A high-quality speaker enhances your audio experience by delivering clear, balanced sound with rich bass and crisp highs, making music, movies, and calls more immersive. Choosing the right speaker depends on factors like power output, connectivity options, and portability to suit your lifestyle and space. Explore the rest of this article to discover how to select the perfect speaker that matches Your audio needs.
Table of Comparison
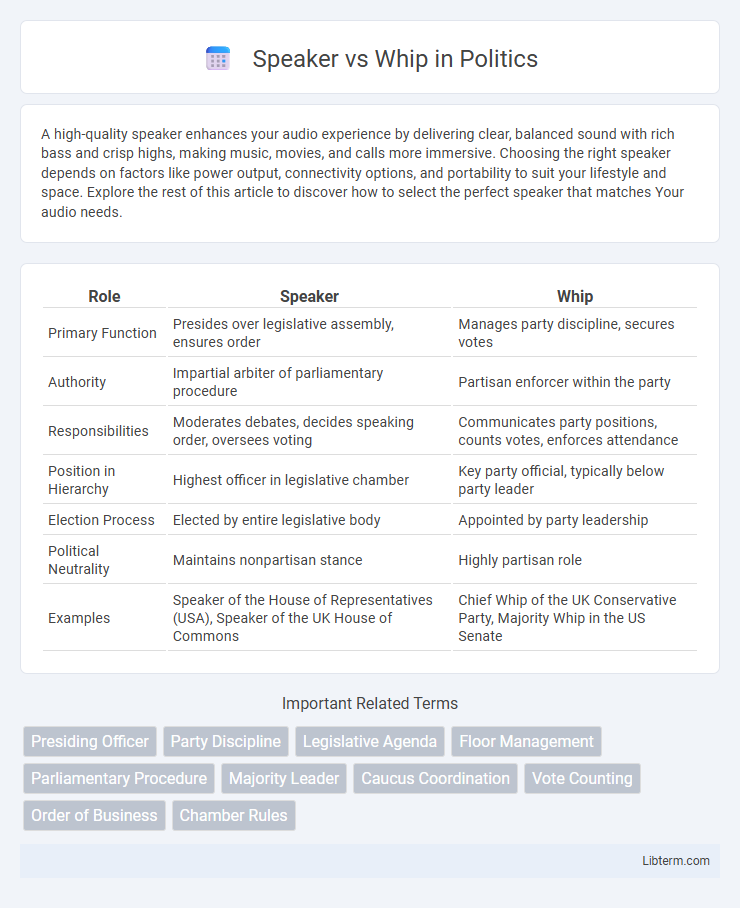
| Role | Speaker | Whip |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Presides over legislative assembly, ensures order | Manages party discipline, secures votes |
| Authority | Impartial arbiter of parliamentary procedure | Partisan enforcer within the party |
| Responsibilities | Moderates debates, decides speaking order, oversees voting | Communicates party positions, counts votes, enforces attendance |
| Position in Hierarchy | Highest officer in legislative chamber | Key party official, typically below party leader |
| Election Process | Elected by entire legislative body | Appointed by party leadership |
| Political Neutrality | Maintains nonpartisan stance | Highly partisan role |
| Examples | Speaker of the House of Representatives (USA), Speaker of the UK House of Commons | Chief Whip of the UK Conservative Party, Majority Whip in the US Senate |
Introduction: Understanding Speaker and Whip Roles
The Speaker is the presiding officer of a legislative assembly, responsible for maintaining order during debates, deciding who may speak, and ensuring rules are followed. The Whip's role centers on party discipline, coordinating members' votes and attendance to secure majority support for legislative agendas. Both roles are pivotal in parliamentary systems, balancing procedural management and party strategy.
Historical Origins of Speaker and Whip
The roles of Speaker and Whip have origins dating back to medieval England, with the Speaker emerging in the 14th century as the representative of the House of Commons to the monarch, responsible for moderating debates and maintaining order. The Whip position developed later in the 17th century as a party enforcer, tasked with ensuring party discipline and securing votes during parliamentary decision-making. Both roles evolved to structure legislative processes and reinforce party control within modern parliamentary systems.
Core Responsibilities: Speaker vs Whip
The Speaker presides over parliamentary sessions, ensuring order, managing debates, and representing the legislative body officially. The Whip focuses on party discipline by coordinating voting strategies, ensuring member attendance, and communicating party positions to legislators. Both roles are vital for legislative efficiency, with the Speaker maintaining procedural fairness and the Whip enforcing party cohesion.
Selection and Appointment Process
The selection and appointment process of the Speaker involves election by the members of the legislative body, typically requiring a majority vote in the house to secure the position. In contrast, the Whip is usually appointed by the party leadership to enforce party discipline and manage legislative strategy, often chosen based on loyalty and organizational skills rather than a formal vote by the entire assembly. These distinct processes reflect the Speaker's role as an impartial presiding officer and the Whip's function as a party enforcer within the legislature.
Authority and Influence in the Legislature
The Speaker of the House holds the highest authority in the legislature, presiding over sessions, setting the legislative agenda, and guiding the passage of bills, thereby shaping policy outcomes significantly. The Whip, while subordinate to the Speaker, wields considerable influence through party discipline, ensuring members vote according to party lines and facilitating communication between leadership and rank-and-file legislators. Together, their roles balance formal authority and strategic influence to maintain order and advance legislative priorities.
Speaker vs Whip: Power Dynamics
The Speaker holds the highest authority in the legislative assembly, controlling debates, maintaining order, and interpreting procedural rules, which positions them as a central figure in parliamentary power dynamics. The Whip enforces party discipline and coordinates members' voting behavior, acting as a vital link between party leadership and rank-and-file legislators. The power dynamic between Speaker and Whip centers on the Speaker's neutral authority within the chamber versus the Whip's partisan influence on legislative outcomes.
Role in Parliamentary Procedure
The Speaker presides over parliamentary sessions, ensuring order, managing debates, and enforcing procedural rules to facilitate legislative processes. The Whip is responsible for party discipline, organizing members' votes, and ensuring attendance during key decisions. Both roles are essential for maintaining structure and party cohesion within legislative assemblies.
Impact on Party Discipline
The Speaker maintains order and neutrality in parliamentary proceedings, often exerting indirect influence on party discipline by ensuring fair debate and procedural compliance. Whips play a critical role in enforcing party discipline directly by managing attendance, securing votes, and communicating party positions to legislators. Their impact is more immediate and strategic, shaping legislative outcomes through coordinated member participation and adherence to party lines.
Speaker and Whip in Crisis Situations
The Speaker and Whip play distinct yet crucial roles in crisis situations within legislative bodies, with the Speaker maintaining order and facilitating urgent debates to ensure smooth governance. The Whip focuses on party discipline, coordinating votes and rallying support among members to pass critical emergency legislation effectively. Their collaboration ensures that procedural efficiency and party unity are upheld during high-pressure decision-making moments.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Importance
The Speaker presides over legislative debates and ensures orderly conduct, while the Whip is responsible for party discipline and vote management. Understanding these roles clarifies the balance between procedural authority and political strategy in legislative bodies. Their distinct functions are crucial for maintaining effective parliamentary governance and party cohesion.
Speaker Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com