A base voter consistently supports a particular political party or candidate, often demonstrating strong loyalty and high voter turnout. Understanding the motivations and behaviors of base voters is crucial for campaign strategies aiming to mobilize core support. Discover how base voters influence elections and what that means for your political engagement in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
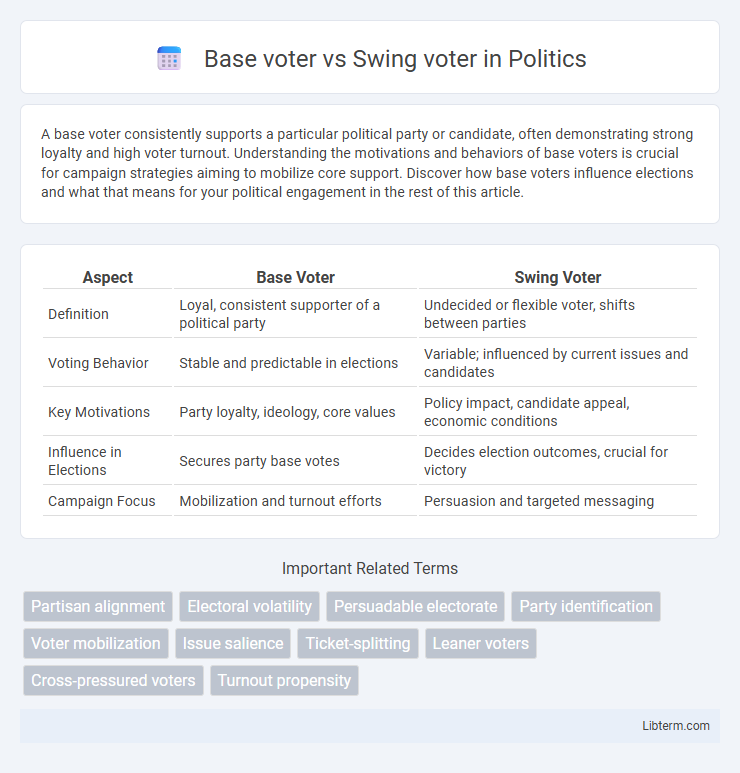
| Aspect | Base Voter | Swing Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loyal, consistent supporter of a political party | Undecided or flexible voter, shifts between parties |
| Voting Behavior | Stable and predictable in elections | Variable; influenced by current issues and candidates |
| Key Motivations | Party loyalty, ideology, core values | Policy impact, candidate appeal, economic conditions |
| Influence in Elections | Secures party base votes | Decides election outcomes, crucial for victory |
| Campaign Focus | Mobilization and turnout efforts | Persuasion and targeted messaging |
Understanding Base Voters: Core Supporters Defined
Base voters represent the core supporters of a political party, characterized by their consistent loyalty and high voter turnout across multiple election cycles. These individuals hold strong ideological commitments and prioritize party alignment over individual candidate appeal. Understanding base voters is crucial for campaign strategies, as energizing this group ensures a reliable foundation of electoral support.
Who Are Swing Voters? Key Characteristics
Swing voters are individuals who do not have a consistent allegiance to a single political party and can be persuaded to vote for different candidates in various elections. They often exhibit moderate political views, prioritize specific issues over party loyalty, and tend to be undecided until late in the election cycle. Their voting behavior is crucial in closely contested elections, making them a primary focus for targeted campaign strategies and voter outreach efforts.
Motivations Behind Base Voter Loyalty
Base voters exhibit strong party allegiance driven by ideological alignment and identity politics, often prioritizing core values such as economic policy, social justice, or national security. Their motivation stems from a deep sense of loyalty and belief that their party best represents their interests and worldview. This unwavering support contrasts with swing voters, who are more influenced by current issues and candidate appeal.
Swing Voters: Factors Influencing Their Decisions
Swing voters, a pivotal group in elections, are influenced by factors such as current economic conditions, candidate charisma, and specific policy proposals rather than party loyalty. Media exposure and social networks significantly shape their perceptions and voting intentions, making targeted campaign messaging crucial. Understanding demographic variables like age, education, and geographic location helps predict swing voter behavior and mobilize this flexible electorate.
Demographic Profiles: Base vs Swing Voters
Base voters typically consist of highly engaged individuals who strongly identify with a political party, often characterized by consistent voting patterns and strong ideological leanings. Demographically, base voters often include older adults, racial and ethnic minorities aligned with a party, and those with higher political interest or activism. Swing voters usually represent a more diverse demographic, including younger voters, independents, and individuals with moderate political views, making them less predictable and highly sought after in election campaigns.
Electoral Impact: Why Base Voters Matter
Base voters are crucial in elections because they consistently turn out to support their party regardless of the race's competitiveness, ensuring a reliable foundation of votes. Swing voters, while influential, often decide races in closely contested districts but can be unpredictable and less motivated to vote in non-competitive elections. Maintaining a strong base voter turnout provides candidates with essential electoral stability and a dependable margin to build upon in both local and national contests.
The Pivotal Role of Swing Voters in Elections
Swing voters play a crucial role in determining election outcomes by shifting their support between parties, often deciding tightly contested races. Unlike base voters, who consistently back a specific party, swing voters exhibit flexible political preferences that can be influenced by campaign strategies, current events, and candidate appeal. Understanding swing voter behavior is essential for campaigns aiming to target moderate and undecided electorates to secure a decisive victory.
Campaign Strategies for Mobilizing Base Voters
Campaign strategies for mobilizing base voters prioritize targeted outreach through personalized communication, emphasizing core party values, and leveraging grassroots organizations to increase voter engagement. Utilizing data analytics and micro-targeting enables campaigns to identify and galvanize loyal supporters effectively, boosting turnout rates among base demographics. Consistent messaging that reinforces party identity and policy priorities helps maintain enthusiasm and commitment throughout the election cycle.
Effective Tactics to Persuade Swing Voters
Targeted messaging that addresses specific concerns and values effectively persuades swing voters by resonating with their unique priorities. Personalized outreach, including direct communication through social media, phone calls, or canvassing, increases engagement and trust among swing voters. Utilizing data analytics to identify swing voter demographics and tailoring campaign messages accordingly enhances the likelihood of shifting their support.
The Future of Base and Swing Voter Dynamics
The future of base and swing voter dynamics will be shaped by increasing political polarization and demographic shifts, with base voters continuing to provide reliable support for parties while swing voters remain key targets for winning elections. Emerging technologies like data analytics and micro-targeting enhance campaigns' ability to tailor messages, potentially transforming how swing voters engage and decide. Understanding evolving voter priorities and the impact of social media is crucial for adapting strategies to sustain base loyalty and capture the changing swing voter landscape.
Base voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com