The National Congress serves as the legislative backbone of a country, responsible for drafting, debating, and enacting laws that shape the nation's policies and governance. Its members represent the diverse interests of the population, ensuring that different voices contribute to the decision-making process. Explore the complexities and power dynamics within the National Congress in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
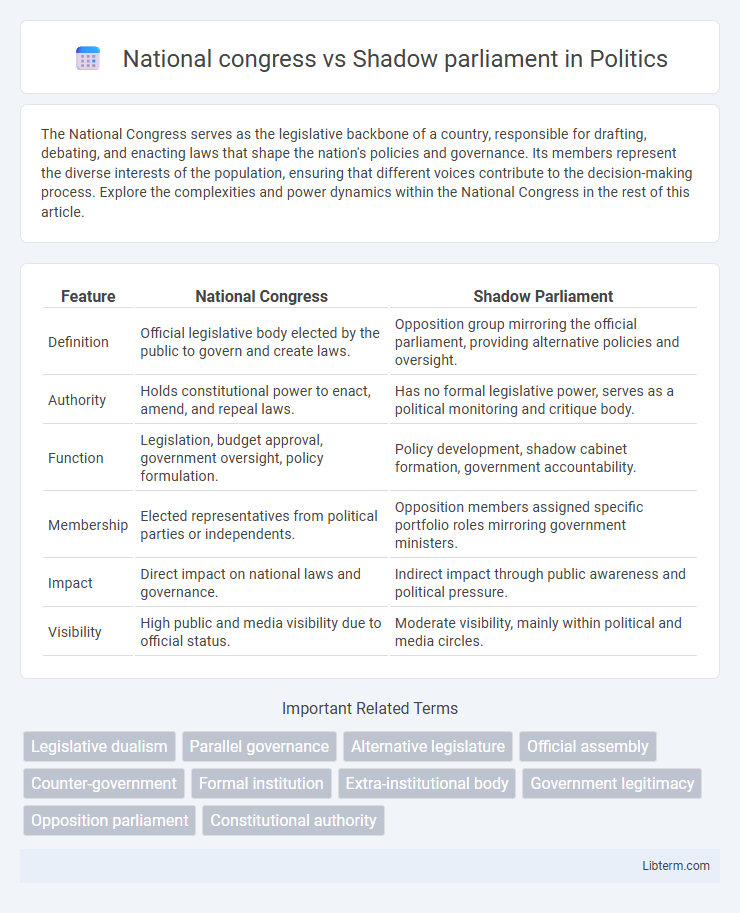
| Feature | National Congress | Shadow Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official legislative body elected by the public to govern and create laws. | Opposition group mirroring the official parliament, providing alternative policies and oversight. |
| Authority | Holds constitutional power to enact, amend, and repeal laws. | Has no formal legislative power, serves as a political monitoring and critique body. |
| Function | Legislation, budget approval, government oversight, policy formulation. | Policy development, shadow cabinet formation, government accountability. |
| Membership | Elected representatives from political parties or independents. | Opposition members assigned specific portfolio roles mirroring government ministers. |
| Impact | Direct impact on national laws and governance. | Indirect impact through public awareness and political pressure. |
| Visibility | High public and media visibility due to official status. | Moderate visibility, mainly within political and media circles. |
Introduction to National Congress and Shadow Parliament
The National Congress serves as the principal legislative body, responsible for enacting laws, representing citizens, and overseeing government functions within a democratic framework. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament functions as an alternative or unofficial assembly, often composed of opposition members who scrutinize government policies and propose alternative agendas. Both institutions play critical roles in ensuring political accountability and democratic participation.
Historical Background and Evolution
The National Congress originated in the late 19th century as a pivotal organization advocating for Indian independence from British colonial rule, evolving through key phases including the Non-Cooperation Movement and the Quit India Movement. The concept of a Shadow Parliament emerged in the mid-20th century as an institutional mechanism in parliamentary democracies, primarily in the United Kingdom, designed to provide an organized opposition reflecting alternative policies and governance strategies. Both institutions have evolved to shape political accountability and democratic engagement, with the National Congress transitioning from a liberation movement to a major political party and the Shadow Parliament institutionalizing the checks and balances within parliamentary systems.
Core Functions and Responsibilities
The National Congress serves as the supreme legislative authority responsible for enacting laws, approving the national budget, and overseeing the executive branch's activities. Conversely, the Shadow Parliament operates as an alternative or oppositional assembly, primarily tasked with scrutinizing government policies, proposing alternative legislation, and holding the ruling party accountable. Both bodies play crucial roles in governance; the National Congress exercises formal legislative power, while the Shadow Parliament enhances democratic accountability through oversight and critique.
Structure and Composition Compared
The National Congress typically comprises elected representatives from constituencies across the country, with a well-defined structure including a lower house (House of Representatives) and an upper house (Senate or Council of States) depending on the nation. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament is an informal or opposition-based body that mirrors the official parliament, composed mainly of opposition members who shadow corresponding government ministers to provide checks and critiques. While the National Congress operates with full legislative authority and formal procedures, the Shadow Parliament functions without legislative power, focusing on accountability and alternative policy proposals.
Decision-Making Processes
The National Congress operates as the supreme legislative body, where decision-making processes involve formal plenary sessions, voting by deputies, and structured committee reviews to enact laws and policies. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament functions as an opposition entity, conducting informal debates, policy critiques, and strategic planning to influence the official legislative agenda without formal legislative power. The efficiency of the National Congress lies in its constitutional authority, while the Shadow Parliament relies on persuasive tactics and public engagement to shape decision-making outcomes.
Legal Authority and Legitimacy
The National Congress holds formal legal authority as the constitutionally recognized legislative body with the power to enact laws and oversee government functions. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament operates symbolically without official legal status, serving primarily as an opposition platform to challenge and scrutinize government policies. The legitimacy of the National Congress is grounded in constitutional mandates and electoral processes, whereas the Shadow Parliament derives legitimacy mainly from political support and public advocacy.
Impact on Governance and Policy
The National Congress drives governance and policy through legally binding legislation, budget approvals, and executive oversight, directly shaping national priorities and public administration. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament influences governance by scrutinizing government actions, presenting alternative policies, and holding officials accountable, enhancing transparency and democratic debate. While the National Congress implements policy, the Shadow Parliament safeguards checks and balances, promoting more effective and responsive governance.
Relationship With the Public and Stakeholders
The National Congress maintains direct accountability to the public through elected representatives, ensuring transparency and responsiveness in legislative processes. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament engages stakeholders by scrutinizing government actions and proposing alternative policies, fostering informed public debate and political awareness. Both institutions play crucial roles in shaping public opinion and influencing democratic participation.
Key Differences and Similarities
The National Congress serves as the official legislative body responsible for creating and passing laws, while the Shadow Parliament functions as an opposition group that monitors and critiques government policies without legislative authority. Both entities involve elected representatives organized by political parties and engage in debates on national issues, reflecting democratic principles. Key differences include the formal legislative power held by the National Congress versus the advisory and oversight role of the Shadow Parliament.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The National Congress is increasingly integrating digital platforms to enhance legislative transparency and citizen participation, reflecting a global shift towards e-governance. Shadow parliaments are emerging as influential bodies in multiparty democracies by providing structured opposition and policy critique, leveraging social media for wider public engagement. Future trends suggest both institutions will collaborate more closely through hybrid political models, fostering dynamic checks and balances in governance.
National congress Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com