Assembly language offers a low-level programming approach that closely interacts with computer hardware, providing efficient and precise control over system resources. Understanding its syntax and instructions can enhance your ability to optimize software performance and troubleshoot complex issues. Dive into the full article to discover how mastering assembly can boost your programming skills and system knowledge.
Table of Comparison
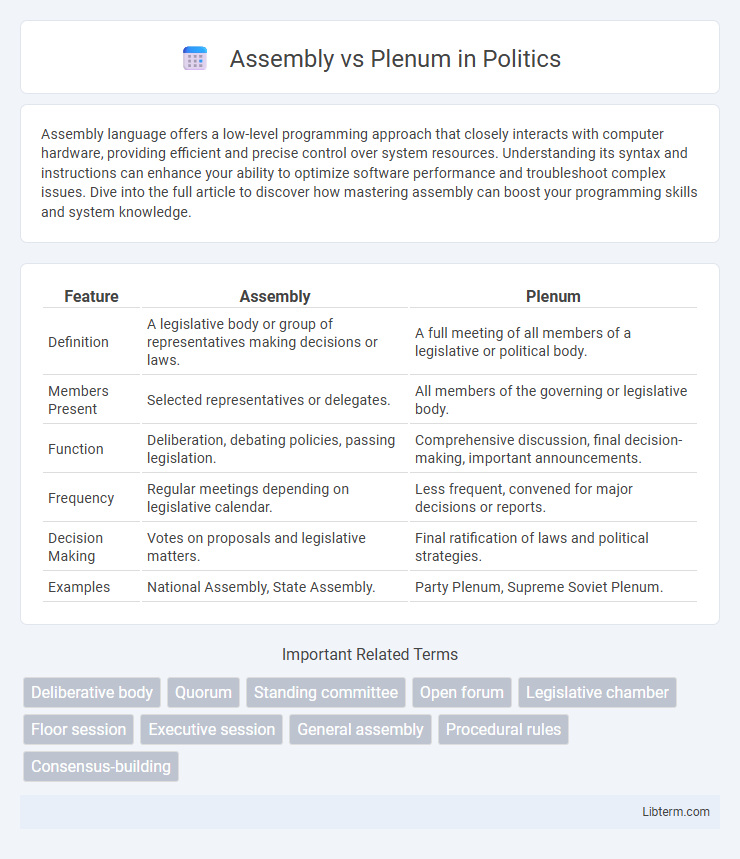
| Feature | Assembly | Plenum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legislative body or group of representatives making decisions or laws. | A full meeting of all members of a legislative or political body. |
| Members Present | Selected representatives or delegates. | All members of the governing or legislative body. |
| Function | Deliberation, debating policies, passing legislation. | Comprehensive discussion, final decision-making, important announcements. |
| Frequency | Regular meetings depending on legislative calendar. | Less frequent, convened for major decisions or reports. |
| Decision Making | Votes on proposals and legislative matters. | Final ratification of laws and political strategies. |
| Examples | National Assembly, State Assembly. | Party Plenum, Supreme Soviet Plenum. |
Understanding Assembly and Plenum: Key Definitions
Assembly refers to the process of putting together multiple components or parts to form a complete unit or system, often emphasizing mechanical or structural integration. Plenum denotes a sealed chamber or enclosed space within HVAC systems designed to distribute air evenly, crucial for maintaining pressure balance and airflow efficiency. Understanding the distinctions highlights that assembly focuses on construction and combination of parts, whereas plenum centers on air distribution and system functionality within mechanical frameworks.
Core Differences Between Assembly and Plenum
Assembly refers to a mechanical process or unit where multiple components are combined to form a complete product, emphasizing the integration of parts and precise alignment. Plenum, in contrast, denotes an enclosed space within HVAC systems designed to distribute air evenly, often acting as a central chamber between the air handler and ductwork. The core difference lies in assembly focusing on constructing physical units contrasted with plenum centering on air distribution and pressure regulation within building ventilation systems.
Material Properties: Assembly vs Plenum
Assembly materials typically emphasize structural integrity, durability, and load-bearing capabilities, often utilizing metals or rigid plastics designed for mechanical strength. Plenum materials prioritize fire resistance, low smoke emission, and non-toxicity, commonly using specialized PVC or fluoropolymer-coated fabrics compliant with ASTM E84 standards. The contrasting material properties reflect distinct functional requirements: assemblies need robustness for support, while plenums demand safety in air handling systems.
Fire Safety Standards and Ratings
Assembly materials and plenum-rated cables differ significantly in fire safety standards and ratings, with plenum cables required to meet stricter fire retardant properties as defined by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 70 and UL 910 standards. Assemblies, often used in general construction, typically comply with UL 1581 and ASTM E84 for flame spread and smoke development but lack the low smoke, low flame characteristics mandatory for plenum environments. Plenum cables are rated for use in air handling spaces due to their reduced toxicity and limited smoke production, essential for fire containment and occupant safety in building ventilation systems.
Typical Applications for Assembly Cables
Assembly cables are primarily used in industrial environments, providing power and signal transmission for machinery and automation systems. They are ideal for fixed installations where flexibility and durability are required, such as factory floors, control panels, and manufacturing equipment. Their construction supports resistance to mechanical stress, chemicals, and oils, making them suitable for harsh operational conditions.
Typical Applications for Plenum Cables
Plenum cables are primarily used in building air handling spaces, including drop ceilings and raised floors, where fire safety and low smoke emission are critical factors. These cables are ideal for commercial offices, hospitals, schools, and data centers that require adherence to strict fire codes such as NFPA 90A. Their fire-resistant and low-smoke materials make plenum cables suitable for environments with significant airflow or ventilation systems.
Cost Comparison: Assembly vs Plenum
The cost comparison between assembly and plenum systems reveals significant differences driven by material, labor, and installation complexity. Assembly systems typically incur higher upfront expenses due to the manufacturing and precise fabrication processes, while plenum systems often offer lower installation costs with simpler, modular components. Long-term maintenance and operational costs further influence the overall investment, with assembly systems benefiting from durability and efficiency, potentially offsetting initial price disparities in extensive projects.
Compliance with Building Codes
Assembly refers to the construction of building components meeting specific fire resistance and structural requirements to comply with building codes. Plenum spaces must adhere to strict regulations regarding materials with low flame spread and smoke development indexes to ensure safety and proper air quality. Compliance with building codes for both assemblies and plenums is essential to prevent fire hazards and achieve certification during inspections.
Installation Considerations and Best Practices
Assembly installation requires precise alignment and secure fastening to ensure structural integrity and prevent air leaks, with attention to manufacturer's specifications for torque and sealant application. Plenum installations demand careful handling of materials to maintain fire ratings and avoid compromising air quality, emphasizing the use of UL-listed components and proper sealing techniques to prevent contamination and leakage. Best practices in both scenarios include thorough pre-installation inspection, adherence to local building codes, and regular maintenance checks to sustain performance and safety.
Choosing Between Assembly and Plenum: Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between Assembly and Plenum depends on your project's communication and air handling needs; Assembly cables are suitable for general use with basic insulation, while Plenum cables meet strict fire safety standards for air handling spaces. Plenum cables have a special insulation that emits low smoke and toxic fumes, making them ideal for HVAC and building plenum spaces where fire codes demand higher safety. Evaluate your building's environment, fire codes, and budget constraints to determine which cable type aligns best with regulatory compliance and safety requirements.
Assembly Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com