An independent candidate runs for office without the backing of a political party, emphasizing their commitment to personal principles and direct accountability to voters. They often appeal to those seeking alternatives beyond traditional party lines, highlighting unique platforms and individual leadership qualities. Explore the article to understand how independent candidates influence modern elections and what this means for your political choices.
Table of Comparison
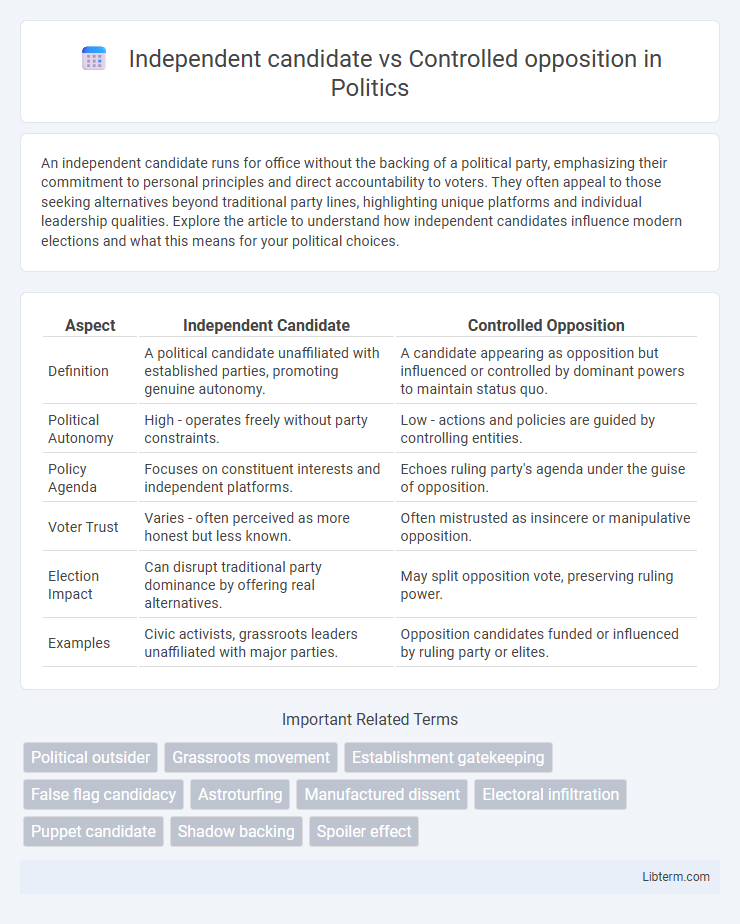
| Aspect | Independent Candidate | Controlled Opposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A political candidate unaffiliated with established parties, promoting genuine autonomy. | A candidate appearing as opposition but influenced or controlled by dominant powers to maintain status quo. |
| Political Autonomy | High - operates freely without party constraints. | Low - actions and policies are guided by controlling entities. |
| Policy Agenda | Focuses on constituent interests and independent platforms. | Echoes ruling party's agenda under the guise of opposition. |
| Voter Trust | Varies - often perceived as more honest but less known. | Often mistrusted as insincere or manipulative opposition. |
| Election Impact | Can disrupt traditional party dominance by offering real alternatives. | May split opposition vote, preserving ruling power. |
| Examples | Civic activists, grassroots leaders unaffiliated with major parties. | Opposition candidates funded or influenced by ruling party or elites. |
Introduction: Defining Independent Candidates and Controlled Opposition
Independent candidates run for office without formal affiliation to established political parties, emphasizing autonomy and grassroots support in their campaigns. Controlled opposition refers to individuals or groups presented as challengers but are covertly influenced or managed by dominant political entities to maintain power dynamics. Distinguishing between genuine independent candidates and controlled opposition is crucial for understanding electoral integrity and democratic representation.
Historical Context of Political Independence
Historical political independence often emerged from grassroots movements seeking representation outside established party systems, contrasting with controlled opposition designed to simulate dissent while maintaining existing power structures. Independent candidates frequently gained traction in periods of social unrest or political realignment, exemplified by figures like Bernie Sanders and Ross Perot, who challenged mainstream party dominance. Controlled opposition, historically seen in authoritarian regimes or manipulated democracies, serves to fragment opposition votes and legitimize the ruling party without ceding actual control.
Key Characteristics of Independent Candidates
Independent candidates exhibit autonomy from established political parties, emphasizing personalized platforms tailored to local or specific issues. Their campaign financing typically relies on grassroots support rather than party funds, enhancing transparency and reducing external influence. Voter appeal often centers on the promise of unbiased decision-making and direct accountability to constituents rather than party agendas.
Identifying Controlled Opposition: Red Flags and Tactics
Controlled opposition often uses scripted narratives that subtly reinforce the ruling party's agenda while appearing to challenge the status quo. Red flags include sudden shifts in messaging, unexplained funding sources, and consistent failure to gain substantial support despite high visibility. Independent candidates maintain authentic grassroots connections and transparent funding, contrasting with controlled opposition's reliance on astroturf campaigns and coordinated disinformation tactics.
Public Perception: Trust and Skepticism
Public perception of independent candidates often centers on trust due to their perceived autonomy from established political parties, making them appear as genuine alternatives. Controlled opposition, however, faces skepticism as the public suspects these candidates may be strategically positioned by dominant powers to maintain the status quo. This dynamic significantly influences voter confidence and election outcomes.
Impact on Democracy and Voter Choice
Independent candidates enhance democracy by providing voters with genuine alternatives outside established party systems, increasing political competition and voter engagement. Controlled opposition, often orchestrated by dominant parties, undermines democratic integrity by limiting authentic choice and manipulating electoral outcomes. The presence of true independent candidates strengthens voter sovereignty, whereas controlled opposition compromises accountability and transparency in the political process.
Media Representation and Narrative Control
Independent candidates often struggle to gain equitable media representation as mainstream outlets may prioritize coverage of established political parties, limiting their exposure and influencing public perception. Controlled opposition is frequently portrayed favorably or within a predetermined narrative framework, which serves to reinforce existing power structures by shaping audience understanding in alignment with dominant political agendas. Media conglomerates and political interests synergize to craft narratives that marginalize genuine independent voices while amplifying those that maintain the status quo.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples and Outcomes
Analyzing the 2016 U.S. presidential election reveals how independent candidate Evan McMullin attracted disaffected voters yet lacked institutional support compared to controlled opposition campaigns designed to split votes deliberately. In Venezuela, Henrique Capriles' opposition candidacies often faced accusations of being controlled opposition, potentially limiting dissent while maintaining regime stability. These case studies demonstrate that independent candidates face significant systemic barriers, whereas controlled opposition may serve to legitimize existing power structures under the guise of democratic competition.
Challenges Faced by True Independents
True independent candidates face significant challenges including limited access to major party funding, restricted media coverage, and systemic barriers in ballot access laws. These obstacles hinder their ability to compete effectively against controlled opposition, who often benefit from established political networks and resources. Consequently, genuine independents struggle to gain visibility and voter trust in a political landscape dominated by party-affiliated candidates.
Conclusion: Navigating the Political Landscape
Independent candidates offer fresh perspectives unbound by party agendas, providing voters with genuine alternatives in the political landscape. Controlled opposition, however, often serves to maintain the status quo by creating the illusion of choice while safeguarding entrenched power structures. Voters must critically evaluate candidates' affiliations and actions to discern authenticity and make informed decisions.
Independent candidate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com