General elections determine the leadership and direction of a country by allowing citizens to vote for their preferred representatives. Understanding the electoral process, key issues, and candidate platforms can empower your decision-making and ensure your voice is heard. Explore the rest of this article to gain insights into how general elections shape governance and impact your future.
Table of Comparison
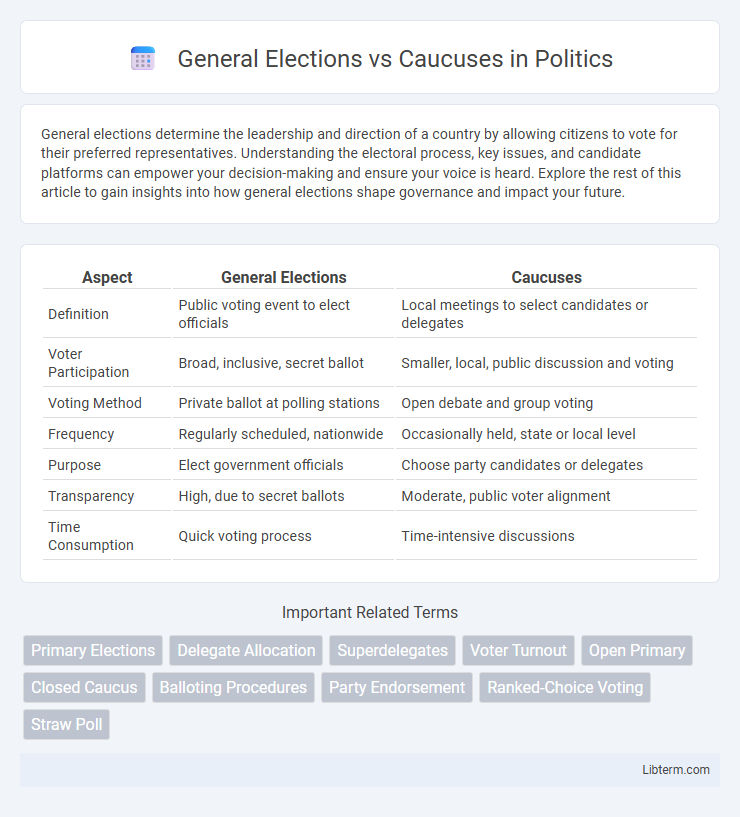
| Aspect | General Elections | Caucuses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public voting event to elect officials | Local meetings to select candidates or delegates |
| Voter Participation | Broad, inclusive, secret ballot | Smaller, local, public discussion and voting |
| Voting Method | Private ballot at polling stations | Open debate and group voting |
| Frequency | Regularly scheduled, nationwide | Occasionally held, state or local level |
| Purpose | Elect government officials | Choose party candidates or delegates |
| Transparency | High, due to secret ballots | Moderate, public voter alignment |
| Time Consumption | Quick voting process | Time-intensive discussions |
Introduction to General Elections and Caucuses
General elections allow registered voters to cast ballots directly for their preferred candidates, determining public officeholders through a straightforward voting process. Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members discuss and select delegates to represent their choices at higher-level conventions, emphasizing community engagement and deliberation. Both systems play critical roles in shaping political outcomes, with general elections directly reflecting voter preferences and caucuses fostering party organization and grassroots participation.
Definition and Key Differences
General elections are formal voting processes where registered voters cast ballots to choose officeholders, typically involving secret ballots and broad public participation. Caucuses are local meetings of party members who openly discuss and select candidates or delegates through group consensus rather than individual ballot voting. Key differences include the method of voting--secret ballot in general elections versus public discussion in caucuses--and the scale, with general elections involving the entire electorate and caucuses limited to active party members.
Historical Background of Elections and Caucuses
General elections and caucuses have distinct historical roots, with general elections originating in ancient democratic practices to enable direct citizen voting for political leaders. Caucuses developed later, particularly in the United States during the early 19th century, as localized meetings where party members selected candidates and supported policies through group consensus. These evolving mechanisms reflect the broader development of representative democracy and political party structures over centuries.
How General Elections Work
General elections determine the winner of public office by allowing registered voters to cast ballots for their preferred candidates across all parties. These elections use a straightforward voting process, usually a secret ballot, where the candidate with the most votes wins office, either by plurality or majority depending on the election rules. Voter participation is open to the general public on a designated election day, making it a direct and inclusive method of selecting government representatives.
How Caucuses Operate
Caucuses operate as local gatherings where registered party members discuss and vote on their preferred candidates through a series of rounds or group alignments, rather than casting secret ballots like in general elections. Participants physically group themselves by candidate preference, allowing for real-time persuasion and coalition-building before final tallies are made. This process emphasizes direct voter engagement and deliberation, often requiring more time and participation than traditional polling methods.
Voter Participation and Accessibility
General elections typically see higher voter participation due to their widespread accessibility, allowing all registered voters to cast ballots at numerous polling locations or via mail-in voting. Caucuses often have lower turnout because they require voters to attend specific meetings at set times, which can be difficult for people with tight schedules or limited mobility. The complexity and time commitment of caucuses can create barriers, making general elections a more inclusive and accessible option for broad voter engagement.
State-by-State Variations
General elections and caucuses differ significantly in how states conduct voting and delegate selection processes. States like Iowa utilize caucuses, involving local gatherings and discussions to choose party nominees, while most states hold primary elections where voters cast secret ballots. Variations in rules, timing, and voter participation methods across states impact candidate strategies and campaign dynamics in presidential nomination races.
Impact on Political Parties and Candidates
General elections provide political parties with a broad platform to consolidate support and appeal to a diverse electorate, influencing candidates to adopt more moderate policies to attract centrist voters. Caucuses tend to favor candidates with strong grassroots organization and passionate base supporters, often benefiting more ideologically driven candidates within a party. The differing structures impact party strategies by shifting focus between broad voter outreach in general elections and intensive local engagement during caucuses.
Pros and Cons of General Elections vs Caucuses
General elections offer broader voter participation and straightforward ballot casting, increasing democratic inclusiveness and clarity in candidate selection. Caucuses encourage deeper community engagement and deliberation, fostering informed voter decisions but require more time and commitment, which can limit participation. While general elections provide accessibility and efficiency, caucuses enhance dialogue and consensus-building, each presenting trade-offs between inclusivity and depth of electoral involvement.
Future Trends and Reforms
Future trends in general elections and caucuses indicate a shift toward increased digital voting methods and enhanced voter accessibility to address declining participation rates. Proposed reforms include standardizing caucus procedures to reduce complexity and incorporating blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. Emphasis on alternative voting systems like ranked-choice voting aims to better capture voter preferences and reduce partisan polarization.
General Elections Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com