |
| Enforcement | Legal penalties, fines, and regulations enforced by authorities | Self-regulation based on moral values and social norms |
| Purpose | Ensure public order, safety, and equity | Promote ethical behavior and social responsibility |
| Advantages | Uniformity, accountability, and clear standards | Flexibility, personal empowerment, and creativity |
| Limitations | Potential bureaucracy, inflexibility, and overreach | Inconsistency, lack of accountability, and variable impact |
| Examples | Environmental laws, tax regulations, public health mandates | Recycling, voting, respecting laws, ethical consumption |
Introduction to Government Regulation and Individual Responsibility
Government regulation establishes legal frameworks and policies designed to protect public interests, ensure safety, and maintain order across various sectors such as health, environment, and finance. Individual responsibility emphasizes personal accountability in adhering to laws, ethical standards, and social norms to contribute to societal well-being. Balancing regulatory oversight with personal initiative is essential for effective governance and community development.
Historical Context: Evolving Roles in Society
Government regulation has expanded significantly since the Progressive Era, responding to industrialization challenges such as labor rights, environmental protection, and public health. Individual responsibility gained prominence during periods of limited state intervention, particularly in laissez-faire economies of the 19th century. Contemporary debates reflect a dynamic interplay where historical shifts influence policy decisions balancing collective welfare and personal accountability.
Key Differences: Regulation vs. Personal Choice
Government regulation mandates specific actions or restrictions to protect public interests, often enforced through laws and penalties, ensuring uniform compliance across populations. Individual responsibility emphasizes personal choice and moral judgment in adhering to social norms or ethical standards without external enforcement. The key difference lies in regulation's authoritative, collective approach versus personal responsibility's voluntary, subjective nature.
Benefits of Strong Government Oversight
Strong government oversight ensures the protection of public health, safety, and the environment by enforcing regulations that prevent harmful practices and promote accountability. It creates a framework for consistent standards across industries, reducing risks and fostering consumer trust. Enhanced regulation also supports economic stability by mitigating market failures and encouraging sustainable development.
Advantages of Emphasizing Individual Responsibility
Emphasizing individual responsibility fosters personal accountability and encourages proactive decision-making, reducing dependency on government interventions. This approach enhances efficiency by leveraging local knowledge and personal incentives, often resulting in quicker and more tailored solutions to societal challenges. It also promotes civic engagement and empowerment, strengthening democratic values and social cohesion.
Case Studies: Public Health, Environment, and Economy
Government regulation in public health, environment, and economy ensures standardized safety and equitable resource distribution, exemplified by the Clean Air Act's reduction of pollutants and the FDA's food safety mandates. Individual responsibility complements these regulations through personal health practices and sustainable consumer choices, which case studies show enhance the effectiveness of policies like vaccination campaigns and recycling programs. Balancing enforceable regulations with empowered individual actions leads to optimized outcomes in disease control, environmental preservation, and economic stability.
Challenges and Criticisms of Regulation
Government regulation often faces criticism for creating bureaucratic inefficiencies and stifling innovation, with frequent debates on whether excessive rules impede individual freedoms and market dynamics. Challenges include regulatory capture, where agencies serve industry interests instead of the public, and inconsistencies in enforcement that undermine effectiveness. Balancing the need for public safety and economic growth remains a complex issue, highlighting tensions between collective oversight and personal accountability.
Limitations of Relying on Personal Accountability
Relying solely on individual responsibility often leads to inconsistent outcomes due to varying levels of awareness, resources, and motivation among people. Government regulation creates standardized rules that ensure public safety, environmental protection, and social welfare are maintained regardless of personal behavior differences. Without regulatory frameworks, crucial issues like pollution control and workplace safety can be neglected, highlighting the limitations of personal accountability in addressing collective challenges.
Finding the Right Balance: Policy Approaches
Effective policy approaches require balancing government regulation with individual responsibility by crafting laws that protect public interests without stifling personal freedoms. Implementing adaptive frameworks enables timely responses to societal challenges such as environmental protection, public health, and data privacy, while encouraging citizen engagement and accountability. Optimal balance is achieved through transparent governance, stakeholder collaboration, and evidence-based decision-making to align regulatory scope with collective and individual wellbeing.
Future Trends and Implications for Society
Government regulation and individual responsibility are increasingly intersecting as digital technology advances, requiring adaptive policy frameworks to address privacy, cybersecurity, and environmental sustainability. Emerging trends suggest that collaborative governance models, combining state oversight with empowered citizen participation, will enhance societal resilience and innovation. This shared approach influences future social norms by fostering accountability, ethical behavior, and sustainable development at both institutional and individual levels.
Government regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com