Spin doctoring manipulates information to influence public perception and shape opinions in favor of a particular agenda or individual. This practice often involves selectively presenting facts or using persuasive language to sway audiences while minimizing negative aspects. Discover how spin doctoring affects media and politics and what you can do to recognize it in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
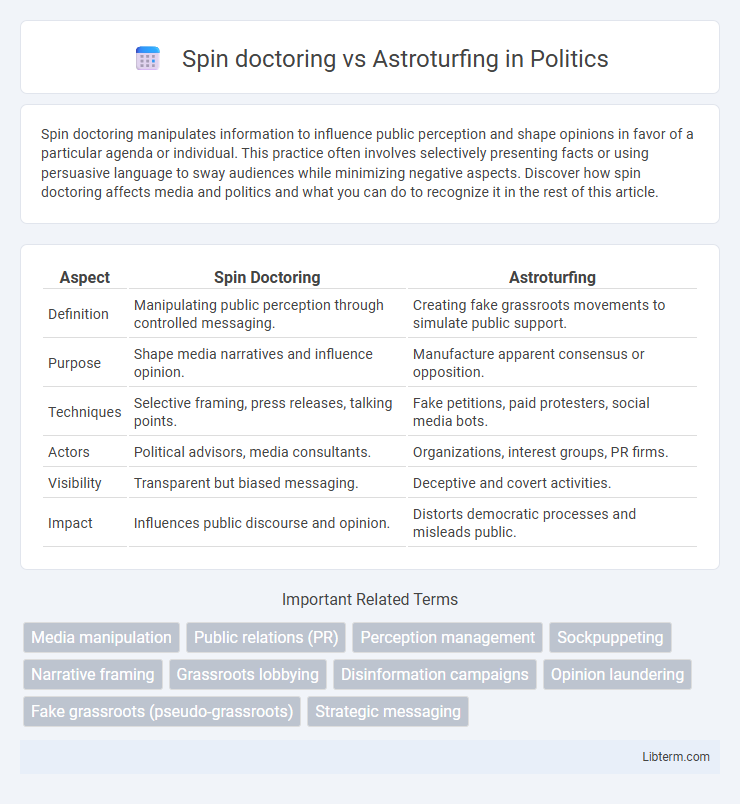
| Aspect | Spin Doctoring | Astroturfing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulating public perception through controlled messaging. | Creating fake grassroots movements to simulate public support. |
| Purpose | Shape media narratives and influence opinion. | Manufacture apparent consensus or opposition. |
| Techniques | Selective framing, press releases, talking points. | Fake petitions, paid protesters, social media bots. |
| Actors | Political advisors, media consultants. | Organizations, interest groups, PR firms. |
| Visibility | Transparent but biased messaging. | Deceptive and covert activities. |
| Impact | Influences public discourse and opinion. | Distorts democratic processes and misleads public. |
Understanding Spin Doctoring: Definition and Origins
Spin doctoring refers to the strategic crafting and presentation of information by public relations experts to influence public perception, often by highlighting positive aspects while minimizing negatives. Originating in the political arena during the late 20th century, spin doctors aim to shape media narratives and public opinion to benefit politicians or organizations. This practice involves controlled messaging, selective disclosure, and persuasive communication techniques to manage crises and enhance reputations.
Decoding Astroturfing: Meaning and Evolution
Astroturfing refers to the deceptive practice of creating fake grassroots movements to manipulate public opinion, often orchestrated by corporations or political groups to simulate widespread support. Its evolution has intensified with digital platforms, where coordinated efforts disguise paid or biased endorsements as genuine public sentiment, complicating transparency in media and politics. Understanding astroturfing's role is crucial for identifying misleading campaigns and preserving authentic public discourse.
Key Differences Between Spin Doctoring and Astroturfing
Spin doctoring involves strategically shaping public perception by framing information positively through media and communication channels, while astroturfing creates a deceptive appearance of grassroots support using fake or orchestrated campaigns. The key difference lies in transparency: spin doctoring openly engages with media narratives, whereas astroturfing conceals the true source of support to manipulate public opinion covertly. Both practices influence public discourse, but astroturfing undermines democratic processes by fabricating citizen involvement.
Tactics Used in Spin Doctoring
Spin doctoring employs tactics such as selective storytelling, strategic framing, and controlled media releases to shape public perception and influence opinions. Techniques include emphasizing positive aspects, downplaying negatives, and using persuasive language to steer narratives in favor of clients or causes. This approach often involves preparing spokespersons for interviews and orchestrating events that generate favorable publicity without overtly manipulating grassroots authenticity seen in astroturfing.
Common Techniques of Astroturfing Campaigns
Astroturfing campaigns commonly employ deceptive tactics such as fake grassroots support through fabricated online reviews, impersonation of genuine activists, and coordinated posting of misleading comments on social media platforms to manipulate public opinion. These efforts often involve the use of bots and paid influencers to create an illusion of widespread consensus, masking the true source behind the messaging. Unlike spin doctoring, which mainly reframes existing information, astroturfing fabricates authentic-seeming mass movements to covertly influence political or commercial agendas.
Impact on Public Opinion and Democracy
Spin doctoring shapes public opinion by selectively framing information to favor specific political agendas, often manipulating perceptions without outright deception, which can subtly undermine informed democratic decision-making. Astroturfing, involving orchestrated fake grassroots campaigns, deliberately deceives the public by simulating widespread support or opposition, eroding trust in genuine civic engagement and distorting democratic processes. Both tactics compromise transparency and accountability, weakening the foundation of democracy by skewing authentic representation and diminishing citizens' ability to make informed choices.
Real-World Examples: Spin Doctoring vs. Astroturfing
Spin doctoring was notably employed during the 1992 U.S. presidential campaign when political consultants shaped public perception despite scandals, while astroturfing surfaced prominently in the 2010 Citizens United debate, where corporate-funded groups created fake grassroots campaigns to influence voter opinion. The Volkswagen emissions scandal highlighted spin doctoring as the company managed public narrative to downplay the crisis, contrasting with astroturfing tactics used by fossil fuel industries to fabricate citizen opposition to environmental regulations. These examples illustrate how spin doctoring manipulates media narratives directly, whereas astroturfing fabricates deceptive, grassroots-like support to sway public and political outcomes.
Ethical Implications in Media and Politics
Spin doctoring involves strategic communication to shape public perception by selectively presenting information, often blurring truth and bias, raising ethical concerns about manipulation and transparency in media and politics. Astroturfing fabricates grassroots support through deceptive means, undermining genuine public opinion and eroding trust in democratic processes. Both practices challenge ethical standards by prioritizing influence over honesty, compromising informed decision-making and accountability.
How to Spot Spin Doctoring and Astroturfing
Spin doctoring manipulates public perception through selective framing and biased information, often identifiable by exaggerated claims and inconsistent facts. Astroturfing mimics grassroots movements but reveals itself through orchestrated social media activity, suspiciously uniform messaging, and lack of genuine community engagement. Spotting these tactics requires scrutinizing source credibility, checking for transparent funding, and analyzing message patterns for artificial coordination.
Combating Misinformation: Transparency and Accountability
Spin doctoring manipulates information to shape public perception, often obscuring facts, while astroturfing fabricates grassroots support to deceive audiences about genuine public opinion. Combating misinformation requires transparency from organizations by clearly disclosing sources and intentions, paired with robust accountability mechanisms to identify and penalize deceptive practices. Enhanced media literacy and real-time fact-checking serve as critical tools to expose spin and astroturfing, driving a more informed and truthful public discourse.
Spin doctoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com