Neutrality ensures unbiased decision-making by maintaining an impartial stance in various situations, fostering trust and fairness. It helps your interactions remain balanced, preventing conflicts and promoting open communication. Explore the rest of the article to understand how embracing neutrality can benefit your personal and professional life.
Table of Comparison
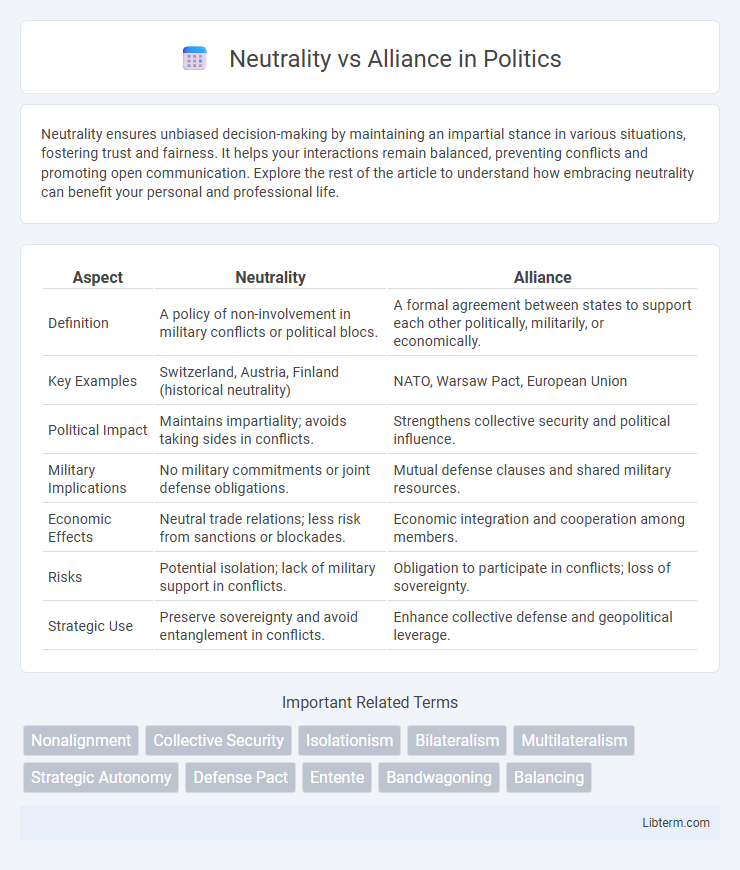
| Aspect | Neutrality | Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A policy of non-involvement in military conflicts or political blocs. | A formal agreement between states to support each other politically, militarily, or economically. |
| Key Examples | Switzerland, Austria, Finland (historical neutrality) | NATO, Warsaw Pact, European Union |
| Political Impact | Maintains impartiality; avoids taking sides in conflicts. | Strengthens collective security and political influence. |
| Military Implications | No military commitments or joint defense obligations. | Mutual defense clauses and shared military resources. |
| Economic Effects | Neutral trade relations; less risk from sanctions or blockades. | Economic integration and cooperation among members. |
| Risks | Potential isolation; lack of military support in conflicts. | Obligation to participate in conflicts; loss of sovereignty. |
| Strategic Use | Preserve sovereignty and avoid entanglement in conflicts. | Enhance collective defense and geopolitical leverage. |
Understanding Neutrality: Definition and Principles
Neutrality refers to a state's commitment to abstain from participating in armed conflicts and alliances that may draw it into war, maintaining impartiality during international disputes. Core principles of neutrality include non-intervention, respect for sovereignty, and the obligation to prevent the use of its territory for hostile actions by belligerents. This status is recognized under international law, particularly the Hague Conventions, which outline the rights and duties of neutral powers in wartime.
The Concept of Alliance: Key Characteristics
The concept of alliance embodies a formal agreement between two or more states to cooperate for mutual benefit, often solidified through treaties that outline shared objectives and defense commitments. Key characteristics include collective security arrangements, joint military or economic support, and a strategic alignment aimed at enhancing member states' power and influence. Alliances contrast with neutrality by actively engaging in cooperative defense and political collaboration, often requiring member states to abandon impartiality in favor of mutual obligations.
Historical Perspectives on Neutrality and Alliances
Historical perspectives on neutrality and alliances reveal how states balanced strategic interests and security concerns. Neutrality, exemplified by Switzerland during both World Wars, allowed countries to avoid entanglement in conflicts while maintaining sovereignty. Conversely, alliances like the Triple Entente and Axis Powers in World War I and II demonstrated how collective defense agreements shaped global power dynamics and escalated wars.
Advantages of Maintaining Neutrality
Maintaining neutrality offers significant advantages including the avoidance of armed conflicts and the preservation of diplomatic relationships with multiple nations. Neutral countries often benefit from increased economic stability as they remain open to trade partnerships without aligning with potentially hostile blocs. Staying neutral also enhances a nation's role as a mediator in international disputes, fostering global peace and cooperation.
Strategic Benefits of Forming Alliances
Forming alliances enhances strategic benefits by enabling shared resources, increased military capabilities, and collective security against common threats. Alliances foster diplomatic influence and economic cooperation, boosting national power more effectively than neutrality. Joint intelligence and technology exchange within alliances amplify defense readiness and geopolitical leverage on the global stage.
Neutrality vs Alliance: Security Implications
Neutrality offers a state protection from being directly involved in conflicts and reduces the risk of retaliatory attacks, but it may limit access to collective defense resources and intelligence sharing. Alliances enhance security through mutual defense agreements, joint military exercises, and intelligence cooperation, which can deter aggressors more effectively. However, alliance commitments may also drag members into conflicts that do not directly threaten their national interests, increasing their exposure to geopolitical risks.
Economic Impacts of Neutral and Allied Positions
Neutral countries often maintain stable trade relations by avoiding sanctions and blockades, fostering continuous economic growth amid global conflicts. Allied nations benefit from mutual defense agreements and shared resources, potentially gaining access to broader markets and increased foreign investments. However, alliances may also expose member economies to wartime economic disruptions, including resource allocation shifts and trade restrictions linked to conflict participation.
Political and Diplomatic Considerations
Neutrality in international relations involves a state refraining from joining military alliances or conflicts, emphasizing impartiality and sovereignty to maintain diplomatic flexibility and avoid entanglement in external disputes. Alliances, conversely, are formal agreements between states to support mutual defense or political interests, strengthening collective security but potentially compromising independent policy decisions. The choice between neutrality and alliance significantly impacts a nation's diplomatic relations, balancing the benefits of security guarantees against the risks of geopolitical commitments and loss of autonomy.
Case Studies: Countries Practicing Neutrality and Alliance
Switzerland exemplifies enduring neutrality, maintaining its non-aligned status since the early 19th century and avoiding military conflicts while hosting diplomatic negotiations. In contrast, NATO members such as the United States and Germany demonstrate alliance commitments, engaging in collective defense and multinational military operations. Sweden's recent shift from neutrality towards closer EU and NATO cooperation highlights evolving security dynamics in response to regional threats.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Neutrality and Alliances
Future trends indicate a shift in global diplomacy where traditional neutrality transforms into strategic non-alignment, balancing economic and security interests without formal alliances. Emerging geopolitical tensions and multilateral partnerships suggest increasing complexity in maintaining neutral stances, as countries leverage soft power and regional blocs to safeguard sovereignty. Technological advances in cybersecurity and space exploration further influence the evolving roles of neutrality and alliances, pushing states towards flexible, issue-based cooperation frameworks.
Neutrality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com