Autocracy is a system of government where a single individual holds absolute power without effective constitutional limitations, often resulting in centralized decision-making and limited political freedoms. This form of governance can lead to rapid policy implementation but also risks abuses of power and suppressed dissent. Explore the rest of the article to understand how autocracy shapes societies and impacts your rights.
Table of Comparison
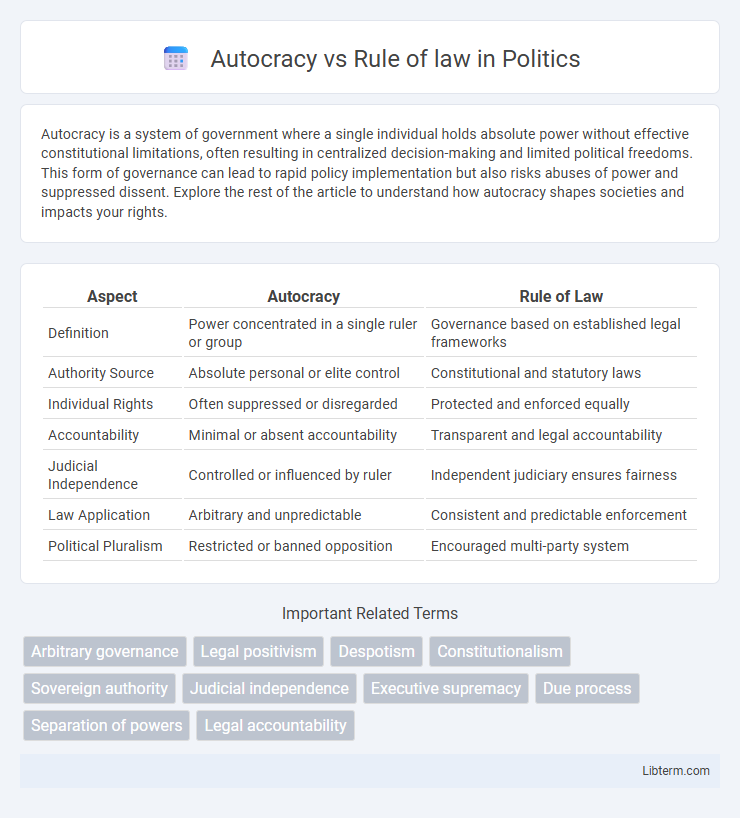
| Aspect | Autocracy | Rule of Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power concentrated in a single ruler or group | Governance based on established legal frameworks |
| Authority Source | Absolute personal or elite control | Constitutional and statutory laws |
| Individual Rights | Often suppressed or disregarded | Protected and enforced equally |
| Accountability | Minimal or absent accountability | Transparent and legal accountability |
| Judicial Independence | Controlled or influenced by ruler | Independent judiciary ensures fairness |
| Law Application | Arbitrary and unpredictable | Consistent and predictable enforcement |
| Political Pluralism | Restricted or banned opposition | Encouraged multi-party system |
Defining Autocracy and Rule of Law
Autocracy is a system of government where absolute power is concentrated in the hands of a single ruler or a small group, often without legal constraints. Rule of law refers to the principle that all individuals and institutions, including the government, are accountable to laws that are transparently enacted, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated. While autocracy centralizes authority, rule of law ensures that power is limited and exercised within a framework of established legal norms.
Historical Evolution of Governance Systems
Autocracy, characterized by centralized power held by a single ruler, dominated ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Imperial China, where absolute authority ensured stability but limited citizen rights. The historical evolution of governance systems saw a gradual shift towards rule of law, rooted in Roman law and medieval Magna Carta principles, establishing that all individuals, including rulers, are subject to legal codes. This transition laid the foundation for modern democratic institutions emphasizing accountable governance, legal equality, and protection of individual freedoms.
Key Features of Autocratic Regimes
Autocratic regimes centralize power in a single leader or a small group, often lacking political pluralism and suppressing opposition. Key features include the absence of independent judiciary, limited civil liberties, and concentration of authority without constitutional constraints. These regimes prioritize control over legal accountability, contrasting sharply with rule of law principles that ensure equality, transparency, and protection of individual rights.
Principles Underlying the Rule of Law
Principles underlying the rule of law include legal certainty, equality before the law, and accountability of government officials, ensuring that no one is above the law. In contrast to autocracy, where power is centralized and arbitrary, the rule of law mandates transparency, protection of fundamental rights, and independent judiciary to prevent abuse of authority. These principles foster democratic governance by limiting governmental powers and safeguarding individual freedoms.
Power Concentration vs Institutional Checks
Autocracy centralizes power in the hands of a single leader or a small group, minimizing or eliminating institutional checks that prevent abuse of authority. Rule of law establishes a framework where power is distributed across various institutions, each with defined limits and functions to ensure accountability and prevent arbitrary governance. The balance between power concentration and institutional checks is crucial for safeguarding individual rights and maintaining political stability.
Impact on Civil Liberties and Human Rights
Autocracy often centralizes power in a single leader or ruling elite, resulting in limited civil liberties and frequent human rights violations due to the absence of checks and balances. In contrast, rule of law ensures accountability and the protection of individual rights through transparent legal frameworks and independent judiciary systems. Societies governed by rule of law tend to uphold freedom of expression, assembly, and due process, fostering an environment where civil liberties are respected and safeguarded.
Economic Outcomes: Autocracy vs Rule of Law
Autocracies often enable rapid decision-making and policy implementation, potentially accelerating short-term economic growth, but they risk inefficiencies and corruption due to weak legal frameworks. In contrast, economies grounded in the rule of law provide stable property rights, transparent contracts, and predictable regulations that foster sustainable investment and innovation. Empirical studies indicate that countries with strong rule of law tend to achieve higher long-term GDP growth rates and attract more foreign direct investment compared to autocratic regimes.
Governance Accountability and Transparency
Autocracy centralizes power in a single ruler or small group, often resulting in limited governance accountability and reduced transparency due to the absence of checks and balances. Rule of law ensures that all individuals and institutions, including government officials, are subject to clear, enforced laws that promote accountability and transparency in decision-making processes. Transparent governance under the rule of law fosters public trust and prevents arbitrary use of power, contrasting with the secretive and unaccountable nature common in autocratic regimes.
Social Stability and Public Trust
Autocracy often undermines social stability by concentrating power and limiting civic participation, leading to public distrust and potential unrest. In contrast, the rule of law promotes social stability through transparent governance, accountability, and equal application of laws, fostering public trust. Empirical studies show societies governed by rule of law exhibit higher social cohesion and citizen confidence in institutions.
Lessons for Modern Societies
Autocracy often concentrates power in a single authority, risking abuse and undermining citizens' rights, while the rule of law ensures legal equality and accountability, safeguarding democratic principles. Modern societies learn that institutional checks and balances prevent tyranny, promote transparency, and uphold justice by limiting arbitrary power. Historical evidence from autocratic regimes highlights the importance of independent judiciary and codified laws to protect human rights and maintain social stability.
Autocracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com