Reactive policy focuses on responding to issues after they arise, aiming to mitigate damage and address problems swiftly. This approach contrasts with proactive strategies by prioritizing immediate resolution over long-term prevention, often shaping organizational adaptability in fast-changing environments. Discover how adopting reactive policies can influence your decision-making and operational resilience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
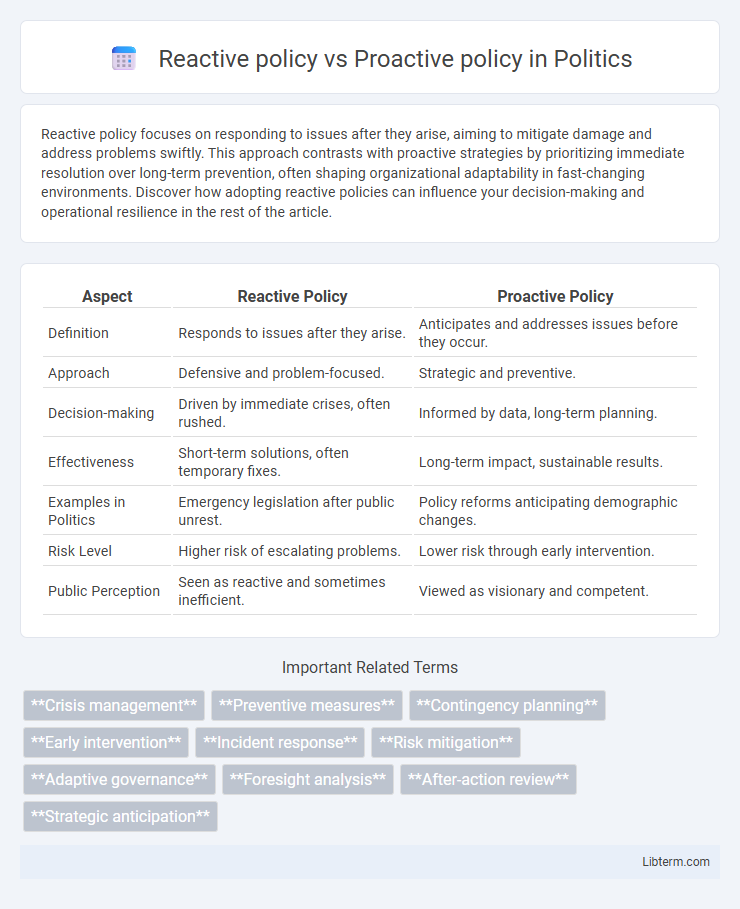
| Aspect | Reactive Policy | Proactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Responds to issues after they arise. | Anticipates and addresses issues before they occur. |
| Approach | Defensive and problem-focused. | Strategic and preventive. |
| Decision-making | Driven by immediate crises, often rushed. | Informed by data, long-term planning. |
| Effectiveness | Short-term solutions, often temporary fixes. | Long-term impact, sustainable results. |
| Examples in Politics | Emergency legislation after public unrest. | Policy reforms anticipating demographic changes. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk of escalating problems. | Lower risk through early intervention. |
| Public Perception | Seen as reactive and sometimes inefficient. | Viewed as visionary and competent. |
Understanding Reactive Policy
Reactive policy involves responding to issues only after they have occurred, aiming to mitigate damage or solve problems as they arise. This approach often leads to short-term fixes rather than long-lasting solutions and can increase operational risks or costs due to delayed interventions. Understanding reactive policy highlights its reliance on crisis management, contrasting with proactive strategies that emphasize prevention and planning.
Defining Proactive Policy
Proactive policy involves strategic planning and implementation of measures designed to anticipate and prevent potential issues before they arise. It prioritizes forecasting risks and opportunities through data analysis, stakeholder engagement, and early intervention to achieve long-term objectives. This approach contrasts with reactive policy, which addresses problems only after they have occurred, often resulting in higher costs and reduced effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Reactive and Proactive Policies
Reactive policies respond to issues after they occur, focusing on damage control and immediate problem-solving, whereas proactive policies aim to prevent problems by anticipating risks and implementing measures in advance. Reactive policies often result in short-term fixes, while proactive policies prioritize long-term planning and sustainable outcomes. Organizations adopting proactive policies typically experience greater resilience and efficiency compared to those relying on reactive strategies.
Advantages of Reactive Policy Approaches
Reactive policy approaches enable quick adaptation to unforeseen challenges by addressing problems as they arise rather than predicting them in advance. This responsiveness minimizes damage and allows policymakers to allocate resources efficiently toward immediate needs. Reactive policies also benefit from real-time data, improving decision-making accuracy and flexibility in dynamic environments.
Benefits of Proactive Policy Implementation
Proactive policy implementation reduces risks by addressing potential issues before they escalate, resulting in enhanced organizational stability and long-term cost savings. It promotes continuous improvement and innovation, allowing organizations to adapt swiftly to market changes and regulatory demands. Early intervention through proactive policies also improves stakeholder trust and compliance, fostering a positive corporate reputation.
Common Challenges in Reactive Policymaking
Reactive policy-making often faces common challenges such as delayed response to emerging issues, resulting in missed opportunities for early intervention and increased costs. This approach tends to rely heavily on crisis management, leading to short-term fixes rather than sustainable solutions. Limited stakeholder engagement and inadequate data analysis also undermine the effectiveness of reactive policies, impeding long-term strategic planning and resilience.
Potential Risks in Proactive Policy Strategies
Proactive policy strategies, while aiming to foresee and mitigate future issues, carry potential risks such as misallocation of resources due to inaccurate predictions and unintended consequences from preemptive actions. Overemphasis on anticipated scenarios may lead to neglecting current pressing issues, creating vulnerabilities in the system. Moreover, resistance from stakeholders affected by early interventions can hinder policy implementation and effectiveness.
Real-World Examples: Reactive vs Proactive Policies
Reactive policies often emerge in response to crises, such as the U.S. government increasing airport security after the 9/11 attacks, exemplifying immediate action following an event. Proactive policies anticipate potential issues, as seen in Singapore's water management strategy, which invests in sustainable infrastructure to prevent shortages before they occur. Businesses adopting proactive cybersecurity measures reduce breach risks, contrasting with reactive approaches that address vulnerabilities only after an attack.
Building an Effective Policy Framework
Building an effective policy framework requires understanding the distinctions between reactive and proactive policies. Reactive policies address issues after they arise, focusing on mitigation and adaptation to existing challenges, whereas proactive policies anticipate future risks and implement preventive measures to minimize potential impacts. Combining data-driven insights with stakeholder engagement enhances the development of balanced policies that optimize resource allocation and promote sustainable outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Policy Success
Choosing the right approach between reactive and proactive policies depends on the specific context, risk tolerance, and desired outcomes. Reactive policies provide flexibility by addressing issues as they arise, making them suitable for unpredictable environments, while proactive policies emphasize prevention and long-term planning to minimize risks and enhance sustainability. Evaluating factors such as resource availability, stakeholder engagement, and impact urgency is essential to ensure policy effectiveness and success.
Reactive policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com