Populism often emerges as a political approach that seeks to represent the interests of ordinary people against perceived elites or establishment powers. It can influence elections, policy-making, and public discourse by tapping into widespread social frustrations and promoting direct appeals to "the people." Explore the rest of the article to understand how populism shapes modern political landscapes and what it means for your engagement as a voter.
Table of Comparison
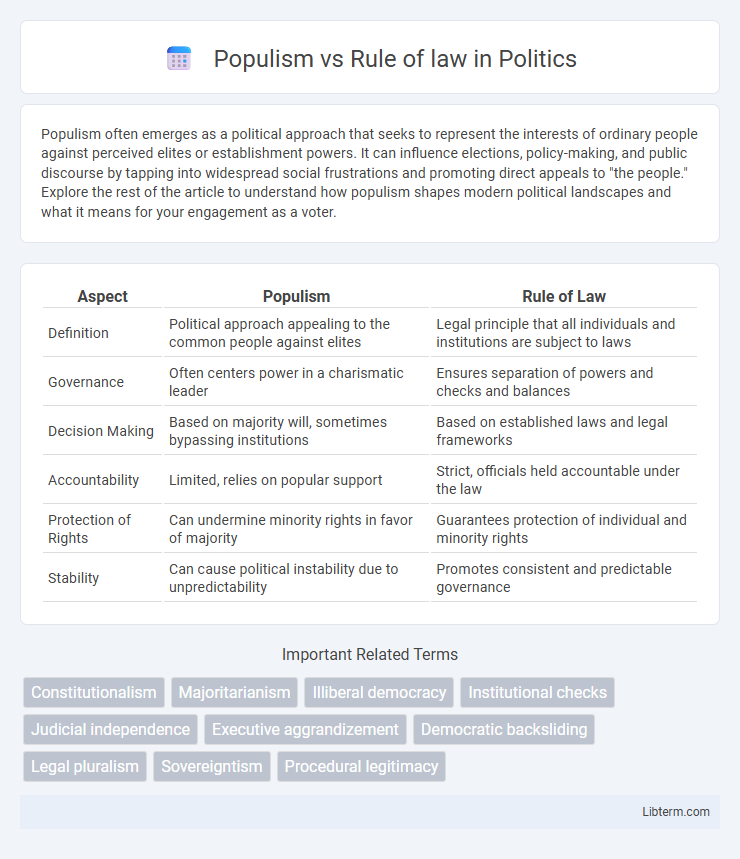
| Aspect | Populism | Rule of Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach appealing to the common people against elites | Legal principle that all individuals and institutions are subject to laws |
| Governance | Often centers power in a charismatic leader | Ensures separation of powers and checks and balances |
| Decision Making | Based on majority will, sometimes bypassing institutions | Based on established laws and legal frameworks |
| Accountability | Limited, relies on popular support | Strict, officials held accountable under the law |
| Protection of Rights | Can undermine minority rights in favor of majority | Guarantees protection of individual and minority rights |
| Stability | Can cause political instability due to unpredictability | Promotes consistent and predictable governance |
Defining Populism and the Rule of Law
Populism is a political approach that seeks to represent the interests of ordinary people, often by opposing established elites and institutions, emphasizing direct appeals to the public. The Rule of Law is a foundational legal principle that ensures all individuals and government entities are accountable to laws that are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated. Defining Populism and the Rule of Law highlights the tension between populist movements that may challenge institutional frameworks and the Rule of Law that maintains legal stability and protects democratic governance.
Historical Roots of Populism
Populism traces its historical roots to the late 19th century, notably with the People's Party in the United States and the Russian Narodnik movement, both emphasizing the struggle against elite dominance and advocating for the common people's rights. These early movements capitalized on widespread social and economic grievances, positioning themselves against established legal and political institutions associated with the ruling classes. The tension between populism and the rule of law arises from populism's often extra-legal or anti-establishment rhetoric, challenging established legal frameworks designed to ensure accountability and protect minority rights.
Core Principles of the Rule of Law
The core principles of the rule of law include the supremacy of law, equality before the law, accountability of government officials, and the protection of fundamental rights. Populism often challenges these principles by promoting majoritarian rule and undermining independent judiciary and legal institutions. Maintaining the rule of law ensures legal predictability, limits arbitrary power, and upholds democratic governance.
Populist Rhetoric: Threat or Reform?
Populist rhetoric often frames the political establishment as corrupt and disconnected, challenging traditional rule of law by prioritizing direct appeal to "the people" over institutional checks and balances. This approach can threaten legal norms and democratic stability by undermining the impartiality of courts and weakening constitutional constraints. However, some argue populist rhetoric acts as a catalyst for reform, exposing systemic failures and demanding accountability in governance.
Institutional Vulnerabilities Exploited by Populism
Populism exploits institutional vulnerabilities by undermining checks and balances designed to uphold the rule of law, often eroding judicial independence and weakening legislative oversight. Populist leaders capitalize on public distrust in formal institutions, manipulating legal frameworks to consolidate power and sideline opposition. This erosion of institutional integrity threatens democratic norms and allows for arbitrary governance, destabilizing the foundational principles of accountability and legality.
Case Studies: Populism Challenging Legal Systems
Populism challenges legal systems by undermining judicial independence and promoting majoritarian rule over constitutional safeguards, as seen in Hungary and Poland where governments have reshaped courts to consolidate power. In Brazil, populist rhetoric has fueled attacks on institutional checks, weakening the rule of law amid political polarization. These case studies reveal a trend of populist leaders leveraging legal reforms to erode democratic norms and institutional accountability.
Erosion of Checks and Balances
Populism often undermines the rule of law by eroding established checks and balances, weakening the independence of judicial and legislative institutions. This erosion allows populist leaders to consolidate power, bypass accountability mechanisms, and diminish the separation of powers essential for democratic governance. The resulting concentration of authority threatens legal stability and equitable enforcement of laws.
Public Trust in Law vs Populist Movements
Public trust in law is undermined by populist movements that challenge legal institutions and portray the judiciary as part of an elitist conspiracy. Research shows that when populist rhetoric delegitimizes the rule of law, citizens' confidence in fair legal processes declines sharply. Maintaining robust, transparent legal frameworks is essential to counteract populist narratives and preserve public trust in justice.
Safeguarding Democracy Against Populist Pressures
Safeguarding democracy against populist pressures requires reinforcing the rule of law as the foundation for accountable governance and protecting institutional checks and balances. Populism often undermines legal frameworks by promoting majoritarianism and disregarding minority rights, which threatens democratic stability. Strengthening judicial independence and ensuring transparency are essential steps to uphold democratic norms amidst populist challenges.
Pathways to Harmonize Popular Will and Legal Integrity
Balancing populism and the rule of law requires establishing robust institutional frameworks that translate popular will into legal norms without compromising judicial independence. Mechanisms such as participatory democracy, transparent legislative processes, and constitutional checks and balances ensure that public demands align with legal principles. Strengthening civic education and promoting inclusive dialogue foster a political culture where popular sovereignty and legal integrity coexist harmoniously.
Populism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com