State sovereignty embodies a nation's supreme authority to govern itself without external interference, ensuring control over its territory, population, and laws. This principle underpins international relations, defining the legal rights and responsibilities of states within the global system. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of how state sovereignty affects world politics and your place within it.
Table of Comparison
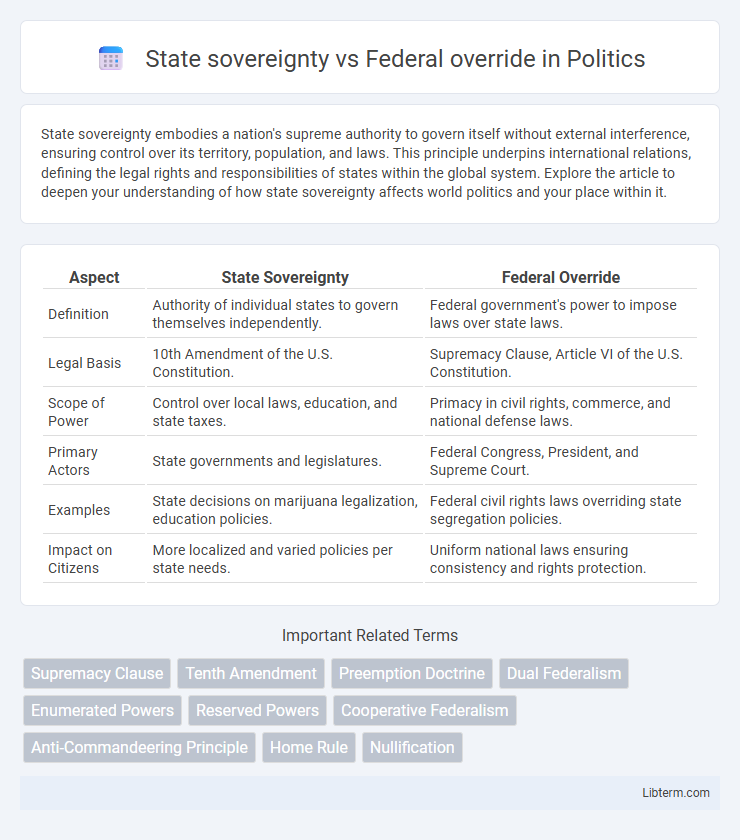
| Aspect | State Sovereignty | Federal Override |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority of individual states to govern themselves independently. | Federal government's power to impose laws over state laws. |
| Legal Basis | 10th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. | Supremacy Clause, Article VI of the U.S. Constitution. |
| Scope of Power | Control over local laws, education, and state taxes. | Primacy in civil rights, commerce, and national defense laws. |
| Primary Actors | State governments and legislatures. | Federal Congress, President, and Supreme Court. |
| Examples | State decisions on marijuana legalization, education policies. | Federal civil rights laws overriding state segregation policies. |
| Impact on Citizens | More localized and varied policies per state needs. | Uniform national laws ensuring consistency and rights protection. |
Understanding State Sovereignty
State sovereignty refers to the authority and autonomy of individual states to govern themselves without undue interference from the federal government. This principle is rooted in the Tenth Amendment, which reserves powers not delegated to the federal government to the states or the people. Understanding state sovereignty is crucial for analyzing conflicts where federal override challenges state laws or policies, particularly in areas like education, healthcare, and law enforcement.
The Foundations of Federal Override
The foundations of federal override stem from the Supremacy Clause established in Article VI of the U.S. Constitution, which asserts that federal law takes precedence over conflicting state laws. This principle ensures uniformity in national policies, particularly in areas such as civil rights, commerce, and immigration, where federal authority is deemed essential. Supreme Court rulings, including McCulloch v. Maryland and Gibbons v. Ogden, have further solidified federal override powers as a means to maintain national cohesion while balancing state sovereignty.
Historical Context: States vs Federal Power
The tension between state sovereignty and federal override has deep roots in American history, originating from the Constitution's balance of power. Landmark events such as the Nullification Crisis of the 1830s and the Civil War underscored disputes over states' rights versus federal authority. Legal precedents, including McCulloch v. Maryland and the supremacy clause, have continually shaped the dynamic interplay between state autonomy and federal intervention.
Constitutional Basis for Each Authority
State sovereignty is rooted in the Tenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which reserves powers not delegated to the federal government to the states or the people. Federal override authority is established under the Supremacy Clause in Article VI, Clause 2, which mandates that federal law prevails over conflicting state laws. Balancing these constitutional provisions remains central to ongoing legal debates about the scope of state versus federal power.
Notable Legal Battles: Key Supreme Court Cases
The landmark case McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) established federal supremacy by affirming Congress's implied powers, limiting states' ability to tax federal institutions. In Cooper v. Aaron (1958), the Supreme Court reinforced federal authority by declaring that states cannot nullify federal court decisions, particularly regarding desegregation mandates. More recently, National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius (2012) highlighted tensions between state sovereignty and federal power by upholding the Affordable Care Act while restricting the federal government's ability to coerce states through Medicaid expansion.
Impact on Civil Rights and Liberties
State sovereignty often limits the ability of states to enact policies that restrict civil rights, while federal override mechanisms, such as the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act, have historically ensured the protection of individual liberties across all states. Federal intervention has been crucial in dismantling segregation and enforcing anti-discrimination laws, counteracting state laws that perpetuate inequality. The ongoing tension between state autonomy and federal authority shapes the enforcement and expansion of civil rights, affecting access to voting, education, and equal protection under the law.
Policy Implications: Healthcare, Education, and More
State sovereignty in healthcare policy allows for tailored public health initiatives and Medicaid management, which can lead to more effective responses to local needs. Federal overrides, such as the Affordable Care Act mandates, standardize essential benefits and ensure broader coverage, impacting state autonomy but enhancing nationwide healthcare access. In education, state control shapes curriculum and funding priorities, while federal policies like Title IX and the Every Student Succeeds Act impose standards to promote equity and accountability across all states.
The Role of Federalism in Modern Governance
Federalism balances state sovereignty and federal authority by delineating powers to maintain unity while respecting regional autonomy. The role of federalism in modern governance involves resolving conflicts through constitutional boundaries, where federal overrides occur primarily in areas affecting national interests, such as civil rights and interstate commerce. This system allows states to tailor policies locally while ensuring consistent application of federal laws critical to national cohesion and economic stability.
Contemporary Debates: Where Lines Are Drawn
Contemporary debates on state sovereignty versus federal override center on issues such as healthcare, immigration, and environmental regulations where states seek autonomy to tailor policies reflecting local preferences while the federal government asserts supremacy to ensure national uniformity and enforce constitutional mandates. Legal battles often hinge on the interpretation of the Supremacy Clause and the Tenth Amendment, with courts determining the balance between states' rights and federal authority. Recent cases, including challenges to federal environmental rules and immigration enforcement policies, illustrate the evolving boundaries and ongoing tensions in American federalism.
Future Trends in State-Federal Dynamics
Evolving legal frameworks and technological advancements are shaping future state-federal dynamics, with increasing debates over jurisdictional boundaries and regulatory authority. Emerging issues like cybersecurity, environmental regulation, and healthcare are prompting states to assert greater sovereignty while federal agencies seek broader override powers to ensure national consistency. Legal scholars forecast a complex interplay of cooperative federalism and contested sovereignty, driven by shifting political landscapes and societal demands.
State sovereignty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com