Charismatic leadership inspires and motivates followers through a leader's personal charm and vision, fostering strong emotional connections that drive commitment and performance. This leadership style enhances organizational loyalty and encourages proactive behaviors by instilling confidence and enthusiasm. Discover how charismatic leadership can transform your team and elevate success by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
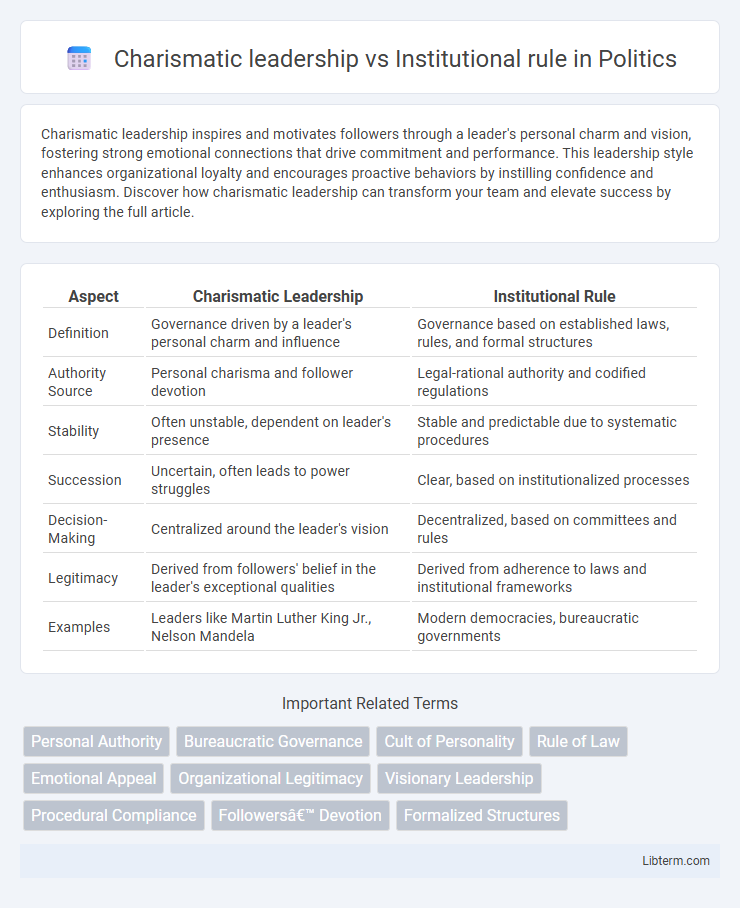
| Aspect | Charismatic Leadership | Institutional Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance driven by a leader's personal charm and influence | Governance based on established laws, rules, and formal structures |
| Authority Source | Personal charisma and follower devotion | Legal-rational authority and codified regulations |
| Stability | Often unstable, dependent on leader's presence | Stable and predictable due to systematic procedures |
| Succession | Uncertain, often leads to power struggles | Clear, based on institutionalized processes |
| Decision-Making | Centralized around the leader's vision | Decentralized, based on committees and rules |
| Legitimacy | Derived from followers' belief in the leader's exceptional qualities | Derived from adherence to laws and institutional frameworks |
| Examples | Leaders like Martin Luther King Jr., Nelson Mandela | Modern democracies, bureaucratic governments |
Defining Charismatic Leadership
Charismatic leadership is defined by a leader's ability to inspire and influence followers through personal charm, vision, and emotional appeal, often creating strong loyalty and devotion. Unlike institutional rule, which relies on established laws, procedures, and formal authority, charismatic leadership depends on the leader's exceptional qualities and the followers' belief in their extraordinary mission. This type of leadership can drive rapid change but may lack the stability and continuity found in institutional governance.
Understanding Institutional Rule
Institutional rule relies on established laws, procedures, and formal structures to ensure stable governance and consistent decision-making within organizations or states. This form of leadership emphasizes accountability through bureaucratic frameworks and predictable systems rather than personal authority or charisma. Understanding institutional rule requires analyzing its role in maintaining order, legitimacy, and continuity beyond individual leaders' influence.
Historical Contexts of Both Approaches
Charismatic leadership often emerges during periods of crisis or social upheaval, exemplified by figures like Napoleon Bonaparte or Martin Luther King Jr., who inspire loyalty through personal vision and charisma. Institutional rule, rooted in established systems such as monarchies, bureaucracies, or constitutional governments, ensures continuity and stability with structured norms and codified laws, as seen in the Roman Republic or modern democratic states. Historical contexts reveal charismatic leadership's temporary and transformative impact contrasted with institutional rule's emphasis on enduring governance frameworks.
Core Principles and Values
Charismatic leadership centers on the personal vision, magnetism, and emotional influence of the leader, prioritizing innovation, inspiration, and loyalty to the individual's charisma. Institutional rule is grounded in established laws, formal procedures, and systemic governance, emphasizing consistency, accountability, and organizational stability. Core principles of charismatic leadership involve transformative change and visionary guidance, whereas institutional rule upholds order, legitimacy, and structured authority.
Influence on Organizational Culture
Charismatic leadership shapes organizational culture through personal vision and emotional appeal, fostering innovation and strong employee loyalty. Institutional rule emphasizes established protocols and formal authority, promoting stability, consistency, and adherence to organizational values. The balance between charismatic influence and institutional frameworks determines the adaptability and cohesion of an organization's culture.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Charismatic leadership centralizes decision-making through the leader's personal vision and influence, enabling rapid and flexible responses but risking subjectivity and inconsistency. Institutional rule emphasizes formalized, rule-based processes involving multiple stakeholders, promoting stability, accountability, and predictable outcomes in decisions. The contrast lies in charismatic leaders' reliance on individual authority versus institutional systems' dependence on structured procedures and collective input.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Charismatic leadership excels in inspiring followers through vision and personal appeal, fostering strong loyalty and rapid decision-making, yet it risks dependence on the leader and potential instability during succession. Institutional rule promotes consistency, accountability, and adherence to established procedures, ensuring long-term stability but may suffer from rigidity and slower response to change. Balancing the dynamism of charismatic influence with the structured governance of institutional frameworks can optimize organizational effectiveness.
Impact on Change and Innovation
Charismatic leadership drives rapid change and innovation by inspiring vision and motivating followers to embrace new ideas with enthusiasm. Institutional rule relies on established norms and formal processes, promoting stability but often slowing transformative change and innovation. The dynamic tension between visionary charisma and structured governance shapes an organization's adaptability and long-term growth potential.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Charismatic leadership, exemplified by figures like Nelson Mandela and Elon Musk, depends on personal appeal and visionary charisma to inspire followers and drive change, often leading to rapid organizational or societal transformations. Institutional rule, demonstrated by stable democracies like Germany and Japan, relies on established laws, procedures, and bureaucratic structures that ensure predictability, accountability, and continuity regardless of individual leaders. Case studies of the Iranian Revolution illustrate the shift from institutional monarchy to charismatic leadership under Ayatollah Khomeini, highlighting the tension and transition between these two governance models.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style
Choosing the right leadership style depends on organizational goals and context, with charismatic leadership inspiring innovation and strong personal loyalty through vision and emotional appeal, while institutional rule emphasizes stability, consistency, and adherence to established protocols. Charismatic leaders excel in times of change or crisis by motivating followers towards transformative goals, whereas institutional leadership ensures long-term governance through structured policies and formal authority. Effective leadership often balances charisma with institutional frameworks to optimize both adaptability and sustainable order.
Charismatic leadership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com