A government agency is an organization established by the government to implement specific functions, enforce laws, and provide public services. These agencies play a crucial role in maintaining order, regulating industries, and supporting community welfare. Discover how understanding government agencies can help you navigate public services more effectively in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
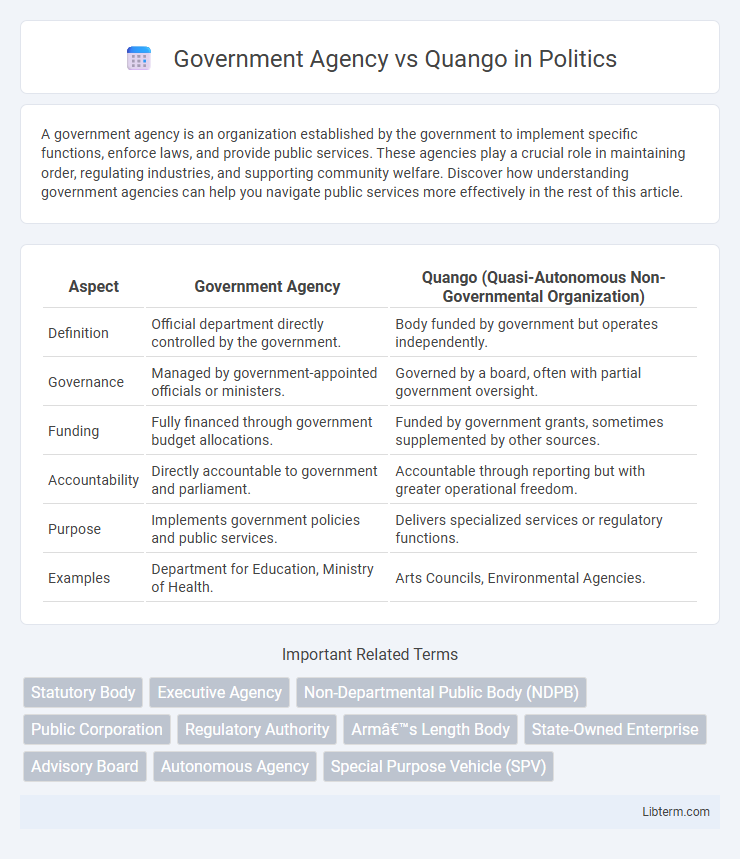
| Aspect | Government Agency | Quango (Quasi-Autonomous Non-Governmental Organization) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official department directly controlled by the government. | Body funded by government but operates independently. |
| Governance | Managed by government-appointed officials or ministers. | Governed by a board, often with partial government oversight. |
| Funding | Fully financed through government budget allocations. | Funded by government grants, sometimes supplemented by other sources. |
| Accountability | Directly accountable to government and parliament. | Accountable through reporting but with greater operational freedom. |
| Purpose | Implements government policies and public services. | Delivers specialized services or regulatory functions. |
| Examples | Department for Education, Ministry of Health. | Arts Councils, Environmental Agencies. |
Understanding Government Agencies: Definitions and Functions
Government agencies are public organizations established by legislation to perform specific administrative functions such as regulating industries, providing public services, or enforcing laws. Quangos, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations, operate with government funding and oversight but retain a degree of independence to manage public tasks like policy advisory or service delivery. Understanding the distinctions between government agencies and quangos is essential for grasping how public services are structured and governed in different administrative frameworks.
What Is a Quango? Key Characteristics Explained
A Quango, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization, operates independently from direct government control while receiving public funding to perform specific administrative, regulatory, or service functions. Key characteristics include a degree of operational autonomy, accountability to government departments, and membership appointed by the government, distinguishing it from a traditional government agency that is fully integrated within the public sector hierarchy. Quangos often manage specialized tasks such as public health oversight, cultural promotion, or economic regulation, balancing independent decision-making with government policy objectives.
Historical Evolution of Government Agencies and Quangos
Government agencies originated in the early 20th century as specialized bodies within the public sector, designed to execute government policies and deliver public services efficiently. Quangos (Quasi-Autonomous Non-Governmental Organizations) emerged in the mid-20th century as semi-independent entities, created to operate with greater flexibility and reduce direct political interference while still relying on government funding. The historical evolution of both reflects shifting government strategies to balance control, accountability, and operational efficiency in public administration.
Structural Differences: Government Agency vs Quango
Government agencies operate directly under government departments and are fully funded and controlled by the state, ensuring accountability to elected officials. Quangos, or quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations, function independently with varying degrees of government funding and oversight, allowing more operational flexibility though less direct political control. Structural differences include governance models, funding sources, and accountability mechanisms, with government agencies typically exhibiting stricter regulations and quangos enjoying greater autonomy in decision-making.
Accountability and Governance Comparison
Government agencies operate under direct government control with clear lines of accountability to elected officials and the public, ensuring transparent governance and adherence to statutory mandates. Quangos (quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations) function with greater independence, often managed by appointed boards, which can create blurred accountability and less direct political oversight. The governance structure of quangos allows operational flexibility but may reduce transparency and complicate public scrutiny compared to traditional government agencies.
Funding Sources: Public Funds, Autonomy, and Transparency
Government agencies receive funding directly from public budgets, ensuring strict accountability and transparency in their financial operations, while quangos (quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations) often combine public funds with private or grant-based sources, granting them greater financial autonomy but sometimes reducing transparency. Public agencies operate under rigorous government oversight, which mandates detailed reporting and adherence to public sector regulations, whereas quangos enjoy more operational independence, allowing flexibility in policy implementation but often leading to varied transparency standards. The funding model impacts how each entity manages public resources, balances autonomy with accountability, and engages stakeholders in fiscal governance.
Roles in Policy Implementation and Public Services
Government agencies directly implement policies and deliver public services under the authority of central or local government, ensuring compliance with legislation and administrative regulations. Quangos (quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations) operate at arm's length from government, tasked with specific functions like regulatory oversight or service delivery, often allowing for specialized expertise and operational independence. Both structures contribute to effective governance, with agencies focused on executing policy mandates and quangos providing flexible, expert-driven support in public administration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Government Agencies
Government agencies benefit from direct funding and oversight by the central government, ensuring accountability and alignment with national policy objectives. However, they can face bureaucratic inefficiencies and limited flexibility in responding to local needs or rapid changes. Unlike quangos, government agencies often have less operational independence, which may restrict innovation but enhances transparency in public service delivery.
Pros and Cons of Quangos in Modern Governance
Quangos (Quasi-Autonomous Non-Governmental Organizations) offer flexibility and specialized expertise, enabling more efficient delivery of public services compared to traditional government agencies. However, their semi-independent status can lead to reduced accountability, potential overlap with other entities, and challenges in maintaining transparency. Despite these drawbacks, quangos often enhance innovation and responsiveness in modern governance by operating outside bureaucratic constraints.
Choosing the Right Model: Implications for Public Administration
Selecting between a government agency and a Quango shapes public administration efficiency and accountability, with government agencies providing direct control and funding from the central government, ensuring clear hierarchical oversight. Quangos offer operational flexibility and specialized expertise while often operating at arm's length, balancing autonomy with public accountability through appointed boards. Understanding the specific policy goals, required autonomy level, and stakeholder engagement needs is critical for determining the optimal organizational model for effective service delivery.
Government Agency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com