Caucusing is a strategic meeting process where members of a group gather separately to discuss policies, select candidates, or coordinate actions privately. It plays a critical role in shaping party platforms and influencing political outcomes, often requiring strong negotiation and consensus-building skills. Discover how caucusing impacts your political engagement and decision-making by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
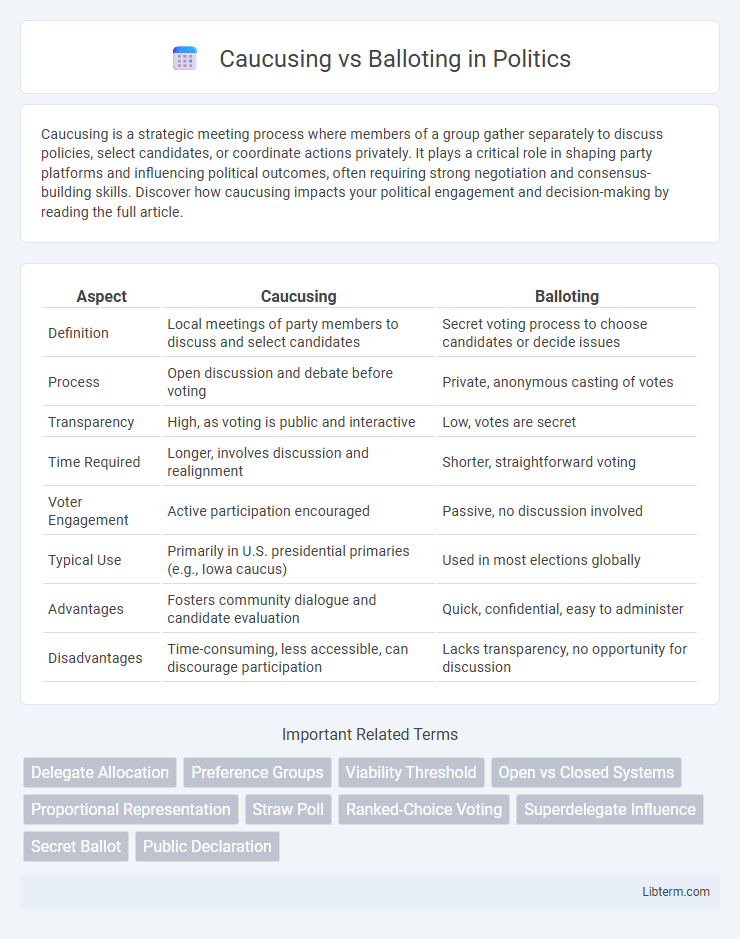
| Aspect | Caucusing | Balloting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Local meetings of party members to discuss and select candidates | Secret voting process to choose candidates or decide issues |
| Process | Open discussion and debate before voting | Private, anonymous casting of votes |
| Transparency | High, as voting is public and interactive | Low, votes are secret |
| Time Required | Longer, involves discussion and realignment | Shorter, straightforward voting |
| Voter Engagement | Active participation encouraged | Passive, no discussion involved |
| Typical Use | Primarily in U.S. presidential primaries (e.g., Iowa caucus) | Used in most elections globally |
| Advantages | Fosters community dialogue and candidate evaluation | Quick, confidential, easy to administer |
| Disadvantages | Time-consuming, less accessible, can discourage participation | Lacks transparency, no opportunity for discussion |
Introduction to Caucusing and Balloting
Caucusing involves local meetings where party members openly discuss and select candidates through consensus or show of hands, emphasizing direct community engagement and debate. Balloting is a formal voting process where individuals cast secret ballots to choose candidates, ensuring privacy and reducing peer influence. Both methods are fundamental in democratic elections, with caucusing fostering group deliberation and balloting providing a straightforward, confidential vote count.
Definition of Caucusing
Caucusing is a political process where members of a party gather in local meetings to discuss and select candidates or policies through open debate and consensus-building. It emphasizes direct voter engagement and collective decision-making within small groups, contrasting with balloting's private, individual voting method. This approach fosters community involvement and can influence candidate selection at various levels of government.
Definition of Balloting
Balloting is a formal voting process in which participants cast secret ballots to select candidates or make decisions, ensuring confidentiality and reducing peer pressure. Unlike caucusing, which involves open discussion and consensus-building within a group, balloting provides a private method for individuals to express their preferences directly. This voting mechanism is widely used in political primaries and organizational elections to guarantee fairness and accuracy in the selection process.
Historical Context: Caucuses vs. Ballots
Caucuses originated in the early 19th century as local gatherings where party members debated and selected candidates, emphasizing direct voter engagement within communities. Balloting emerged later, evolving into formalized, secret ballots to increase privacy and reduce manipulation in elections. The historical shift from caucusing to balloting reflects a broader democratization of the voting process, aiming to enhance fairness and transparency in candidate selection.
Key Differences Between Caucusing and Balloting
Caucusing involves participants gathering to discuss and select candidates through open debate and consensus-building, whereas balloting is a private voting process where individuals cast secret ballots. Caucuses emphasize public participation and deliberation, making them more time-consuming and interactive compared to the quick, confidential nature of balloting. Key differences include the level of transparency, voting method, and procedural complexity, with caucusing fostering group engagement and balloting prioritizing voter privacy.
Advantages of Caucusing
Caucusing fosters direct, face-to-face discussions that encourage participant engagement and deeper understanding of candidates, leading to more informed decision-making. This process enhances community involvement by allowing voters to deliberate and build consensus rather than simply casting secret ballots. By promoting transparency and active participation, caucusing strengthens grassroots political activism and accountability within local party organizations.
Advantages of Balloting
Balloting provides a secret and private voting process that enhances voter confidentiality and minimizes peer pressure influence, ensuring more genuine electoral outcomes. This method allows a larger number of participants to cast votes efficiently, streamlining decision-making in group settings with diverse opinions. Balloting also facilitates accurate vote counting and record-keeping, contributing to transparent and verifiable election results.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Method
Caucusing faces challenges such as limited accessibility for individuals with disabilities or tight schedules, leading to lower participation rates and potential bias toward more vocal or organized groups. Balloting encounters criticisms related to voter privacy concerns, the risk of ballot tampering, and slower result tabulation, which can undermine trust in election outcomes. Both methods struggle with ensuring inclusive, transparent processes that accurately reflect voter intent while minimizing logistical and security issues.
Impact on Voter Participation
Caucusing generally results in lower voter participation compared to balloting due to its time-consuming and public nature, which can discourage busy or private voters from engaging. Balloting offers a more accessible and private voting method, increasing turnout by accommodating a broader range of schedules and comfort levels. States using balloting often report higher participation rates, highlighting the method's positive impact on inclusive democratic engagement.
Future Trends in Political Nomination Methods
Future trends in political nomination methods indicate a gradual shift towards digital balloting systems, enhancing voter accessibility and data security compared to traditional caucusing. Increased use of blockchain technology and mobile voting apps aims to improve transparency, reduce fraud, and expand participation beyond physical locations. Despite this, caucuses may persist in localized settings due to their community engagement benefits, but scalability challenges will likely favor balloting in national-level elections.
Caucusing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com