A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal agreement between two or more parties outlining the terms and details of a mutual understanding or partnership. It serves as a non-binding document that clarifies the roles, responsibilities, and expectations without creating legal obligations. Explore the full article to understand how an MOU can benefit your business arrangements and collaborations.
Table of Comparison
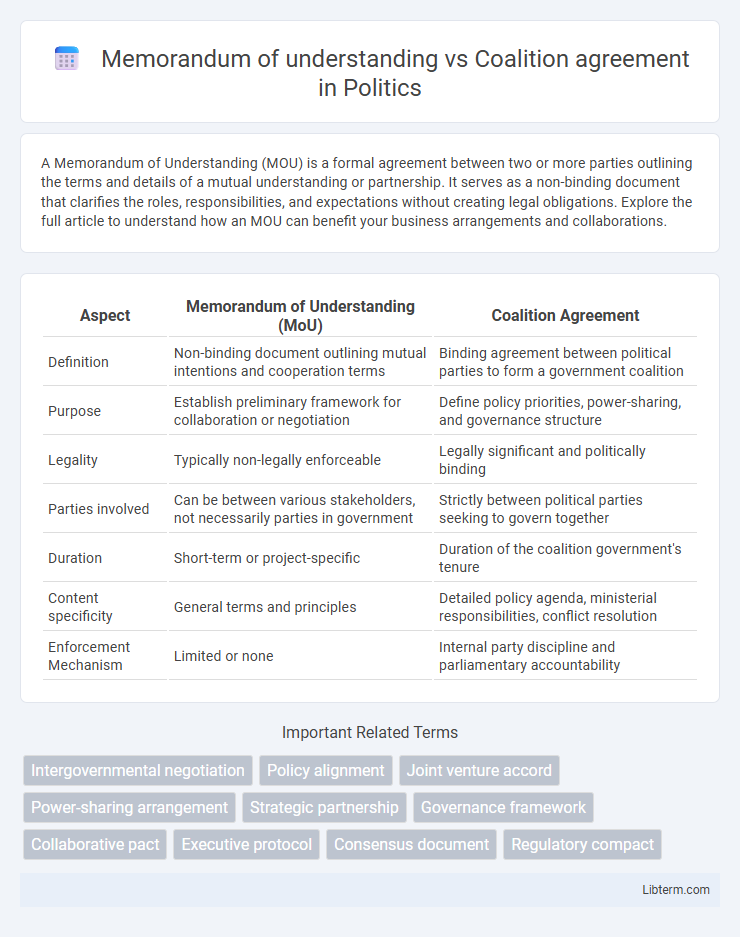
| Aspect | Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) | Coalition Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-binding document outlining mutual intentions and cooperation terms | Binding agreement between political parties to form a government coalition |
| Purpose | Establish preliminary framework for collaboration or negotiation | Define policy priorities, power-sharing, and governance structure |
| Legality | Typically non-legally enforceable | Legally significant and politically binding |
| Parties involved | Can be between various stakeholders, not necessarily parties in government | Strictly between political parties seeking to govern together |
| Duration | Short-term or project-specific | Duration of the coalition government's tenure |
| Content specificity | General terms and principles | Detailed policy agenda, ministerial responsibilities, conflict resolution |
| Enforcement Mechanism | Limited or none | Internal party discipline and parliamentary accountability |
Introduction to Memorandum of Understanding and Coalition Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) is a formal but non-binding agreement that outlines the intentions and roles of parties collaborating on a project or initiative, serving as a foundational document for cooperation. A Coalition Agreement, often used in political and business contexts, is a binding contract that details the specific commitments, responsibilities, and shared objectives of coalition members working together towards a common goal. Both documents establish frameworks for collaboration, but MoUs emphasize mutual understanding whereas Coalition Agreements focus on enforceable obligations and governance.
Definition of Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) is a formal, non-binding agreement that outlines the intentions and terms between two or more parties, serving as a preliminary step towards a potential contract or partnership. MoUs typically clarify mutual expectations and responsibilities without creating enforceable obligations, emphasizing cooperation and understanding. Unlike coalition agreements, which are legally binding and formalize the collaboration in political or business coalitions, MoUs focus on establishing a framework for future negotiations or joint initiatives.
Definition of Coalition Agreement
A Coalition Agreement is a formal contract between two or more political parties or organizations that outlines the terms, responsibilities, and shared goals for collaboration, often to form a government or achieve common objectives. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding, which serves as a non-binding, preliminary agreement, a Coalition Agreement carries legal weight and includes specific provisions on resource allocation, decision-making processes, and conflict resolution. This legally binding document ensures commitment from all parties, provides clear governance structures, and aims to promote long-term cooperation and stability within the coalition.
Core Purposes: MoU vs Coalition Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) outlines the foundational intentions and broad terms between parties intending to collaborate, serving as a non-binding framework for cooperation. In contrast, a Coalition Agreement specifies detailed commitments, roles, and responsibilities among coalition members, often establishing binding obligations to govern joint actions. The MoU primarily clarifies mutual understanding and shared goals, while the Coalition Agreement focuses on operational execution and formalized cooperation within a structured alliance.
Legal Status and Enforceability
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) generally lacks binding legal status, serving as a formal agreement expressing mutual intentions without enforceable obligations. In contrast, a Coalition Agreement is a binding contract among political parties or entities that outlines specific commitments and responsibilities, making it legally enforceable. The enforceability of a Coalition Agreement can lead to legal consequences if breached, whereas an MOU typically relies on the goodwill and cooperation of the parties involved.
Key Elements and Structure Comparison
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) typically outlines mutual intentions, responsibilities, and general terms without being legally binding, emphasizing purpose, scope, and roles within a concise, flexible format. In contrast, a Coalition Agreement is a detailed, formal contract designed for political or organizational alliances, containing specific commitments, governance mechanisms, decision-making procedures, and conflict resolution methods structured in clearly defined sections. The MoU's simplicity facilitates cooperation initiation, whereas the Coalition Agreement's comprehensive framework ensures sustained collaboration and accountability among parties.
Use Cases: When to Use Each Document
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) is ideal for outlining preliminary intentions and establishing a framework for collaboration between organizations without creating legally binding commitments, making it suitable for early-stage partnerships or joint research projects. A Coalition Agreement, by contrast, is used to formalize alliances between political parties or groups with defined responsibilities, decision-making protocols, and power-sharing arrangements, essential for governance or legislative collaboration. Choosing between these documents depends on the level of legal commitment and detail required; MoUs facilitate flexible cooperation, while Coalition Agreements ensure structured, binding partnerships.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) offers flexibility and clarity in outlining mutual intentions without legal binding, promoting trust in early-stage collaborations but lacks enforceability which can lead to potential misunderstandings. In contrast, a Coalition Agreement provides a legally binding framework that clearly defines roles, responsibilities, and dispute resolution mechanisms, ensuring commitment but possibly reducing adaptability due to its rigid terms. Choosing between an MoU and a Coalition Agreement depends on the level of formality required and the desired balance between flexibility and legal protection in partnerships.
Common Pitfalls and Challenges
Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) often lacks legal enforceability, leading to ambiguity in roles and responsibilities, whereas Coalition Agreements are legally binding but can face complexities in negotiation and management. Common pitfalls in MOUs include vague language and insufficient detail on conflict resolution, while Coalition Agreements struggle with balancing power dynamics and aligning diverse stakeholder interests. Both documents require clear communication, precise terms, and robust mechanisms for dispute resolution to minimize misunderstandings and operational challenges.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Agreement
Selecting the appropriate agreement depends on the parties' goals and the level of legal commitment desired. A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) suits collaborations outlining general intentions without binding obligations, ideal for preliminary partnerships. In contrast, a Coalition Agreement establishes formal responsibilities and joint decision-making structures, essential for cohesive political or business alliances seeking enforceable commitments.
Memorandum of understanding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com