An independent candidate runs for office without the backing of a major political party, relying on personal credibility and grassroots support to reach voters. Campaign strategies often emphasize direct communication and unique policy positions tailored to local or national concerns. Discover how an independent candidate can impact elections and what challenges they face by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
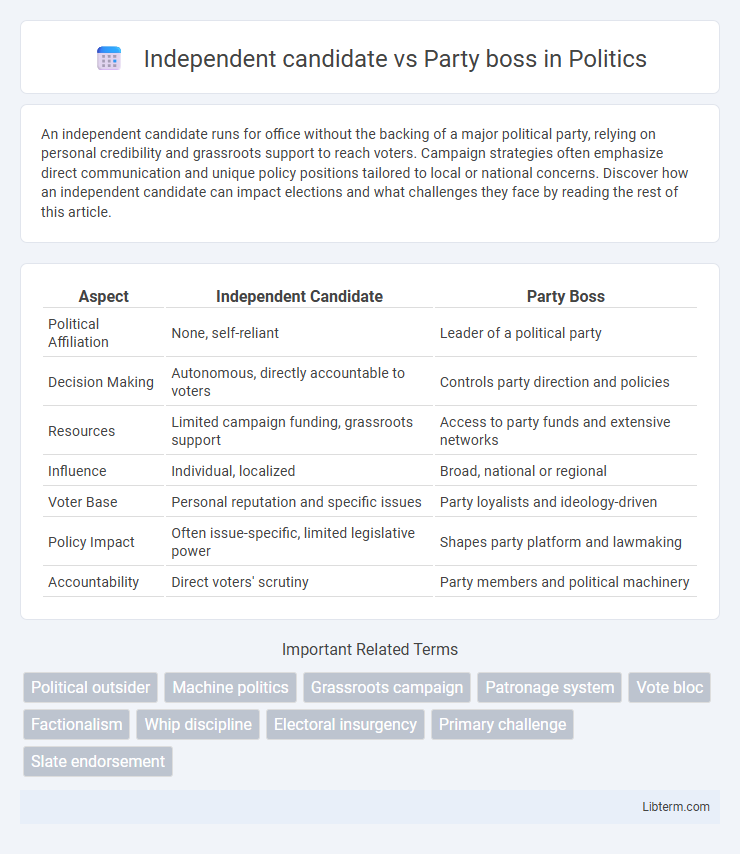
| Aspect | Independent Candidate | Party Boss |
|---|---|---|
| Political Affiliation | None, self-reliant | Leader of a political party |
| Decision Making | Autonomous, directly accountable to voters | Controls party direction and policies |
| Resources | Limited campaign funding, grassroots support | Access to party funds and extensive networks |
| Influence | Individual, localized | Broad, national or regional |
| Voter Base | Personal reputation and specific issues | Party loyalists and ideology-driven |
| Policy Impact | Often issue-specific, limited legislative power | Shapes party platform and lawmaking |
| Accountability | Direct voters' scrutiny | Party members and political machinery |
Understanding the Role of Independent Candidates
Independent candidates offer voters choices beyond traditional party lines, emphasizing individual accountability and local interests without direct influence from party bosses. Their role in democratic systems highlights the importance of representation based on personal conviction rather than party agendas, often driving grassroots support. Understanding this dynamic reveals how independents can challenge entrenched political hierarchies and promote diverse policy perspectives.
Who Are Party Bosses?
Party bosses are influential leaders who control candidate nominations, campaign resources, and party strategy within political organizations, often wielding significant power over local and national elections. Their authority stems from established networks, financial clout, and the ability to mobilize loyal voter bases, shaping party agendas and policy priorities. Unlike independent candidates who rely on personal platforms and grassroots support, party bosses leverage institutional frameworks to maintain control and influence electoral outcomes.
Historical Context: Independents vs Party Establishment
Independent candidates historically challenge the entrenched power of party bosses who control candidate selection and political patronage within party establishments. The rise of independents often reflects public dissatisfaction with party monopolies on political representation and governance. Electoral reforms and grassroots movements have periodically disrupted party dominance, enabling independents to gain traction against traditionally powerful party machines.
Election Dynamics: Advantages and Disadvantages
Independent candidates often capitalize on personal reputation and direct voter appeal, bypassing party hierarchies and enabling a focus on localized issues. Party bosses wield extensive organizational resources, strategic networks, and influence over candidate selection, enhancing campaign reach and voter mobilization. However, independents may lack funding and institutional support, while party bosses face criticism for potential nepotism and constrained candidate autonomy, impacting election dynamics significantly.
Voter Perceptions and Trust
Independent candidates often garner voter trust by emphasizing personal integrity, transparency, and commitment to constituent interests without party influence. Party bosses, conversely, may face skepticism due to perceived allegiance to party agendas over public needs, which can diminish voter confidence. Voter perceptions are significantly shaped by the candidate's ability to demonstrate accountability and responsiveness beyond party lines.
Campaign Strategies: Grassroots vs Machine Politics
Independent candidates often rely on grassroots campaign strategies emphasizing direct voter engagement, local events, and social media outreach to build authentic connections. In contrast, party bosses leverage machine politics, utilizing established party infrastructure, voter mobilization networks, and financial resources to influence electoral outcomes. This dichotomy highlights the contrast between personalized voter contact and systematic organizational power in political campaigns.
Policy Positions: Flexibility vs Party Line
Independent candidates often emphasize flexibility in policy positions, allowing them to adapt their stances based on constituents' needs and emerging issues. Party bosses typically enforce strict adherence to the party line, ensuring unified messaging and cohesive strategy across all candidates. This contrast highlights the tension between individualized representation and centralized party control in political decision-making.
Fundraising and Campaign Resources
Independent candidates often face significant challenges in fundraising due to limited access to established donor networks and party funding channels. Party bosses control substantial campaign resources, including voter databases, financial contributions, and coordinated volunteer efforts, which significantly boost the party-backed candidate's electoral reach. The disparity in financial backing and infrastructure frequently places independent candidates at a disadvantage in mounting competitive campaigns.
Impact on Democratic Representation
An independent candidate often provides voters with diverse policy choices free from party constraints, enhancing democratic representation by reflecting individual constituent interests more authentically. In contrast, party bosses wield significant influence in candidate selection and agenda-setting, potentially limiting voter agency and reinforcing party-centric priorities. This dynamic affects how representative democracy functions, balancing personal political accountability against organized political power structures.
Future Trends: The Rise of Political Independents
The rise of political independents reflects growing voter dissatisfaction with traditional party bosses who dominate candidate selection and policymaking. Increasing access to social media platforms and direct voter engagement tools empowers independent candidates to build grassroots support without party infrastructure. Future trends suggest a continued surge in independent representation, challenging established party hierarchies and promoting more diverse political voices.
Independent candidate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com