The Assemblee plays a crucial role in shaping legislation and representing the interests of the public within a parliamentary system. Understanding its functions and influence can help you appreciate how laws and policies are developed and enacted. Explore the details of the Assemblee's structure and responsibilities in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
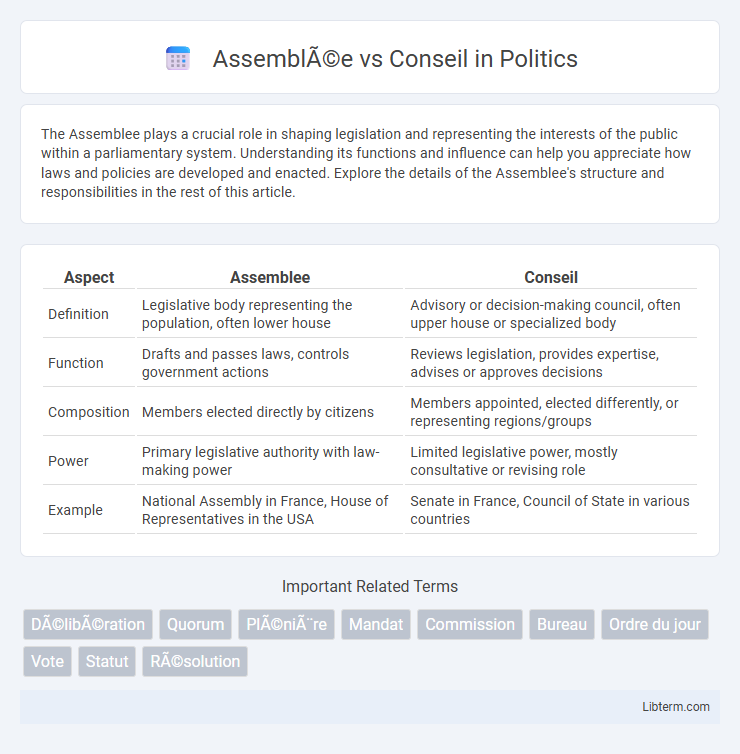
| Aspect | Assemblee | Conseil |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legislative body representing the population, often lower house | Advisory or decision-making council, often upper house or specialized body |
| Function | Drafts and passes laws, controls government actions | Reviews legislation, provides expertise, advises or approves decisions |
| Composition | Members elected directly by citizens | Members appointed, elected differently, or representing regions/groups |
| Power | Primary legislative authority with law-making power | Limited legislative power, mostly consultative or revising role |
| Example | National Assembly in France, House of Representatives in the USA | Senate in France, Council of State in various countries |
Introduction: Understanding Assemblée and Conseil
Assemblee refers to a formal gathering of members within an organization or government body, tasked with discussing and making decisions on legislative or administrative matters. Conseil typically denotes a council or advisory board composed of selected individuals who provide guidance, strategic planning, or governance oversight. Understanding the distinct roles, decision-making processes, and legal frameworks of Assemblee and Conseil is essential for navigating political, corporate, and institutional structures effectively.
Definitions: What is an Assemblée?
An Assemblee is a formal gathering or meeting of members, typically within legislative or organizational contexts, where decisions are made or discussions occur. It involves the collective participation of representatives or stakeholders to deliberate on policies, laws, or organizational matters. Unlike a Conseil, which often serves as an advisory or executive board, an Assemblee functions as a deliberative body with decision-making authority.
Definitions: What is a Conseil?
A Conseil is a formal advisory or decision-making body within an organization, typically composed of appointed or elected members who oversee governance, strategy, or policy implementation. Unlike an Assemblee, which usually refers to a larger gathering or assembly of members, a Conseil often functions with a specific mandate and smaller, focused membership to deliberate and decide on crucial matters. Common types include Conseil d'Administration (Board of Directors) and Conseil Municipal (City Council), emphasizing structured deliberation and governance roles.
Historical Background of Assemblée and Conseil
The Assemblee and Conseil have distinct historical origins rooted in French governance structures, with the Assemblee traditionally representing a broader legislative assembly established during the French Revolution to embody popular sovereignty. The Conseil, historically, functioned as a smaller, advisory body drawn from noble or elite classes, tracing back to the Ancien Regime where it acted as a royal advisory council. These differing foundations underscore their contrasting roles: the Assemblee as a democratic legislative entity and the Conseil as a consultative or executive organ within French political evolution.
Key Differences Between Assemblée and Conseil
Assemblee refers to a large gathering or legislative body where members discuss and make decisions collectively, often seen in parliamentary systems or general meetings. Conseil typically denotes a smaller, more specialized council or advisory board focused on strategic planning, governance, or providing expert recommendations. The key differences lie in their size, function, and decision-making scope, with Assemblee being broader and more deliberative, while Conseil is more focused and consultative.
Roles and Responsibilities of an Assemblée
An Assemblee serves as a legislative body responsible for debating and enacting laws, overseeing government activities, and representing the electorate's interests. It holds powers such as approving budgets, ratifying treaties, and scrutinizing executive actions to ensure accountability. Members of an Assemblee engage in drafting legislation, participating in committee work, and voting on key national policies.
Functions and Duties of a Conseil
A Conseil primarily functions as a deliberative body responsible for making key decisions, setting policies, and overseeing the execution of laws or organizational rules. Its duties include approving budgets, supervising the administration, and ensuring compliance with legal frameworks. Unlike a general assembly, the Conseil often holds ongoing authority to implement strategic governance and provide continuous guidance.
Assemblée vs Conseil: Structural Comparison
The Assemblee and Conseil differ significantly in structure, with the Assemblee typically comprising all eligible members or representatives of a group, often forming a larger, more inclusive body, while the Conseil generally consists of a smaller, selective committee or board entrusted with decision-making authority. Assemblees tend to operate through collective voting mechanisms and foster broad participation, whereas Conseils emphasize efficiency and expertise through delegated responsibilities and focused discussions. The structural distinction influences their respective roles in governance, with Assemblees serving as deliberative forums and Conseils acting as executive or advisory bodies.
Decision-Making Processes: Assemblée vs Conseil
The Assemblee typically involves a large group of members who collectively discuss and vote on decisions, promoting transparency and broad participation in the decision-making process. The Conseil, usually a smaller, more specialized committee, enables faster and more focused decision-making through concentrated expertise and streamlined discussions. Decision-making in the Assemblee emphasizes democratic input, while the Conseil prioritizes efficiency and strategic deliberation.
Choosing Between Assemblée and Conseil in Organizational Governance
Choosing between Assemblee and Conseil in organizational governance depends on the scope of decision-making and stakeholder involvement required; Assemblee typically refers to a broader assembly of members or shareholders with voting rights, promoting democratic participation. Conseil, by contrast, usually designates a smaller, specialized board or council responsible for strategic oversight and executive decisions. Organizations valuing inclusive governance favor Assemblee, while those needing focused, expert-driven management opt for Conseil.
Assemblée Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com