The Shadow Cabinet plays a crucial role in scrutinizing government policies and offering alternative solutions that shape political discourse. Comprising members from the opposition party, it mirrors the official Cabinet to hold ministers accountable and prepare for potential governance. Discover how the Shadow Cabinet influences policy-making and impacts your democratic choices by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
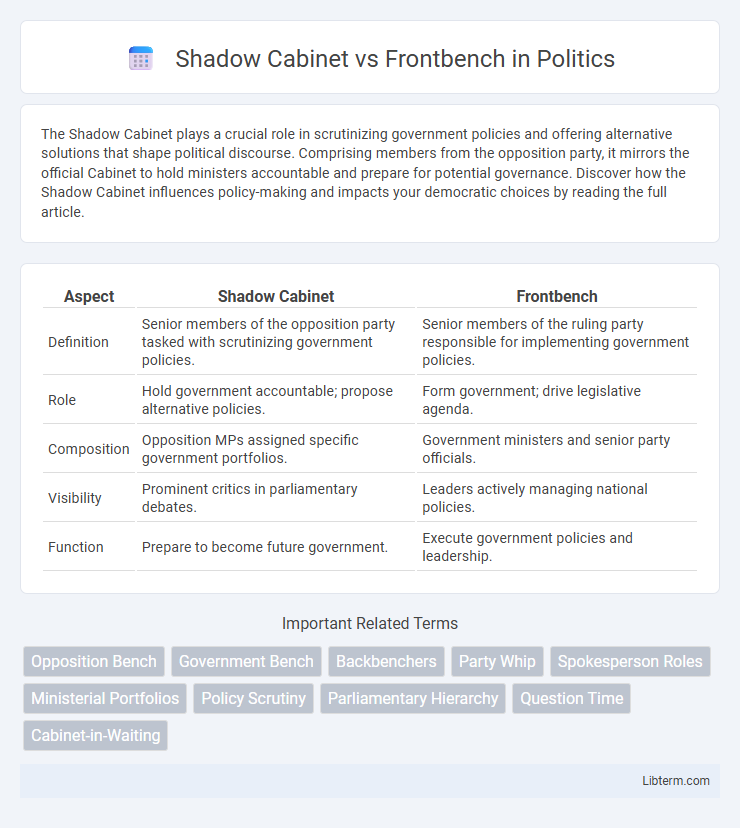
| Aspect | Shadow Cabinet | Frontbench |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Senior members of the opposition party tasked with scrutinizing government policies. | Senior members of the ruling party responsible for implementing government policies. |
| Role | Hold government accountable; propose alternative policies. | Form government; drive legislative agenda. |
| Composition | Opposition MPs assigned specific government portfolios. | Government ministers and senior party officials. |
| Visibility | Prominent critics in parliamentary debates. | Leaders actively managing national policies. |
| Function | Prepare to become future government. | Execute government policies and leadership. |
Understanding the Shadow Cabinet
The Shadow Cabinet consists of senior opposition party members tasked with scrutinizing government policies and presenting alternative solutions, directly mirroring the official Cabinet roles. Each Shadow Cabinet member shadows a specific government minister, providing critical debate and holding the government accountable within parliamentary systems. This structure enhances democratic checks and balances by ensuring opposition parties remain organized and government actions are continuously challenged.
Defining the Frontbench
The frontbench refers to senior members of a parliamentary party who hold official positions as government ministers or spokespeople in the opposition. These politicians sit on the front rows of the legislative chamber, signaling their leadership roles and responsibility for policy development and debate. Contrasting with the shadow cabinet, which mirrors the frontbench of the government to scrutinize and challenge policies, the frontbench directly shapes and implements government strategy.
Historical Origins of Shadow Cabinet and Frontbench
The historical origins of the Shadow Cabinet trace back to the British parliamentary system in the 19th century as a formal opposition structure mirroring the government's frontbench ministers. The Frontbench, representing current government ministers and key opposition spokespeople, evolved as central figures seated on the front benches in the House of Commons to facilitate debate and decision-making. This arrangement established a clear distinction of roles within parliamentary governance, enhancing accountability and policy scrutiny.
Structure and Roles in the Shadow Cabinet
The Shadow Cabinet consists of senior members of the opposition party who mirror the government's Frontbench by holding specific portfolios, such as finance, health, or foreign affairs, to scrutinize and challenge current policies effectively. Each Shadow Cabinet member is responsible for developing alternative policies, preparing to assume government roles, and holding government ministers accountable during parliamentary sessions. Structurally, the Shadow Cabinet functions as the opposition's executive team, ensuring organized and focused opposition that provides voters with clear policy alternatives.
Key Responsibilities of the Frontbench
The Frontbench in parliamentary systems is primarily responsible for leading government departments, formulating policies, and representing the ruling party in debates and public communication. Frontbenchers hold ministerial positions, overseeing administrative functions and implementing legislative agendas. Their role involves direct decision-making authority and managing government operations to ensure effective governance.
Differences Between Shadow Cabinet and Frontbench
The Shadow Cabinet consists of senior members of the main opposition party tasked with scrutinizing government policies and proposing alternatives, whereas the Frontbench includes both government ministers and opposition spokespeople who occupy prominent roles during parliamentary debates. Members of the Shadow Cabinet specifically shadow corresponding government ministers, focusing on accountability and policy critique, while Frontbenchers may include junior or senior officials responsible for various parliamentary functions. The Shadow Cabinet operates entirely within the opposition, while the Frontbench encompasses key leadership positions on both sides of the House, influencing legislative agendas and party strategy.
Significance in Parliamentary Democracy
The Shadow Cabinet plays a critical role in parliamentary democracy by providing structured opposition and holding the government accountable through policy scrutiny and alternative proposals. Frontbench members, including government ministers, spearhead legislative agendas and decision-making processes, shaping national policy directly. The dynamic between the Shadow Cabinet and Frontbench ensures democratic checks and balances, fostering transparency and informed debate within the legislature.
Impact on Government Accountability
Shadow Cabinet members play a crucial role in enhancing government accountability by scrutinizing the policies and actions of their corresponding government ministers. Frontbench members, including ministers, drive policy implementation and decision-making within the government, shaping legislative priorities. The dynamic interaction between the Shadow Cabinet's oversight and the Frontbench's executive power fosters transparency and democratic governance.
Prominent Members: Past and Present
Prominent members of the Shadow Cabinet, such as Ed Miliband and Keir Starmer, have played crucial roles in shaping opposition policies and challenging government decisions. In contrast, Frontbench leaders like Winston Churchill and Margaret Thatcher significantly influenced national governance through their executive roles in government. Both groups include influential political figures who have impacted the UK's political landscape through leadership, policy formulation, and parliamentary strategy.
Shadow Cabinet vs Frontbench: Influence on Policy Making
The Shadow Cabinet plays a critical role in shaping opposition policy by scrutinizing government actions and proposing alternative solutions, thereby influencing public debate and legislative priorities. Frontbench members, especially those in the ruling party, drive policy-making directly through ministerial responsibilities and agenda-setting in parliamentary sessions. The interaction between Shadow Cabinet critique and Frontbench authority creates a dynamic policy environment essential for democratic governance and accountability.
Shadow Cabinet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com