A referendum allows citizens to directly participate in the democratic process by voting on specific laws or policies. This mechanism empowers Your voice to influence major decisions without relying solely on elected representatives. Discover more about how referendums shape governance and impact society in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
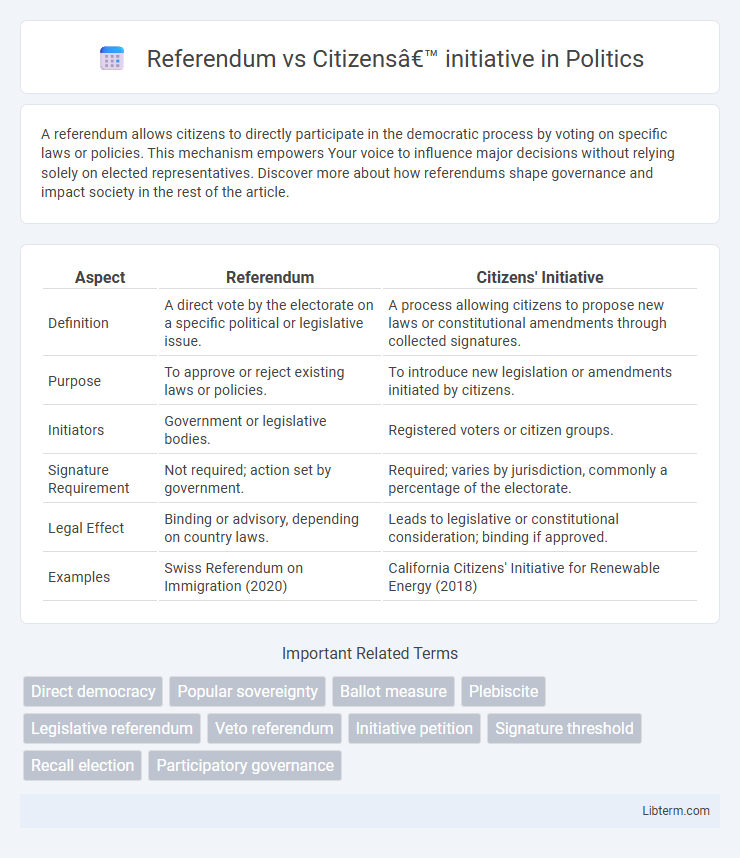
| Aspect | Referendum | Citizens' Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A direct vote by the electorate on a specific political or legislative issue. | A process allowing citizens to propose new laws or constitutional amendments through collected signatures. |
| Purpose | To approve or reject existing laws or policies. | To introduce new legislation or amendments initiated by citizens. |
| Initiators | Government or legislative bodies. | Registered voters or citizen groups. |
| Signature Requirement | Not required; action set by government. | Required; varies by jurisdiction, commonly a percentage of the electorate. |
| Legal Effect | Binding or advisory, depending on country laws. | Leads to legislative or constitutional consideration; binding if approved. |
| Examples | Swiss Referendum on Immigration (2020) | California Citizens' Initiative for Renewable Energy (2018) |
Introduction to Direct Democracy Mechanisms
Referendums and citizens' initiatives are essential components of direct democracy, allowing voters to influence legislation and policy decisions directly. Referendums typically involve a government-initiated vote on specific laws or constitutional changes, while citizens' initiatives enable the public to propose new laws or amendments by gathering a required number of signatures. Both mechanisms enhance democratic participation by giving citizens a direct voice in the legislative process outside of regular elections.
Defining Referendum: Overview and Types
A referendum is a direct democratic process allowing citizens to vote on specific legislative or constitutional issues, often categorized into mandatory, optional, and advisory types based on the legal framework. Mandatory referendums require a vote on particular matters by law, while optional referendums are triggered by a petition or government decision, and advisory referendums provide non-binding public opinion. Understanding these classifications helps clarify the role of referendums in influencing policy decisions and enhancing democratic participation.
Understanding Citizens’ Initiative: Purpose and Process
A Citizens' Initiative empowers voters to propose new laws or amendments by collecting a required number of signatures, enabling direct participation in the legislative process. This democratic tool allows citizens to address issues overlooked by elected officials, fostering public engagement and policy responsiveness. The process typically involves submission of a draft proposal, verification of supporting signatures, and a subsequent public vote or legislative review to enact the initiative.
Key Differences Between Referendum and Citizens’ Initiative
Referendums allow voters to approve or reject laws already passed by the legislature, while citizens' initiatives enable the public to propose new laws or amendments without legislative involvement. In a referendum, the government typically triggers the vote, whereas a citizens' initiative is driven directly by voter petitions meeting specific signature thresholds. The scope of referendums is usually limited to existing legislation, but citizens' initiatives can introduce entirely new policies, making the latter a more proactive form of direct democracy.
Legal Frameworks Governing Both Tools
Referendums are typically governed by constitutional or statutory laws that specify when and how they can be initiated, often requiring parliamentary approval or specific thresholds of voter turnout. Citizens' initiatives usually operate under specific legal frameworks that allow citizens to propose new legislation or amendments directly by gathering a mandated number of signatures within a defined timeframe. Both tools are regulated to ensure legitimacy, with clear provisions on eligibility, procedural requirements, and validation processes to balance direct democracy with legal oversight.
Real-World Examples of Referendums
Referendums, such as the 2016 Brexit vote in the United Kingdom, allow citizens to directly approve or reject government proposals, impacting national policies immediately. In contrast, citizens' initiatives, like California's Proposition 13 in 1978, enable voters to introduce new laws or constitutional amendments independently of the legislature. Real-world referendums often address critical issues of sovereignty and constitutional changes, while citizens' initiatives typically focus on specific local or state-level concerns.
Notable Cases of Citizens’ Initiatives
Notable cases of citizens' initiatives include Switzerland's frequent use of popular initiatives, such as the 2014 initiative to restrict executive pay, demonstrating direct public influence on policy. In the United States, the California Proposition 13 in 1978 significantly limited property taxes through a citizens' initiative, highlighting its fiscal impact. These instances showcase how citizens' initiatives empower voters to shape laws independently of legislative bodies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Referendums
Referendums offer direct democratic participation, allowing citizens to vote on specific legislative or policy issues, which can enhance government legitimacy and accountability. However, they may oversimplify complex topics, leading to decisions based on limited information or populist sentiments rather than expert analysis. Furthermore, referendums can be costly to administer and risk undermining representative democracy by bypassing elected officials.
Pros and Cons of Citizens’ Initiatives
Citizens' initiatives empower the electorate to propose new laws or amendments, fostering direct democratic participation and increasing government responsiveness to public concerns. However, they may also lead to voter fatigue, oversimplification of complex issues, and the influence of well-funded interest groups that can skew outcomes. The process encourages civic engagement but requires safeguards to ensure informed decision-making and balanced representation.
The Future Impact of Citizen-Led Decision-Making
Citizen-led decision-making through referendums and citizens' initiatives empowers direct democracy, enabling voters to influence legislation and policy outside traditional representative mechanisms. As digital platforms expand access and lower barriers to participation, these tools are likely to increase in frequency and impact, shaping governance with greater public input on issues such as climate change, social justice, and economic reforms. The future impact of these mechanisms includes enhanced political engagement, increased governmental accountability, and potential challenges in balancing expert policymaking with popular opinion.
Referendum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com