A partisan voter strongly supports a specific political party and consistently aligns their votes with that party's candidates and policies. Understanding the motivations and behaviors of partisan voters can provide valuable insights into election outcomes and campaign strategies. Explore the rest of this article to learn how partisan voting influences your political landscape.
Table of Comparison
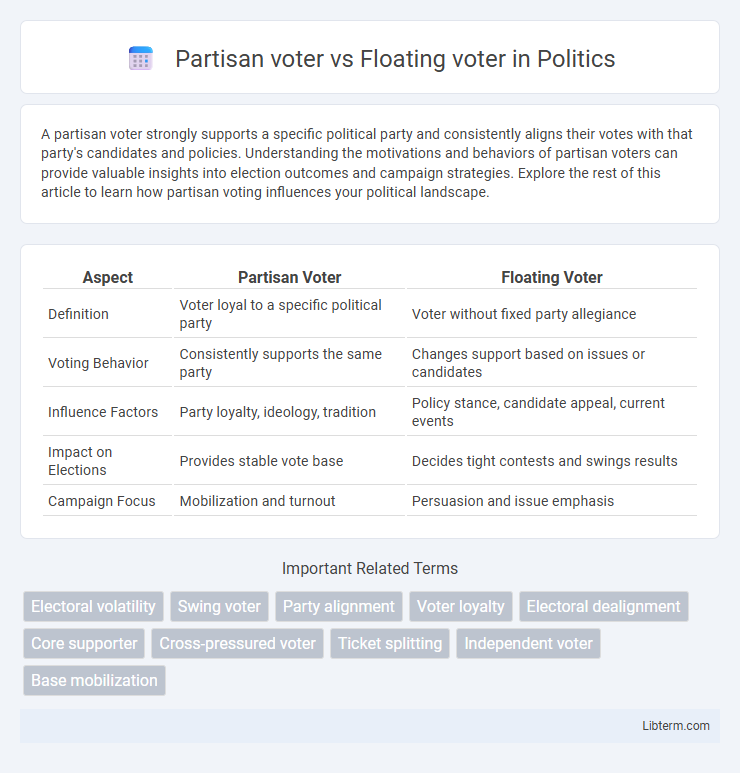
| Aspect | Partisan Voter | Floating Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voter loyal to a specific political party | Voter without fixed party allegiance |
| Voting Behavior | Consistently supports the same party | Changes support based on issues or candidates |
| Influence Factors | Party loyalty, ideology, tradition | Policy stance, candidate appeal, current events |
| Impact on Elections | Provides stable vote base | Decides tight contests and swings results |
| Campaign Focus | Mobilization and turnout | Persuasion and issue emphasis |
Understanding Partisan and Floating Voters
Partisan voters consistently support a specific political party based on long-term loyalty, ideology, or identity, contributing to predictable election outcomes. Floating voters lack a firm party allegiance, making them highly influenced by campaign issues, candidate appeal, and current events, thus playing a crucial role in swing elections. Understanding the distinction between partisan and floating voters enables political strategists to tailor messaging and mobilization efforts effectively.
Defining the Partisan Voter
A partisan voter consistently supports a specific political party or candidate based on strong ideological alignment or loyalty, demonstrating predictable voting behavior in elections. This contrasts with floating voters, who do not have fixed party preferences and may change their votes depending on issues, candidates, or campaign dynamics. Understanding the partisan voter is crucial for political campaigns aiming to mobilize a reliable voter base while targeting floating voters for strategic gains.
Characteristics of Floating Voters
Floating voters, also known as swing voters, exhibit unpredictable voting behavior, often shifting support between political parties based on current issues or candidate appeal. They lack strong party allegiance and are influenced by campaign messages, economic conditions, and social factors. Their electoral volatility makes them a critical demographic in tight elections, prompting targeted strategies from political campaigns.
Motivations Behind Partisan Loyalty
Partisan voters exhibit strong loyalty to a specific political party driven by ideological alignment, social identity, and long-term trust in party policies. Their motivation often stems from deep-rooted values, community influence, and perceived efficacy of the party in addressing their core concerns. In contrast, floating voters lack fixed allegiance and base decisions on short-term issues, candidate appeal, or current political climate, making them more volatile and critical in swing elections.
Factors Influencing Floating Voters
Floating voters, also known as swing voters, are influenced by factors such as current political issues, candidate charisma, and recent government performance, making their voting behavior less predictable than partisan voters who consistently support a specific party. Media coverage, campaign strategies, and social influences also significantly impact floating voters' decisions during elections. Economic conditions and policy changes directly affect their preferences, prompting shifts in allegiance based on immediate concerns rather than party loyalty.
Electoral Impact of Partisan Voters
Partisan voters exhibit strong loyalty to a specific political party, significantly influencing election outcomes by providing a reliable voting base that candidates strategically mobilize. Their consistent support stabilizes electoral projections and shapes campaign strategies, often overwhelming the fluctuating preferences of floating voters who lack fixed party allegiance. The electoral impact of partisan voters extends to reinforcing party platforms and ensuring voter turnout, which can decisively determine election results in closely contested races.
Swing Elections and the Role of Floating Voters
Partisan voters consistently support a specific political party, contributing to electoral stability, while floating voters, who lack party loyalty, play a crucial role in swing elections by shifting the balance of power. Swing elections are often decided by the preferences of floating voters, whose decisions can fluctuate based on campaign issues, candidate appeal, and current political climates. Understanding the behavior and motivations of floating voters is essential for political strategists aiming to secure victories in competitive and unpredictable electoral contests.
Political Campaign Strategies for Different Voters
Political campaign strategies targeting partisan voters emphasize reinforcing existing loyalties through tailored messaging that aligns with their core beliefs and party identity. In contrast, campaigns focusing on floating voters employ persuasive tactics highlighting moderate or cross-cutting issues to sway undecided or swing voters prone to changing their preferences. Data analytics and voter segmentation play critical roles in customizing outreach efforts, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing voter turnout efficacy for both voter types.
Demographic Trends Among Voter Types
Partisan voters tend to be older, more politically engaged, and exhibit strong loyalty to a single party, often influenced by longstanding social and cultural identities. Floating voters, typically younger and more diverse, display less consistent party allegiance and are more responsive to current issues and candidate appeal. Demographic trends indicate a growing proportion of floating voters among urban, minority, and first-time voters, highlighting shifting political landscapes.
Future Implications for Democracy
Partisan voters exhibit consistent loyalty to a specific political party, ensuring stable electoral outcomes and predictable policy direction. Floating voters, who switch allegiance based on issues or candidate appeal, introduce volatility that can drive political parties to be more responsive and adaptive. The future of democracy depends on balancing these dynamics, as a high proportion of floating voters may foster competitive elections and innovation, while excessive volatility could undermine governance stability.
Partisan voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com