A marginal seat is a parliamentary constituency where the winning candidate secures only a small majority, making the outcome in the next election highly uncertain. These seats often attract significant attention from political parties, as they can be pivotal in determining overall election results. Discover how marginal seats influence political strategies and election dynamics in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
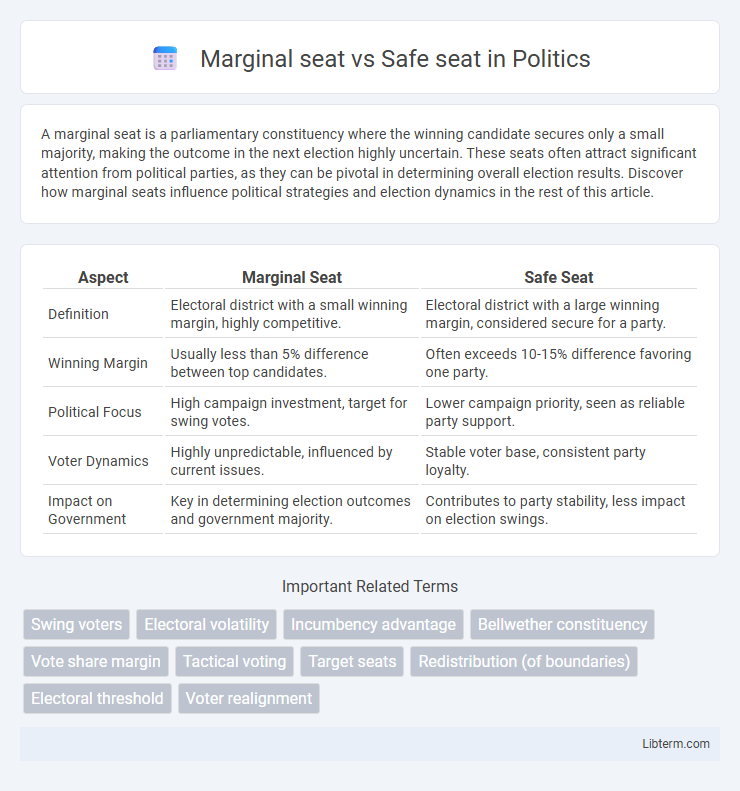
| Aspect | Marginal Seat | Safe Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electoral district with a small winning margin, highly competitive. | Electoral district with a large winning margin, considered secure for a party. |
| Winning Margin | Usually less than 5% difference between top candidates. | Often exceeds 10-15% difference favoring one party. |
| Political Focus | High campaign investment, target for swing votes. | Lower campaign priority, seen as reliable party support. |
| Voter Dynamics | Highly unpredictable, influenced by current issues. | Stable voter base, consistent party loyalty. |
| Impact on Government | Key in determining election outcomes and government majority. | Contributes to party stability, less impact on election swings. |
Understanding Marginal Seats and Safe Seats
Marginal seats are electoral districts where the winning candidate secures victory by a narrow margin, often less than 5%, making these seats highly competitive and key targets during elections. Safe seats, in contrast, exhibit a strong and consistent majority for a particular party, typically winning by over 10%, resulting in predictable outcomes and reduced campaign intensity. Understanding the distinction between marginal and safe seats is crucial for political strategists as it influences resource allocation, campaign focus, and voter engagement strategies in parliamentary systems.
Key Characteristics of Marginal Seats
Marginal seats are electoral districts where the winning candidate's majority is small, typically under 5%, making them highly competitive and susceptible to change in voter sentiment. These seats often receive significant campaign attention and resources due to their pivotal role in determining overall election outcomes. Voter demographics in marginal seats tend to be more diverse and evenly split between major parties, increasing the likelihood of fluctuating election results.
Defining Features of Safe Seats
Safe seats are electoral districts consistently won by a particular political party or candidate with a significant majority, often exceeding a 10% margin. Such seats exhibit stable voter loyalty and low electoral volatility, making them reliable strongholds in elections. The defining features include predictable outcomes, strong party organization, and long-term incumbency advantage.
Historical Trends in Marginal and Safe Seats
Historical trends reveal that marginal seats, characterized by narrow victory margins often less than 5%, experience frequent shifts in party control, reflecting voter volatility and changing political landscapes. Safe seats typically show consistent party dominance, with victory margins exceeding 10%, contributing to electoral stability and reduced campaign intensity in these constituencies. Analysis of UK general elections from 1945 to 2019 demonstrates fluctuations in the number of marginal seats, highlighting key periods of political realignment and strategic targeting by major parties.
Electoral Importance of Marginal Seats
Marginal seats are constituencies where election results are closely contested, with small vote differences determining the winner, making them critical targets for political parties during campaigns. Their electoral importance lies in their potential to swing government control, as winning a few marginal seats can change overall parliamentary majorities. In contrast, safe seats have predictable outcomes with dominant party support, attracting less campaign attention and resources.
Strategies Political Parties Use in Marginal vs Safe Seats
Political parties allocate significant resources and targeted campaigning efforts in marginal seats to sway undecided voters and capitalize on the competitive electoral environment. In contrast, safe seats often see reduced campaign intensity, with parties focusing on maintaining voter loyalty through localized issues and reinforcing existing support networks. Data-driven voter outreach and swing voter identification dominate strategies in marginals, while safe seats benefit from consistent grassroots engagement and incumbent promotion.
Impact of Marginal and Safe Seats on Election Outcomes
Marginal seats, defined by narrow voter majorities, significantly influence election outcomes by determining the balance of power between competing parties in closely contested areas. Safe seats, characterized by consistent party dominance, contribute to political stability but often reduce competitive campaigning, potentially affecting voter turnout. The strategic focus on marginal seats directs resource allocation and policy promises, ultimately shaping overall election results more than safe seats.
Voter Behavior in Marginal vs Safe Seats
Voter behavior in marginal seats is often more dynamic, with constituents showing higher engagement and responsiveness to campaign efforts due to the competitive nature of these areas. In contrast, safe seats tend to exhibit lower voter turnout and less campaign intensity as the outcome is perceived as predetermined, leading to voter complacency. Political parties allocate more resources and tailor messages specifically to marginal seats to sway undecided voters and maximize electoral gains.
Case Studies: Marginal and Safe Seats in Recent Elections
Marginal seats such as Battersea in the 2019 UK General Election saw a narrow victory margin of just 1.6%, highlighting their volatility and importance in determining overall parliamentary control. In contrast, safe seats like Birmingham Erdington, consistently held by Labour with a 20%+ majority, demonstrate electoral stability and predictability. Analysis of these cases reveals how marginal seats attract intense campaign resources, whereas safe seats often experience lower contest intensity due to expected outcomes.
Future Implications for Marginal and Safe Seats
Marginal seats, characterized by narrow victory margins, often receive increased campaign attention and resources as parties focus on winning or defending them, influencing political strategies and policy priorities. Safe seats typically experience less electoral competition, which can lead to voter complacency and reduced accountability but provide stability for party dominance in the legislature. Future political landscapes may see shifting marginal and safe seats due to demographic changes and boundary redistributions, affecting party tactics and governance outcomes.
Marginal seat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com