A party member plays a crucial role in shaping a political organization's direction, contributing ideas, and supporting campaigns to drive collective goals. Engaging actively within the party helps strengthen your influence and promotes democratic participation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how becoming an effective party member can impact both your community and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
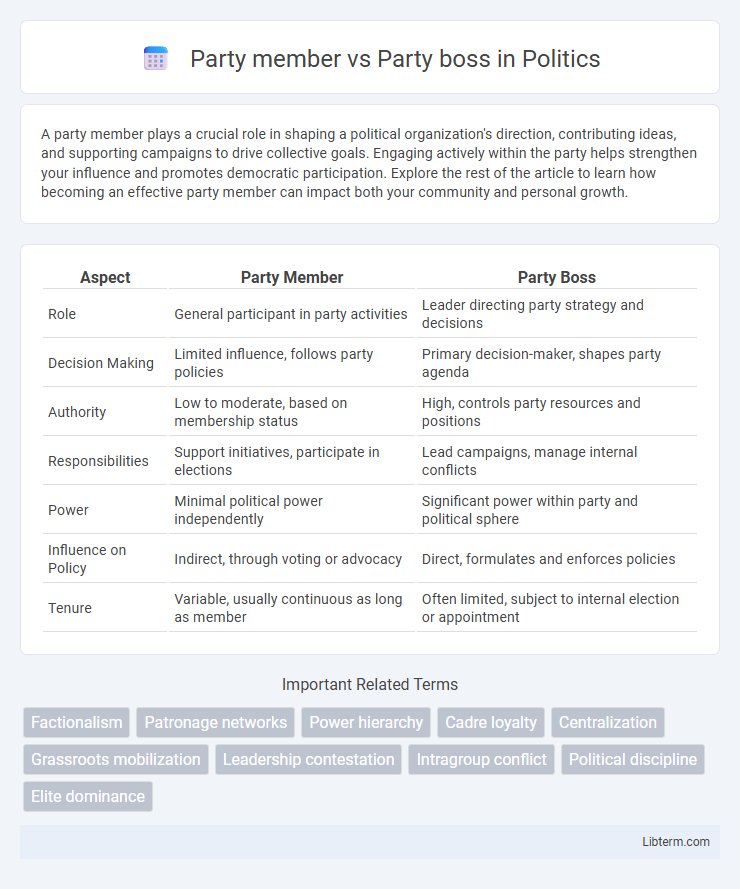
| Aspect | Party Member | Party Boss |
|---|---|---|
| Role | General participant in party activities | Leader directing party strategy and decisions |
| Decision Making | Limited influence, follows party policies | Primary decision-maker, shapes party agenda |
| Authority | Low to moderate, based on membership status | High, controls party resources and positions |
| Responsibilities | Support initiatives, participate in elections | Lead campaigns, manage internal conflicts |
| Power | Minimal political power independently | Significant power within party and political sphere |
| Influence on Policy | Indirect, through voting or advocacy | Direct, formulates and enforces policies |
| Tenure | Variable, usually continuous as long as member | Often limited, subject to internal election or appointment |
Introduction to Party Member vs Party Boss
Party member refers to an individual officially enrolled in a political party, responsible for adhering to party policies and contributing to organizational goals. Party boss denotes a senior leader who wields significant influence and authority over the party's direction, decision-making, and membership management. The distinction between party members and party bosses highlights differing levels of power, responsibility, and control within political party hierarchies.
Defining the Party Member
A party member is an individual formally affiliated with a political party, committed to upholding its principles, policies, and organizational discipline. Defined by active participation in party activities and adherence to internal regulations, party members serve as the foundational support base for the party's ideological and operational goals. Their roles include voting in internal elections, promoting party agendas, and contributing to grassroots mobilization efforts essential for sustaining party influence.
Understanding the Role of the Party Boss
The Party boss holds centralized authority within the political hierarchy, directing strategic decisions, managing party discipline, and overseeing organizational effectiveness. Unlike rank-and-file party members who primarily engage in grassroots activities and support party initiatives, the Party boss exerts significant influence over candidate selection, policy formation, and resource allocation. Understanding the role of the Party boss reveals how power dynamics and leadership shape party cohesion, political outcomes, and governance structures.
Historical Evolution of Party Leadership
The historical evolution of party leadership reveals that party members initially held decentralized influence during early political movements, while the rise of party bosses marked a shift towards centralized control and hierarchical authority. Party bosses often emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as powerful figures who managed political machines, leveraging patronage systems to maintain loyalty and enforce party discipline. Over time, reforms and democratization efforts reduced the dominance of party bosses, promoting greater internal party democracy and the empowerment of rank-and-file party members.
Key Responsibilities: Member vs Boss
Party members primarily engage in grassroots activities, supporting policy implementation and mobilizing community participation, while adhering to party discipline and ideology. In contrast, party bosses hold strategic leadership roles that include setting organizational agendas, making key decisions, and directing campaign strategies to influence broader political outcomes. The distinction in responsibilities highlights members' operational support functions versus bosses' authoritative control and policy direction within the party hierarchy.
Influence on Decision-Making Processes
Party members contribute to decision-making by voicing opinions and supporting policies that align with the party's platform, often influencing local or grassroots initiatives. Party bosses hold significant authority, directing strategic decisions, resource allocation, and candidate endorsements, which shape the overall party agenda and political outcomes. The balance between party members' democratic input and party bosses' centralized control critically impacts the efficiency and inclusivity of policy formulation.
Power Dynamics Within Political Parties
Party members primarily influence political parties through grassroots support, voting, and local mobilization, shaping party ideology and candidate selection. Party bosses hold centralized power, controlling patronage, strategic decisions, and key nominations, thereby consolidating authority within the party hierarchy. The power dynamics reflect a tension between bottom-up participation and top-down control, impacting party cohesion and policy direction.
Case Studies: Notable Party Members and Bosses
Notable party members like Nelson Mandela demonstrated grassroots activism and mobilization, significantly influencing party ideology and public support. In contrast, party bosses such as Richard J. Daley wielded centralized control over political machinery, directing candidate selections and patronage networks to consolidate power. Case studies reveal party members often drive policy initiatives, while party bosses maintain structural dominance within political organizations.
Challenges and Conflicts Between Roles
Party members often face challenges balancing grassroots expectations with directives from party leadership, leading to tensions in loyalty and accountability. Party bosses encounter conflicts managing diverse member interests while maintaining centralized control and enforcing party discipline. These role-based conflicts can result in power struggles, communication breakdowns, and hindered organizational cohesion.
The Future of Party Structures and Leadership
The future of party structures and leadership emphasizes a balance between the grassroots influence of party members and the strategic direction set by party bosses. Evolving political landscapes demand adaptive leadership models where party bosses enable participatory decision-making while maintaining organizational coherence. Technological advancements and increased voter engagement are reshaping roles, enhancing transparency, and decentralizing traditional power dynamics within parties.
Party member Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com