Running as an independent candidate allows you to bypass traditional party structures and appeal directly to voters with unique perspectives and policies. This approach offers greater flexibility in campaign messaging and can attract constituents seeking alternatives to mainstream parties. Explore the rest of the article to understand the key strategies for launching a successful independent candidacy.
Table of Comparison
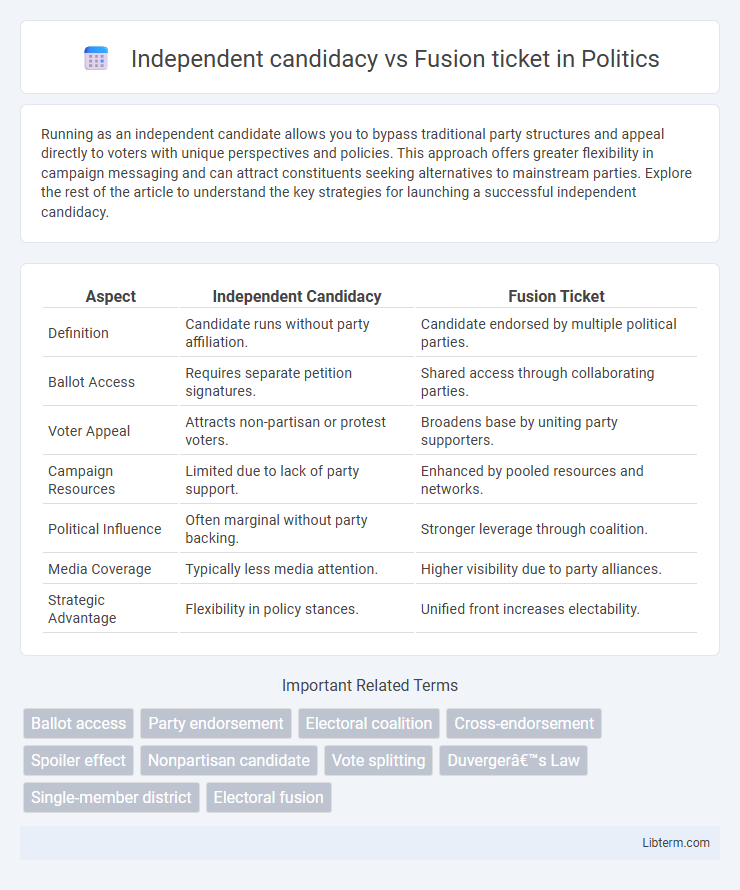
| Aspect | Independent Candidacy | Fusion Ticket |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Candidate runs without party affiliation. | Candidate endorsed by multiple political parties. |
| Ballot Access | Requires separate petition signatures. | Shared access through collaborating parties. |
| Voter Appeal | Attracts non-partisan or protest voters. | Broadens base by uniting party supporters. |
| Campaign Resources | Limited due to lack of party support. | Enhanced by pooled resources and networks. |
| Political Influence | Often marginal without party backing. | Stronger leverage through coalition. |
| Media Coverage | Typically less media attention. | Higher visibility due to party alliances. |
| Strategic Advantage | Flexibility in policy stances. | Unified front increases electability. |
Understanding Independent Candidacy
Independent candidacy allows political candidates to run without formal affiliation to established parties, providing flexibility in platform and voter appeal. Understanding independent candidacy involves recognizing its challenges, including limited access to party resources and ballot access hurdles. This approach contrasts with fusion tickets, where multiple parties endorse a single candidate to consolidate support.
Defining Fusion Ticket Alliances
Fusion ticket alliances occur when multiple political parties endorse a single candidate to consolidate votes and increase electoral chances. This strategy contrasts with independent candidacy, where a candidate runs without official party backing, relying solely on personal support and grassroots efforts. Fusion tickets often optimize ballot access and signal broader coalition-building in multi-party systems.
Historical Context: Origins and Evolution
Independent candidacy emerged as a response to restrictive party systems in the 19th century, allowing individuals outside established parties to seek office. Fusion tickets originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, enabling multiple parties to unite behind a single candidate to consolidate votes against dominant parties. Over time, fusion efforts influenced electoral reforms and third-party strategies, reflecting shifting political alliances and challenges within the U.S. multiparty landscape.
Key Advantages of Independent Candidacy
An independent candidacy offers the key advantage of greater electoral flexibility, allowing candidates to avoid party constraints and appeal directly to a broad voter base. Independent candidates often benefit from a unique position to address specific local issues without being tied to the national party agenda. This freedom can enhance voter trust by emphasizing personal accountability and grassroots connection, distinguishing independents from fusion tickets that rely on multiple party endorsements.
Benefits of Fusion Ticket Strategies
Fusion ticket strategies enhance electoral viability by allowing candidates to appear on multiple party lines, broadening their voter base and increasing overall ballot access. This approach consolidates support from diverse political groups, improving vote totals and reducing vote splitting among aligned parties. Fusion tickets also leverage combined resources and endorsements, amplifying campaign visibility and influence compared to independent candidacies.
Challenges Facing Independent Candidates
Independent candidates face significant challenges including limited access to major party resources, ballot access restrictions, and lower visibility compared to fusion ticket candidates who benefit from multiple party endorsements. They must overcome difficulties in fundraising and garnering media exposure, often resulting in reduced voter recognition and support. The lack of established party infrastructure further complicates campaign organization and voter mobilization efforts for independents.
Drawbacks of Fusion Ticket Approaches
Fusion ticket approaches often face legal challenges due to ballot access laws that restrict multiple party endorsements, limiting the candidate's exposure. These tickets can dilute party identity, causing voter confusion and weakening brand consistency across elections. Financial resources may be strained as campaigns must coordinate among differing party platforms and donor bases, reducing overall campaign efficiency.
Impact on Voter Choice and Representation
Independent candidacy offers voters distinct policy platforms and unfiltered representation, often reflecting localized interests and diverse viewpoints. Fusion tickets combine the strengths of multiple parties, broadening appeal and enhancing coalition-building that may increase voter turnout and representation accuracy. This dynamic influences electoral competition by expanding choices beyond traditional party lines and potentially improving alignment between elected officials and constituents.
Case Studies: Notable Examples Worldwide
Independent candidacies, such as Bernie Sanders' successful runs in U.S. Senate races, demonstrate the power of individual political branding without party backing. Fusion tickets, exemplified by the 1948 New York gubernatorial race where the American Labor Party fused with the Democrats, show strategic alliances enhancing voter reach and influence. Worldwide cases include Italy's Five Star Movement, initially independent and later forming coalitions, illustrating the dynamic interplay between solo runs and fusion strategies.
Future Trends and Electoral Implications
Independent candidacy gains momentum as voters seek alternatives to traditional party structures, influencing future trends by increasing political diversity and voter engagement. Fusion tickets, by combining party strengths, may face challenges adapting to growing demands for transparency and ideological coherence. Electoral implications include potential shifts in coalition-building strategies and the redefinition of voter alignment patterns in increasingly polarized political landscapes.
Independent candidacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com