A shadow government operates covertly to influence political decisions, often undermining public transparency and official governance. This hidden power structure can shape policies behind the scenes, affecting your rights and national stability. Discover the truth behind shadow governments in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
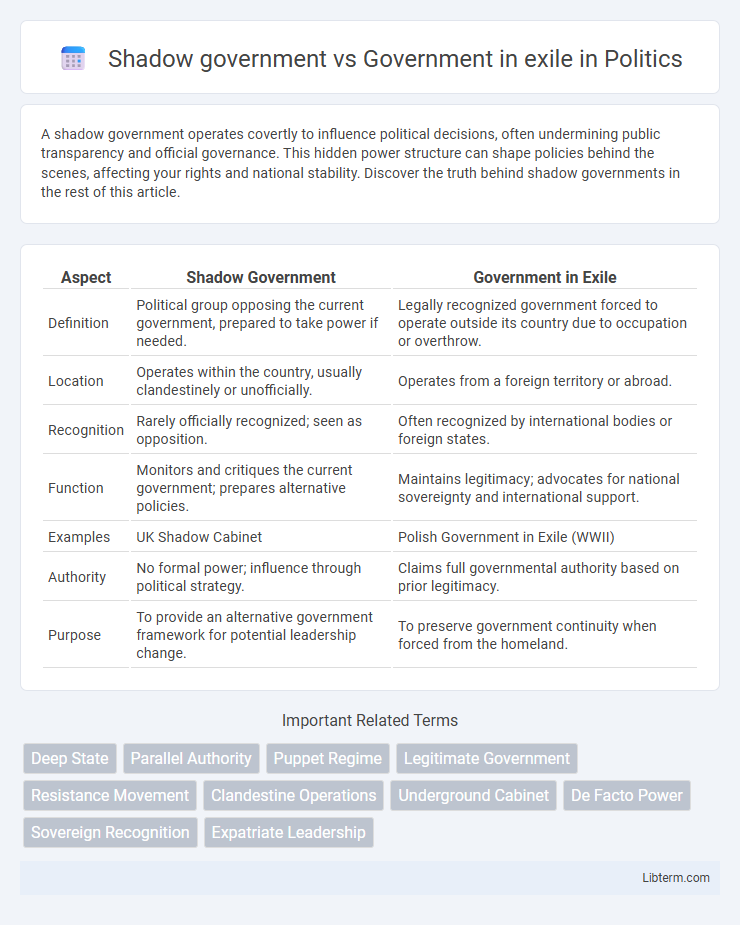
| Aspect | Shadow Government | Government in Exile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political group opposing the current government, prepared to take power if needed. | Legally recognized government forced to operate outside its country due to occupation or overthrow. |
| Location | Operates within the country, usually clandestinely or unofficially. | Operates from a foreign territory or abroad. |
| Recognition | Rarely officially recognized; seen as opposition. | Often recognized by international bodies or foreign states. |
| Function | Monitors and critiques the current government; prepares alternative policies. | Maintains legitimacy; advocates for national sovereignty and international support. |
| Examples | UK Shadow Cabinet | Polish Government in Exile (WWII) |
| Authority | No formal power; influence through political strategy. | Claims full governmental authority based on prior legitimacy. |
| Purpose | To provide an alternative government framework for potential leadership change. | To preserve government continuity when forced from the homeland. |
Defining Shadow Government
A shadow government refers to an unofficial or clandestine group that exercises power or influence covertly, often aiming to control or manipulate the official government without public accountability. Unlike a government in exile, which is a legitimate political body recognized internationally but operating outside its territory due to displacement, a shadow government operates secretly within or alongside the established state structures. The concept of a shadow government is frequently associated with conspiracy theories or authoritarian regimes where power is hidden from public view.
Understanding Government in Exile
Government in exile refers to a political group that claims to be the legitimate authority of a country but operates from outside its national territory, often due to occupation or displacement. Unlike a shadow government, which typically functions covertly within the country to oppose the sitting government, a government in exile maintains official diplomatic relations and seeks international recognition. This entity aims to restore its authority and governance over the home country, relying on external support and symbolic legitimacy rather than direct control.
Key Differences Between Shadow Government and Government in Exile
Shadow governments operate covertly within or alongside an existing state, aiming to influence or replace current authorities without formal recognition. Governments in exile function openly, representing a displaced official regime recognized by foreign powers but lacking control over their native territory. Key differences include legitimacy: governments in exile hold international recognition, whereas shadow governments rely on secrecy and underground networks to achieve political objectives.
Historical Origins of Shadow Governments
Shadow governments trace their historical origins to clandestine resistance groups formed during periods of occupation or authoritarian rule, often operating secretly to influence or overthrow the established regime. Unlike governments in exile, which were formal administrations displaced from their territory during conflicts like World War II, shadow governments typically function covertly within the affected country, maintaining underground networks and covert communication channels. Key examples include the French Resistance during Nazi occupation and anti-colonial movements, which laid the foundation for modern concepts of shadow governmental authority challenging official state power.
Notable Examples of Governments in Exile
Notable examples of governments in exile include the Free French Government led by Charles de Gaulle during World War II, which operated from London after Nazi occupation of France. The Polish government in exile also established its base in London following the 1939 invasion of Poland by Germany and the Soviet Union. These governments maintained international recognition and continued diplomatic relations until they could return to power in their homelands.
Roles and Functions of Shadow Governments
Shadow governments operate covertly to influence or challenge the official state power, often maintaining parallel structures to prepare for potential regime changes or to coordinate opposition activities. They gather intelligence, mobilize support, and develop alternative policies to contest the legitimacy or decisions of the recognized government. Unlike governments in exile, which operate openly from foreign territories to assert their legal authority, shadow governments typically function within the country, leveraging clandestine networks to shape political outcomes.
Challenges Faced by Governments in Exile
Governments in exile face significant challenges including limited access to international recognition and diplomatic support, which hampers their legitimacy and ability to influence global policy. They struggle to maintain communication and control over their territories without a physical presence, complicating efforts to coordinate resistance or governance. Securing resources and sustaining morale among displaced citizens further exacerbates their operational difficulties in pursuing their political objectives.
Impact on Domestic and International Politics
Shadow governments operate covertly within a country, influencing domestic politics by challenging official authority and creating parallel claims to legitimacy that can destabilize governance. Governments in exile maintain a formal structure abroad, leveraging international recognition to exert diplomatic pressure and legitimize opposition movements. Both entities affect international relations by shaping foreign policy decisions, impacting alliances, and influencing the global balance of power through their competing claims to sovereignty.
Legitimacy and Recognition Issues
A shadow government operates covertly within or outside a state, lacking formal recognition but claiming authority, while a government in exile maintains internationally recognized legitimacy despite being displaced from its territory. Legitimacy of a shadow government is often contested due to absence of official endorsement or control, whereas governments in exile rely on diplomatic recognition by other states and international bodies to assert their rightful governance. Recognition issues revolve around the acceptance of authority, where governments in exile have legal standing but limited practical power, contrasting with shadow governments that may wield influence locally but struggle for legitimacy on the international stage.
Future Trends and Evolving Dynamics
Shadow governments, often operating covertly alongside recognized regimes, are expected to leverage increased cyber capabilities and international networks to influence political landscapes without formal legitimacy. Governments in exile continue adapting through digital diplomacy and strategic alliances, seeking international recognition while preparing for potential political reintegration. Future trends indicate a convergence of technological advancements and geopolitical shifts, intensifying the complexity and impact of these parallel power structures on global governance.
Shadow government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com