Nepotism undermines fairness by favoring relatives or friends in professional settings, often at the expense of merit and equal opportunity. This practice can lead to decreased morale, lowered productivity, and a toxic work environment. Discover how understanding nepotism can help you recognize its impact and foster a more equitable workplace in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
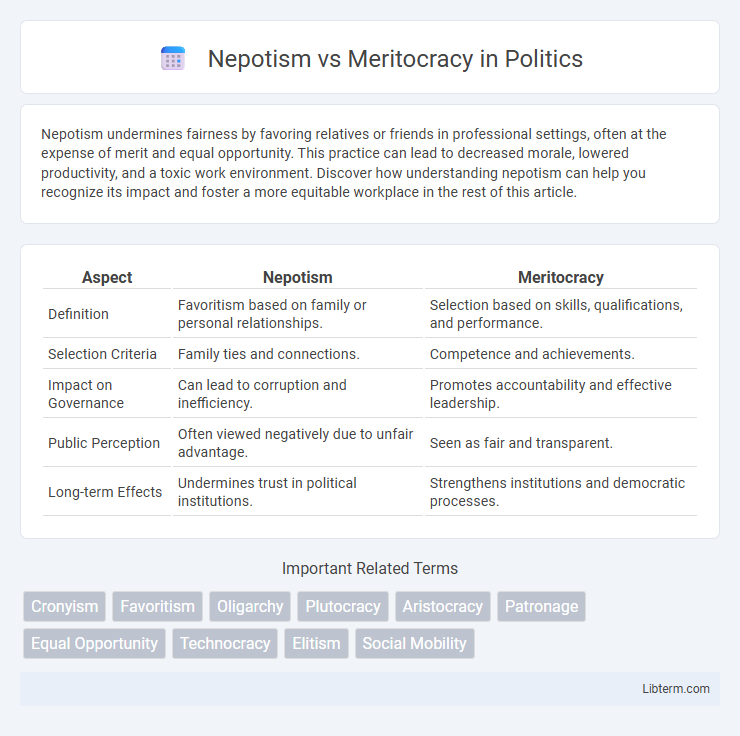
| Aspect | Nepotism | Meritocracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Favoritism based on family or personal relationships. | Selection based on skills, qualifications, and performance. |
| Selection Criteria | Family ties and connections. | Competence and achievements. |
| Impact on Governance | Can lead to corruption and inefficiency. | Promotes accountability and effective leadership. |
| Public Perception | Often viewed negatively due to unfair advantage. | Seen as fair and transparent. |
| Long-term Effects | Undermines trust in political institutions. | Strengthens institutions and democratic processes. |
Understanding Nepotism: Definition and Origins
Nepotism, derived from the Italian word "nipote" meaning nephew, refers to favoritism granted to relatives or close friends, especially in employment or political appointments. Historically, nepotism traces back to the practices of popes in the Middle Ages who appointed family members to high-ranking positions to consolidate power. This practice undermines meritocracy, which emphasizes selection based on ability and talent rather than personal connections.
The Essence of Meritocracy Explained
Meritocracy is a system where individuals are selected and promoted based on their abilities, skills, and achievements rather than personal relationships or favoritism. It emphasizes objective criteria such as talent, performance, and qualifications to ensure fairness and efficiency in organizations or societies. Meritocracy fosters innovation and growth by rewarding merit, contrasting sharply with nepotism, which prioritizes family ties over competence.
Nepotism in the Workplace: Effects and Examples
Nepotism in the workplace often leads to reduced employee morale and decreased productivity as favoritism undermines fair opportunity and merit-based recognition. Studies reveal that organizations with prevalent nepotistic practices suffer from higher turnover rates and diminished innovation due to unqualified individuals occupying key positions. Examples include family-owned businesses where leadership roles are filled by relatives regardless of competency, resulting in inefficiency and resentment among skilled employees.
Meritocracy in Modern Organizations
Meritocracy in modern organizations emphasizes rewarding employees based on skills, performance, and achievements rather than personal connections or family ties. This system improves productivity, fosters innovation, and attracts top talent by creating a fair and transparent environment for career advancement. Organizations prioritizing meritocratic principles benefit from diverse leadership and increased employee motivation, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Nepotism
Nepotism can streamline decision-making processes by placing trusted family members or close associates in key positions, potentially enhancing loyalty and reducing conflicts. However, it often undermines meritocracy by limiting opportunities for qualified candidates, leading to decreased workplace morale and reduced overall organizational efficiency. The reliance on personal relationships rather than professional competence may result in suboptimal performance and hinder innovation.
Benefits and Challenges of Merit-Based Systems
Merit-based systems promote fairness by rewarding skills, performance, and qualifications, leading to higher productivity and innovation. Challenges include potential biases in evaluation and the risk of overlooking teamwork or diverse talents not easily quantified. Implementing transparent criteria and continuous assessment helps maximize the benefits while mitigating the pitfalls of meritocracy.
Navigating the Nepotism vs Meritocracy Debate
Navigating the nepotism vs meritocracy debate requires evaluating organizational policies that prioritize skills and performance over personal connections. Meritocracy fosters innovation, employee motivation, and fairness by rewarding talent and achievement, while nepotism often undermines morale and productivity by favoring family ties. Implementing transparent recruitment processes and performance-based assessments helps businesses balance ethical considerations with strategic growth goals.
Impacts on Employee Morale and Productivity
Nepotism often leads to decreased employee morale as favoritism undermines perceptions of fairness and equal opportunity, resulting in lower motivation and engagement. Meritocracy fosters a culture of performance and recognition, boosting productivity by rewarding skill, effort, and achievement. Organizations emphasizing merit-based advancement typically experience higher employee satisfaction and sustained operational efficiency.
Combating Nepotism: Policies and Best Practices
Combating nepotism requires the implementation of transparent hiring processes, including standardized evaluations and blind recruitment techniques to ensure merit-based selection. Organizations should establish strict conflict-of-interest policies and conduct regular audits to identify and address favoritism. Promoting a culture of accountability and diversity enhances fairness and reinforces meritocracy across all levels of an organization.
Building a Fair and Merit-Driven Culture
Building a fair and merit-driven culture requires clear policies that prioritize skills, performance, and qualifications over familial ties. Implementing transparent recruitment processes and unbiased performance evaluations ensures opportunities are awarded based on merit, enhancing organizational trust and productivity. Cultivating a culture that rewards competence fosters innovation and motivates employees to excel, ultimately driving sustainable success.
Nepotism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com