Straight-ticket voting simplifies elections by allowing voters to select all candidates from a single party with one mark, streamlining the voting process and reinforcing party loyalty. This method can influence election outcomes by boosting party cohesion and minimizing cross-party selections. Explore the rest of the article to understand how straight-ticket voting impacts your choices and the democratic process.
Table of Comparison
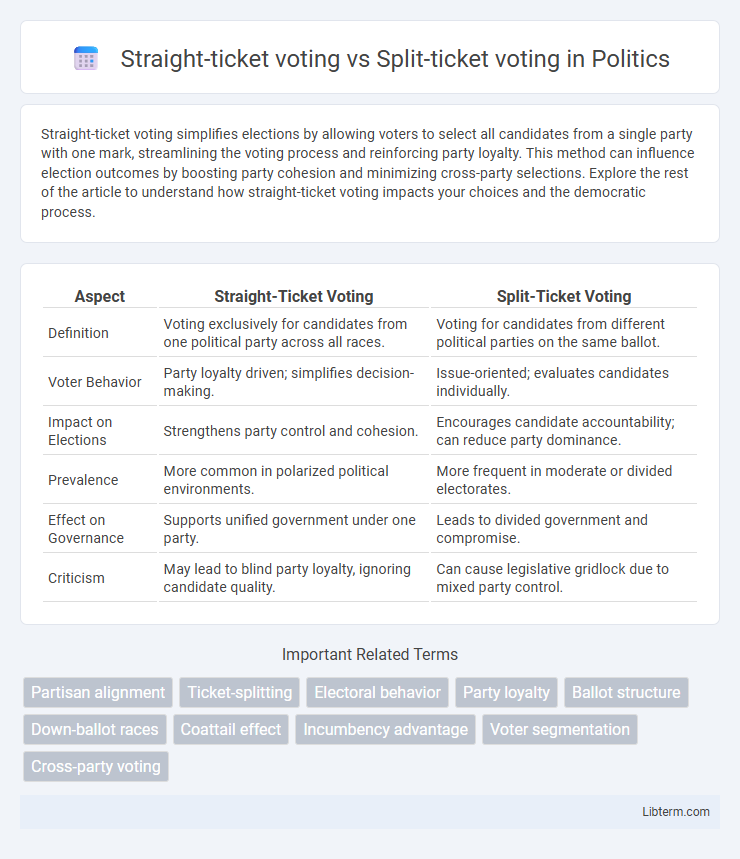
| Aspect | Straight-Ticket Voting | Split-Ticket Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting exclusively for candidates from one political party across all races. | Voting for candidates from different political parties on the same ballot. |
| Voter Behavior | Party loyalty driven; simplifies decision-making. | Issue-oriented; evaluates candidates individually. |
| Impact on Elections | Strengthens party control and cohesion. | Encourages candidate accountability; can reduce party dominance. |
| Prevalence | More common in polarized political environments. | More frequent in moderate or divided electorates. |
| Effect on Governance | Supports unified government under one party. | Leads to divided government and compromise. |
| Criticism | May lead to blind party loyalty, ignoring candidate quality. | Can cause legislative gridlock due to mixed party control. |
Understanding Straight-Ticket Voting
Straight-ticket voting refers to the practice where voters select candidates from the same political party for all positions on a ballot. This voting behavior simplifies decision-making by relying on party affiliation rather than evaluating individual candidates' policies or qualifications, often seen in partisan elections. Straight-ticket voting contrasts with split-ticket voting, where voters choose candidates from different parties for various offices, reflecting a more selective approach.
What is Split-Ticket Voting?
Split-ticket voting occurs when voters select candidates from different political parties for different offices within the same election, reflecting a more individualized choice rather than party loyalty. This behavior contrasts with straight-ticket voting, where voters consistently choose candidates from one party across all races. Split-ticket voting often indicates a more nuanced electorate, considering candidate qualities, policies, and local issues over strict party alignment.
Historical Context of Voting Patterns
Straight-ticket voting has historically been prevalent in the United States during periods of strong party loyalty, particularly in the mid-20th century when political polarization was less pronounced. Split-ticket voting increased notably from the 1960s onward, reflecting growing voter independence and the rise of candidate-centered campaigns amid evolving political ideologies. These shifts in voting patterns correspond with landmark elections such as the 1964 and 1980 presidential races, illustrating changing attitudes toward party allegiance and candidate evaluation.
Key Differences Between Straight and Split-Ticket Voting
Straight-ticket voting involves selecting candidates from the same political party for all offices on the ballot, reflecting strong party loyalty and simplifying the voting process. Split-ticket voting occurs when voters choose candidates from different parties for various offices, indicating a more issue-focused or candidate-centered approach that prioritizes individual qualifications over party affiliation. The key differences lie in voter behavior patterns, with straight-ticket voting enhancing partisan consistency and split-ticket voting contributing to more diverse electoral outcomes and increased cross-party representation.
Advantages of Straight-Ticket Voting
Straight-ticket voting streamlines the election process by allowing voters to select all candidates from one party with a single action, saving time and reducing decision fatigue. This method strengthens party cohesion and promotes clear legislative mandates, which can enhance governmental efficiency and policy implementation. Voters benefit from decreased complexity, particularly in elections with numerous offices or measures, ensuring consistent ideological alignment across all choices.
Benefits of Split-Ticket Voting
Split-ticket voting enhances democratic representation by allowing voters to select candidates from different parties for various offices, ensuring a more personalized and balanced government. This approach fosters accountability by encouraging elected officials to collaborate across party lines and address diverse constituent interests. Voters benefit from increased flexibility, preventing one party's entire platform from dominating and promoting a more nuanced electoral outcome.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Straight-ticket voting, where voters select candidates from the same party for all offices, often leads to more predictable election outcomes and can reinforce party dominance in legislative bodies. Split-ticket voting, which involves choosing candidates from different parties for various offices, increases electoral competitiveness and can result in more balanced government control, reflecting nuanced voter preferences. The prevalence of either voting behavior significantly affects party strategies, campaign focus, and the overall political landscape in national and local elections.
Influence on Political Parties
Straight-ticket voting enhances political parties' power by promoting unified support for their candidates, thereby strengthening party cohesion and increasing electoral predictability. In contrast, split-ticket voting dilutes party dominance by encouraging voter independence and cross-party candidate evaluation, which can lead to more balanced legislative bodies. The prevalence of split-ticket voting often forces parties to broaden their platforms to appeal to a wider electorate, influencing campaign strategies and policy positions.
Voter Behavior and Demographics
Straight-ticket voting reflects voter loyalty to a single political party across all races on the ballot, often driven by strong partisan identification and demographic factors such as age, education, and geographic location. Split-ticket voting, where voters select candidates from different parties for different offices, indicates a more candidate-focused or issue-driven approach, commonly seen among independents, younger voters, and those with higher educational attainment. Demographic trends show that older and less-educated voters are more likely to engage in straight-ticket voting, while younger, urban, and more educated voters demonstrate higher rates of split-ticket behavior.
Future Trends in Voting Preferences
Future trends in voting preferences indicate a gradual decline in straight-ticket voting, driven by increasing voter independence and access to diversified information sources. Split-ticket voting is expected to rise as voters prioritize candidate qualifications and issue-based decisions over partisan loyalty. This shift may lead to more competitive elections and nuanced policymaking.
Straight-ticket voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com