Voter alignment reflects the consistent support individuals give to a particular political party or ideology, heavily influenced by social, economic, and cultural factors. Understanding how voter alignment shapes election outcomes can reveal key trends in public opinion and policy preferences. Explore the rest of this article to see how these patterns impact your voting behavior and the broader political landscape.
Table of Comparison
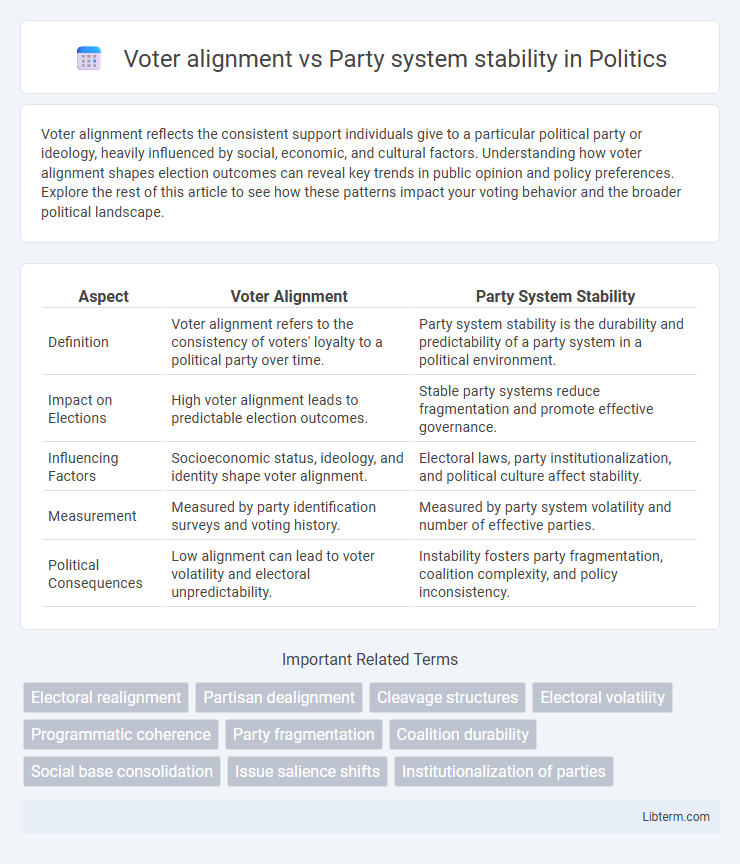
| Aspect | Voter Alignment | Party System Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voter alignment refers to the consistency of voters' loyalty to a political party over time. | Party system stability is the durability and predictability of a party system in a political environment. |
| Impact on Elections | High voter alignment leads to predictable election outcomes. | Stable party systems reduce fragmentation and promote effective governance. |
| Influencing Factors | Socioeconomic status, ideology, and identity shape voter alignment. | Electoral laws, party institutionalization, and political culture affect stability. |
| Measurement | Measured by party identification surveys and voting history. | Measured by party system volatility and number of effective parties. |
| Political Consequences | Low alignment can lead to voter volatility and electoral unpredictability. | Instability fosters party fragmentation, coalition complexity, and policy inconsistency. |
Understanding Voter Alignment: Key Concepts
Voter alignment refers to the consistent pattern of voter loyalty to a specific political party or ideology over time, reflecting deep-seated social, economic, or cultural affiliations. Key concepts include cleavage structures, which are social divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity that shape voter preferences and party identification. Understanding these alignments is crucial for analyzing party system stability, as stable alignments tend to reinforce enduring party systems, while shifts or dealignments can lead to system realignments or fragmentation.
Defining Party System Stability
Party system stability refers to the persistence and predictability of political parties' presence and influence within a political landscape over time. It is measured by the durability of party organizations, consistency in voter support, and the frequency of party realignments or fragmentation. High party system stability often correlates with clear voter-party alignments, reducing electoral volatility and fostering sustained governance structures.
Historical Trends in Voter Alignment
Historical trends in voter alignment reveal shifts driven by social, economic, and ideological changes that influence party system stability. Periods of realignment, such as the New Deal era, showcase how critical elections redefined voter coalitions and strengthened party dominance. Understanding these patterns helps explain fluctuations in party loyalty and the emergence or decline of political parties over time.
Patterns of Party System Development
Patterns of party system development reveal that stable voter alignment often correlates with durable party systems, as consistent electoral support strengthens party institutions and facilitates coherent policy platforms. Fragmentation or volatility in voter preferences can lead to frequent party realignments, weakening system stability and creating opportunities for populist or fringe parties to emerge. Long-term patterns of voter loyalty typically produce entrenched party competition, fostering predictable electoral outcomes and more stable democratic governance.
The Impact of Voter Realignment on Party Systems
Voter realignment significantly influences party system stability by reshaping electoral coalitions and altering traditional party bases. Historical cases demonstrate that major shifts in voter preferences can lead to the emergence or collapse of dominant parties, disrupting established party systems. Such realignments often coincide with critical elections, triggering long-term transformations in political competition and governance structures.
Factors Influencing Party System Stability
Voter alignment significantly impacts party system stability through factors such as the consistency of voter preferences, the strength of party identification, and the socio-economic divisions within the electorate. High voter alignment fosters stable party systems by reducing electoral volatility and reinforcing existing party structures. Conversely, fragmented or shifting voter alignment can lead to party system instability, marked by frequent party emergence, realignment, and volatility in political competition.
Case Studies: Voter Alignment Shifts and Systemic Change
Case studies on voter alignment shifts reveal significant impacts on party system stability, as observed in the realignment of African American voters from the Republican to the Democratic Party during the Civil Rights Movement, leading to a durable two-party system transformation. Similarly, the rise of populist movements in Western Europe showcases voter realignments that undermine traditional party systems, resulting in fragmentation and the emergence of new political actors. These examples highlight how shifts in voter alignment serve as catalysts for systemic change, altering party competition and political landscape stability.
Electoral Systems and Their Role in Alignment and Stability
Electoral systems play a pivotal role in shaping voter alignment and party system stability by influencing how votes translate into seats, thereby affecting political representation and party competition. Proportional representation systems tend to enhance party system stability by allowing multiple parties to gain legislative seats, fostering coalition-building and encouraging voters to align with parties that closely match their preferences. Conversely, majoritarian electoral systems often lead to two-party dominance, which simplifies voter alignment but can reduce overall party system stability by marginalizing smaller parties and limiting political diversity.
Consequences of Misalignment: Fragmentation and Volatility
Voter alignment misalignment with party systems often leads to political fragmentation, characterized by the rise of splinter groups and independent candidates that challenge established parties. This fragmentation fosters electoral volatility, resulting in unpredictable election outcomes and weakened government stability. Such instability undermines coherent policy-making and can diminish public trust in democratic institutions.
Future Challenges for Stable Party Systems
Voter alignment shifts increasingly challenge party system stability by fragmenting traditional support bases and fostering multiparty competition. Emerging political issues and demographic changes intensify volatility, complicating coalition-building and policy coherence within established party systems. Future stability depends on parties' adaptability to evolving voter preferences and the institutional mechanisms that manage electoral fragmentation.
Voter alignment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com