Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values, institutions, and practices to maintain social stability and continuity. It advocates for limited government intervention and a cautious approach to change, prioritizing individual responsibility and cultural heritage. Explore the article to understand how conservatism shapes political and social perspectives in today's world.
Table of Comparison
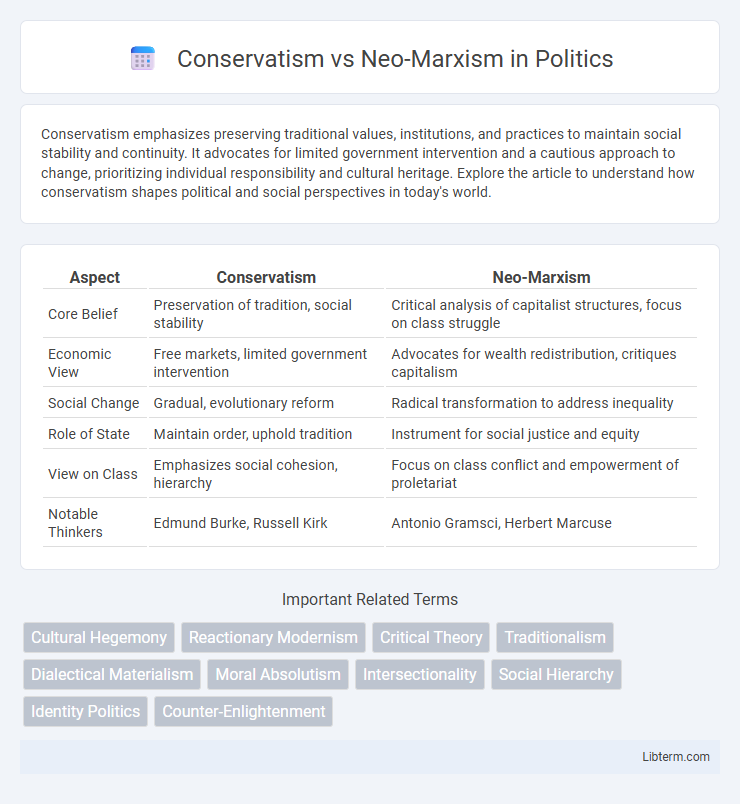
| Aspect | Conservatism | Neo-Marxism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Preservation of tradition, social stability | Critical analysis of capitalist structures, focus on class struggle |
| Economic View | Free markets, limited government intervention | Advocates for wealth redistribution, critiques capitalism |
| Social Change | Gradual, evolutionary reform | Radical transformation to address inequality |
| Role of State | Maintain order, uphold tradition | Instrument for social justice and equity |
| View on Class | Emphasizes social cohesion, hierarchy | Focus on class conflict and empowerment of proletariat |
| Notable Thinkers | Edmund Burke, Russell Kirk | Antonio Gramsci, Herbert Marcuse |
Introduction to Conservatism and Neo-Marxism
Conservatism emphasizes the preservation of traditional institutions, social order, and hierarchy, advocating gradual change and the importance of cultural heritage. Neo-Marxism builds on classical Marxist theory, critiquing capitalism by focusing on cultural and ideological aspects of power, inequality, and social relations beyond mere economic factors. Both frameworks offer distinct perspectives on societal structure and change, shaping political discourse and policy-making globally.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Foundations
Conservatism traces its historical origins to the reaction against the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social order, and gradual change rooted in Edmund Burke's philosophy. Neo-Marxism evolves from classical Marxism, integrating critiques of culture, ideology, and power structures influenced by thinkers like Antonio Gramsci and the Frankfurt School. Both ideologies' philosophical foundations diverge, with conservatism prioritizing stability and hierarchy, while Neo-Marxism advocates for radical social transformation through critical theory and class consciousness.
Core Principles of Conservatism
Conservatism emphasizes the preservation of traditional institutions, social stability, and gradual change rooted in historical continuity. It advocates for limited government intervention, individual responsibility, and the protection of property rights as fundamental to maintaining social order. Core principles include respect for established customs, skepticism toward radical reforms, and the belief that societal progress emerges organically through cultural evolution.
Key Tenets of Neo-Marxism
Neo-Marxism emphasizes the critique of capitalist structures, highlighting the roles of culture, ideology, and power relations in maintaining social inequalities. It expands classical Marxist theory by incorporating elements from psychoanalysis, sociology, and critical theory to address issues such as identity, race, and gender exploitation. Key tenets include the belief in systemic change through addressing both economic base and superstructure, focusing on cultural hegemony, and promoting social justice beyond mere economic redistribution.
Approach to Tradition and Social Change
Conservatism emphasizes preserving established traditions, social institutions, and cultural norms to maintain social stability and continuity. Neo-Marxism advocates for critical analysis of existing traditions as instruments of dominant class power, promoting transformative social change to achieve greater equality and justice. The conservative approach resists rapid change, while Neo-Marxism embraces revolutionary restructuring to address systemic inequalities.
Economic Philosophies and Class Perspectives
Conservatism emphasizes free-market capitalism, private property rights, and limited government intervention to sustain economic stability and social order, often viewing class structures as natural and beneficial. Neo-Marxism critiques capitalist economies through the lens of class struggle, highlighting systemic inequalities and advocating for redistributive policies to address exploitation and empower the working class. These contrasting economic philosophies shape divergent perspectives on social hierarchy, economic justice, and the role of the state in regulating class relations.
Views on Authority, Freedom, and the State
Conservatism upholds traditional authority structures, emphasizing social order and the rule of law as essential for stability, while prioritizing individual freedom within established norms. Neo-Marxism critiques existing authority as a tool of capitalist domination, advocating for collective freedom through the dismantling of hierarchical state power and economic inequality. The state in Conservatism serves to preserve cultural heritage and maintain societal cohesion, whereas Neo-Marxism views the state as an instrument of class oppression requiring radical transformation.
Impact on Modern Politics and Society
Conservatism emphasizes tradition, social stability, and incremental change, influencing modern politics by promoting policies that uphold established institutions and cultural norms. Neo-Marxism critiques capitalist systems and highlights social inequalities, driving movements for economic redistribution and systemic reforms. The tension between these ideologies shapes debates on governance, social justice, and economic policy in contemporary societies worldwide.
Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Each Ideology
Conservatism faces criticism for resisting social progress and perpetuating inequalities by maintaining traditional hierarchies and power structures. Neo-Marxism is controversial due to its focus on class struggle and economic determinism, often criticized for underestimating cultural factors and promoting divisive identity politics. Both ideologies are debated for their approaches to social change, with conservatism viewed as preserving the status quo and Neo-Marxism seen as advocating radical restructuring of society.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Outlook
Conservatism emphasizes tradition, social stability, and free-market principles, influencing current policies that prioritize individual responsibility and national sovereignty. Neo-Marxism critiques capitalist structures and advocates for social justice, addressing economic inequalities and systemic oppression in modern societies. The future outlook reveals ongoing ideological clashes, with conservatism pushing for preservation of existing institutions while Neo-Marxism calls for transformative social reforms amid globalization and technological change.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com