Establishment support plays a crucial role in ensuring that new businesses have access to the necessary resources, funding, and guidance for sustainable growth. By leveraging expert advice and financial assistance, you can navigate early challenges and build a strong foundation for your enterprise. Discover how establishment support programs can transform your business journey by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
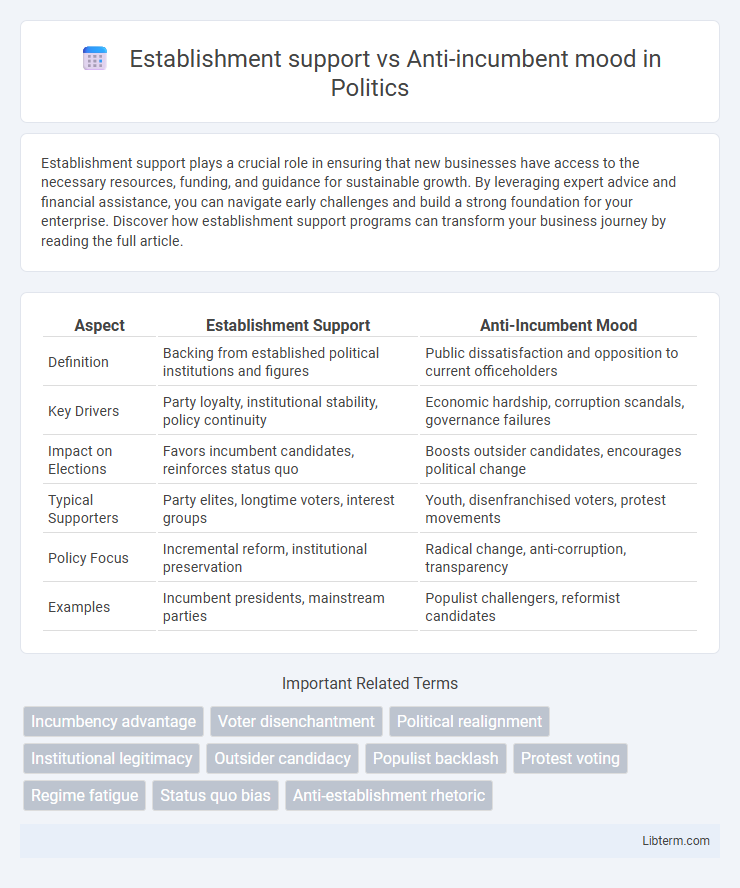
| Aspect | Establishment Support | Anti-Incumbent Mood |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Backing from established political institutions and figures | Public dissatisfaction and opposition to current officeholders |
| Key Drivers | Party loyalty, institutional stability, policy continuity | Economic hardship, corruption scandals, governance failures |
| Impact on Elections | Favors incumbent candidates, reinforces status quo | Boosts outsider candidates, encourages political change |
| Typical Supporters | Party elites, longtime voters, interest groups | Youth, disenfranchised voters, protest movements |
| Policy Focus | Incremental reform, institutional preservation | Radical change, anti-corruption, transparency |
| Examples | Incumbent presidents, mainstream parties | Populist challengers, reformist candidates |
Understanding Establishment Support in Politics
Establishment support in politics refers to backing from entrenched political parties, key interest groups, and influential figures who have historically maintained power and policy continuity. This support often provides candidates with critical resources, extensive networks, and institutional legitimacy, facilitating campaign strategies and media access. Understanding establishment support requires analyzing the mechanisms through which political insiders influence candidate viability and policy platforms amid voter sentiments leaning toward anti-incumbent moods.
The Rise of Anti-Incumbent Sentiment
The rise of anti-incumbent sentiment reflects growing public dissatisfaction with established political elites and traditional parties, driven by perceptions of corruption, inefficiency, and unresponsiveness. Establishment support often diminishes as voters seek alternative candidates promising reform, transparency, and accountability. This shift influences election outcomes globally, empowering outsider movements and reshaping political landscapes.
Factors Fueling Pro-Establishment Loyalty
Factors fueling pro-establishment loyalty include economic stability, effective governance, and perceived competence in crisis management, which reinforce trust in incumbents. Institutional benefits such as public services and social programs create tangible incentives for continued support. Media portrayal and elite endorsements further consolidate favorable perceptions, countering the anti-incumbent mood driven by dissatisfaction and desire for change.
Drivers Behind Anti-Incumbent Movements
Economic disparities, corruption scandals, and unmet public expectations drive anti-incumbent movements by eroding trust in established political institutions. Social media amplification and rising youth activism also fuel dissatisfaction, accelerating demands for political change. Weak establishment support and ineffective governance further intensify the public's desire for alternative leadership.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Establishment support often provides candidates with critical access to funding, organizational resources, and media exposure, significantly boosting their electoral prospects. Conversely, an anti-incumbent mood can undermine this advantage by favoring challengers who campaign on change and reform, disrupting traditional power structures. The interplay of these forces shapes election outcomes, where strong establishment backing may be insufficient if public sentiment overwhelmingly rejects the status quo.
Media Influence on Public Perception
Media influence significantly shapes public perception by amplifying establishment support or fueling anti-incumbent sentiment through framing and agenda-setting techniques. Positive media coverage enhances credibility and trust in establishment figures, while critical or negative portrayals increase skepticism and dissatisfaction among audiences. Social media algorithms and echo chambers further intensify these effects by targeting content that either reinforces establishment authority or mobilizes anti-incumbent mood.
Case Studies: Shifts Between Support and Opposition
Case studies reveal dynamic shifts between establishment support and anti-incumbent moods, highlighting electoral volatility and public sentiment changes. In countries like Italy and Brazil, fluctuating voter alignment reflects reactions to corruption scandals and economic instability, causing drastic swings from establishment backing to populist opposition. Analyzing these shifts underscores the impact of political trust erosion and mobilization strategies on democratic resilience and policy continuity.
Social Media’s Role in Shaping Attitudes
Social media platforms play a crucial role in amplifying anti-incumbent sentiment by facilitating rapid dissemination of critiques against establishment figures. Algorithms prioritize engaging, often polarizing content, which intensifies public scrutiny and skepticism toward political incumbents. This dynamic reshapes voter attitudes by creating echo chambers that bolster opposition movements and challenge traditional establishment support.
Policy Implications of Changing Political Moods
Shifts from establishment support to an anti-incumbent mood significantly influence policy priorities by encouraging governments to adopt populist or reform-oriented agendas that challenge the status quo. These changing political moods often lead to the implementation of more transparent, accountable governance structures and increased responsiveness to public demands. Policymakers must anticipate volatility in electoral support and design flexible, inclusive policies that address widespread dissatisfaction without undermining institutional stability.
Future Trends in Political Support and Opposition
Establishment support remains crucial for resource mobilization and policy implementation, yet the rising anti-incumbent mood, driven by widespread voter dissatisfaction and demand for systemic change, challenges traditional power structures. Future trends indicate an increasing polarization where grassroots movements and outsider candidates gain significant traction, leveraging social media and data analytics to mobilize support. Political landscapes will likely see intensified competition between institutional legitimacy and populist appeals, reshaping electoral dynamics and governance frameworks worldwide.
Establishment support Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com