Abstention occurs when individuals choose not to participate in voting or decision-making processes, impacting election outcomes and organizational choices. Understanding the causes and consequences of abstention is vital for grasping democratic engagement and accountability. Explore this article to learn how abstention affects your influence and the broader political landscape.
Table of Comparison
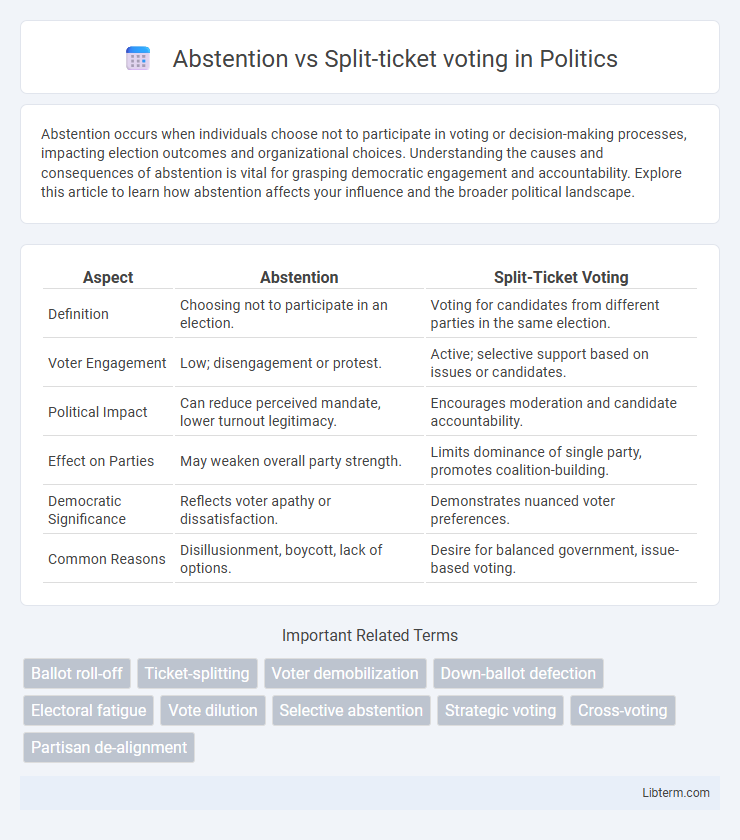
| Aspect | Abstention | Split-Ticket Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Choosing not to participate in an election. | Voting for candidates from different parties in the same election. |
| Voter Engagement | Low; disengagement or protest. | Active; selective support based on issues or candidates. |
| Political Impact | Can reduce perceived mandate, lower turnout legitimacy. | Encourages moderation and candidate accountability. |
| Effect on Parties | May weaken overall party strength. | Limits dominance of single party, promotes coalition-building. |
| Democratic Significance | Reflects voter apathy or dissatisfaction. | Demonstrates nuanced voter preferences. |
| Common Reasons | Disillusionment, boycott, lack of options. | Desire for balanced government, issue-based voting. |
Understanding Abstention: Definition and Implications
Abstention occurs when eligible voters choose not to participate in an election, reflecting disengagement or dissatisfaction with candidates or the political process. This behavior can significantly influence election outcomes by lowering voter turnout and skewing perceived public support. Understanding abstention helps reveal underlying social and political factors that affect democratic participation and legitimacy.
What is Split-Ticket Voting? An Overview
Split-ticket voting occurs when voters select candidates from different political parties for different offices within the same election, reflecting a preference for individual candidates over party loyalty. This voting behavior can influence election outcomes by weakening party dominance and encouraging more moderate or mixed political representation. Understanding split-ticket voting helps analyze voter behavior patterns and the impact on legislative balance and policymaking.
Historical Trends: Abstention Rates vs Split-Ticket Voting
Historical trends reveal that abstention rates often increase during elections with highly polarized candidates, reflecting voter disengagement or dissatisfaction, while split-ticket voting peaks in periods of moderate political competition, indicating voter preference for balancing power within government. Data from U.S. midterm elections shows abstention rates averaged around 40% in the late 20th century, whereas split-ticket voting surged in the 1970s and 1980s before declining in recent decades due to increasing party polarization. These patterns suggest a correlation between voter turnout dynamics and the prevailing political climate, where high polarization discourages participation and reduces cross-party voting.
Key Factors Influencing Voter Abstention
Voter abstention is influenced by factors such as political disillusionment, lack of trust in candidates or parties, and limited access to voting resources. Socioeconomic status, education level, and negative past experiences with the electoral process often discourage participation. In contrast, split-ticket voting typically reflects voter desire for balanced representation rather than outright disengagement.
Why Voters Choose Split-Ticket Voting
Voters choose split-ticket voting to express nuanced political preferences that reflect their approval of candidates or policies across party lines, rather than strict party loyalty. This behavior often indicates a desire for balanced governance, where voters support a mix of ideologies to promote checks and balances in legislative bodies. Split-ticket voting tends to increase in electorates seeking moderation, especially during times of political polarization or dissatisfaction with dominant party agendas.
Impact on Election Outcomes: Abstention vs Split-Ticket Voting
Abstention reduces voter turnout, often skewing election outcomes by amplifying the influence of highly motivated voting blocs, potentially leading to less representative results. Split-ticket voting increases electoral competitiveness by allowing voters to select candidates from different parties for various offices, which can dilute the dominance of a single party and foster a more balanced distribution of power. Both behaviors affect election dynamics by shaping party strategies, campaign focus, and ultimately the composition of elected bodies.
Sociopolitical Drivers Behind Each Voting Behavior
Abstention is often driven by political alienation, distrust in government institutions, or a belief that individual votes do not influence electoral outcomes, reflecting deeper issues of political disengagement and social inequality. Split-ticket voting arises from a desire for balanced governance, ideological moderation, or strategic voting, revealing a nuanced engagement with party platforms and candidates rather than outright rejection of the political system. Sociopolitical drivers like media influence, education level, and socioeconomic status play critical roles in shaping these distinct voting behaviors.
Consequences for Political Parties and Candidates
Abstention reduces voter turnout, undermining the legitimacy and mandate of political parties and candidates while skewing electoral results toward highly mobilized bases. Split-ticket voting fragments party support by encouraging voters to select candidates from different parties, complicating party cohesion and diluting the strength of unified party platforms. Both phenomena challenge traditional party strategies, forcing candidates to appeal to broader or more diverse electorates to secure electoral success.
Strategies to Address Abstention and Split-Ticket Voting
Implement targeted voter education campaigns emphasizing the impact of both abstention and split-ticket voting on election outcomes to foster informed decision-making. Employ tailored outreach strategies, such as community engagement and personalized communication, to address the reasons behind abstention and encourage consistent party-line voting where relevant. Leverage data analytics to identify demographics prone to abstention and split-ticket voting, enabling focused interventions that improve voter participation and party loyalty.
Future Outlook: The Evolving Landscape of Voter Participation
Future trends in voter participation indicate a nuanced shift between abstention and split-ticket voting, influenced by increasing political polarization and voter disengagement. Technological advancements and data-driven campaigns may encourage more informed decision-making, potentially reducing abstention by providing personalized voter outreach. Emerging electoral reforms, such as ranked-choice voting, could further reshape the landscape by promoting split-ticket voting as a strategy for nuanced expression of voter preferences.
Abstention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com