Protests serve as powerful expressions of public sentiment and catalysts for social change, often highlighting urgent issues that demand attention. Understanding the dynamics, causes, and impacts of protests provides valuable insight into how movements shape societies globally. Explore the article to discover how your awareness of protests can deepen and influence your perspective on civic engagement.
Table of Comparison
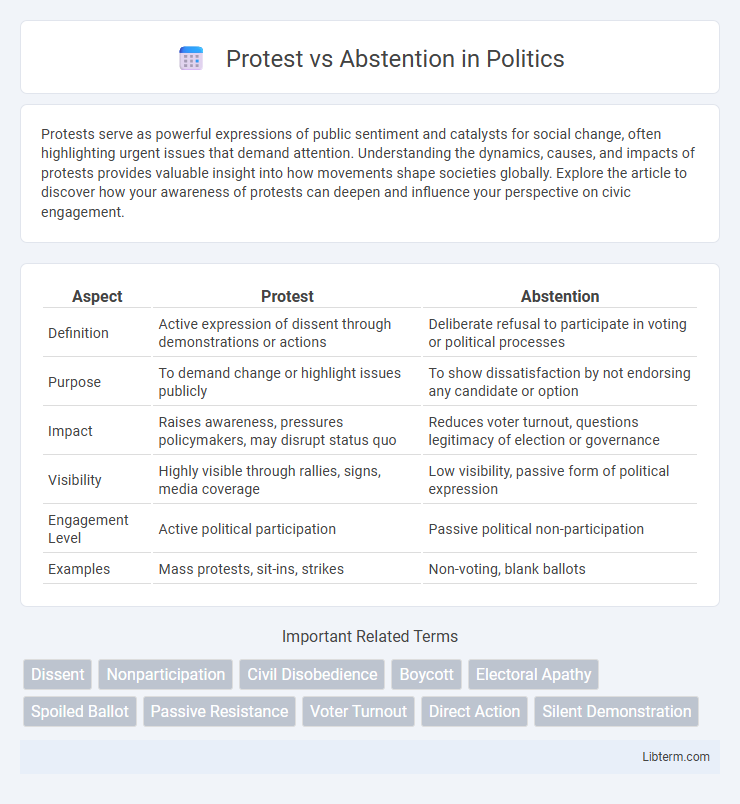
| Aspect | Protest | Abstention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active expression of dissent through demonstrations or actions | Deliberate refusal to participate in voting or political processes |
| Purpose | To demand change or highlight issues publicly | To show dissatisfaction by not endorsing any candidate or option |
| Impact | Raises awareness, pressures policymakers, may disrupt status quo | Reduces voter turnout, questions legitimacy of election or governance |
| Visibility | Highly visible through rallies, signs, media coverage | Low visibility, passive form of political expression |
| Engagement Level | Active political participation | Passive political non-participation |
| Examples | Mass protests, sit-ins, strikes | Non-voting, blank ballots |
Understanding Protest and Abstention
Protest refers to a formal objection or expression of disapproval often demonstrated through organized public actions or legal challenges, aiming to influence decisions or policies. Abstention is the deliberate choice to refrain from participating in a vote or decision-making process, signaling neutrality or dissent without direct opposition. Understanding protest involves recognizing its role as active resistance, while abstention represents passive non-participation within political or organizational contexts.
Defining Political Protest
Political protest involves organized public actions expressing opposition or support for social, economic, or political issues, aiming to influence government policies or societal norms. Abstention refers to the deliberate choice to withhold participation, such as not voting, as a form of silent political expression or dissent. Both protest and abstention serve as mechanisms for citizens to communicate dissatisfaction and demand change within democratic systems.
What Is Electoral Abstention?
Electoral abstention refers to the decision by eligible voters to deliberately refrain from participating in an election by not casting their ballots. This phenomenon can result from political disillusionment, lack of trust in candidates or institutions, or barriers to voting. Understanding electoral abstention is crucial for analyzing voter behavior, election legitimacy, and democratic health.
Historical Contexts of Protest and Abstention
Protest and abstention have served as powerful political tools throughout history, with protests often arising during pivotal moments such as the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s, where mass demonstrations challenged racial segregation and inequality. Abstention, like the boycotts during the Indian Independence Movement led by Mahatma Gandhi, proved effective by withdrawing participation from British goods to undermine colonial economic control. These methods reflect strategic choices shaped by historical contexts, where visible acts of dissent or deliberate non-participation aimed to disrupt established systems and catalyze social or political change.
Motivations Behind Protesting
Protests are driven by motivations such as demanding social justice, opposing government policies, or advocating for human rights, reflecting a desire for active change. Participants are often motivated by a sense of urgency or moral conviction to publicly express dissent and influence public opinion. Motivations contrast with abstention, where individuals choose non-participation due to apathy, disillusionment, or distrust in political systems.
Causes of Voter Abstention
Voter abstention often stems from political disenchantment, lack of trust in electoral processes, and the perception that individual votes will not influence outcomes. Socioeconomic factors such as limited access to voting facilities, feelings of marginalization, and low political efficacy also contribute significantly. Understanding these causes is crucial for addressing democratic participation gaps and enhancing voter turnout strategies.
Impacts on Democratic Processes
Protest and abstention both influence democratic processes by altering voter participation and signaling public dissatisfaction. Protests can mobilize citizens, draw attention to specific issues, and pressure policymakers, potentially leading to policy changes and strengthened democratic accountability. Abstention, often interpreted as political disengagement or discontent, may weaken electoral legitimacy and reduce the responsiveness of elected officials to constituent needs.
Social and Cultural Influences
Social and cultural influences significantly shape the choice between protest and abstention as forms of political expression. Communities with strong collective identities and shared grievances often lean toward protest to actively challenge social injustices, while those feeling politically marginalized or distrustful of institutions may opt for abstention as a silent form of dissent. Cultural norms around civic engagement and historical experiences with political movements also determine whether individuals view voting or protesting as legitimate tools for change.
Case Studies: Protest vs Abstention
Protest and abstention represent two distinct forms of political expression analyzed in several case studies across democracies and authoritarian regimes. Case studies from countries like Venezuela and Hong Kong demonstrate how protests mobilize direct confrontation to demand change, while abstention often signals passive resistance or disenchantment with political options, impacting voter turnout and legitimacy of elections. Research on South Africa's 1994 and 2019 elections shows that strategic abstention can influence political negotiations and highlight systemic barriers within electoral processes, contrasting with visible mass protests that capture immediate public attention.
Choosing Between Protest and Abstention
Choosing between protest and abstention hinges on the desired impact of political or social action; protest actively expresses opposition and demands change, thereby raising awareness and applying public pressure. Abstention, or deliberately refraining from participating, signals dissatisfaction or disengagement without direct confrontation, often highlighting systemic issues like disenfranchisement or lack of viable options. The decision depends on whether the goal is to visibly challenge the status quo or to demonstrate withdrawal as a form of political expression.
Protest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com